List Of Seas
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki
This is a list of seas of the World Ocean, including marginal seas, areas of water, various gulfs, bights, bays, and straits.[2]
Terminology
- Ocean – the four to seven largest named bodies of water in the World Ocean, all of which have "Ocean" in the name. See Borders of the oceans for details.
- Sea has several definitions:[lower-alpha 1]
- A division of an ocean, delineated by landforms,[6] currents (e.g., Sargasso Sea), or specific latitude or longitude boundaries. This includes but is not limited to marginal seas, and this is the definition used for inclusion in this list.
- A marginal sea is a division of an ocean, partially enclosed by islands, archipelagos, or peninsulas, adjacent to or widely open to the open ocean at the surface, and/or bounded by submarine ridges on the sea floor.[7]
- The World Ocean. For example, the Law of the Sea states that all of the World Ocean is "sea",[8][9][10][lower-alpha 2] and this is also common usage for "the sea".
- Any large body of water with "Sea" in the name, including lakes.
- River – a narrow strip of water that flows over land from a higher elevation to a lower one
- Tributary – a small river that flows into a larger one
- Estuary – the piece of a river that flows into the sea or ocean
- Strait – a narrow area of water connecting two wider areas of water, also sometimes known as a passage
- Channel – usually wider than a strait
- Passage – connects waters between islands, also sometimes known as a strait
- Canal – a human-made channel
- Fjard – a large open water between groups of islands
There are several terms used for bulges of ocean that result from indentations of land, which overlap in definition, and which are not consistently differentiated:[12]
- Bay – generic term; though most features with "Bay" in the name are small, some are very large
- Gulf – a very large bay, often a top-level division of an ocean or sea
- Fjord – a long bay with steep sides, typically formed by a glacier
- Bight – a bay that is typically shallower than a sound
- Sound – a large, wide bay which is typically deeper than a bight, or a strait
- Cove – a small, typically sheltered bay with a relatively narrow entrance
- Inlet – a narrow and long bay similar to a land peninsula, but adjoining the sea
- Polynya – least used of these terms, a patch of water surrounded by ice
Many features could be considered to be more than one of these, and all of these terms are used in place names inconsistently; especially bays, gulfs, and bights, which can be very large or very small. This list includes large areas of water no matter the term used in the name.
Largest seas by area
The largest terrestrial seas are:
- Philippine Sea – 5.695 million km2
- Coral Sea – 4.791 million km2
- American Mediterranean Sea – 4.200 million km2
- Arabian Sea – 3.862 million km2
- Sargasso Sea – 3.5 million km2
- South China Sea – 3.5 million km2
- Weddell Sea – 2.8 million km2
- Caribbean Sea – 2.754 million km2
- Mediterranean Sea – 2.510 million km2
- Gulf of Guinea – 2.35 million km2
- Tasman Sea – 2.3 million km2
- Bay of Bengal – 2.172 million km2
- Bering Sea – 2 million km2
- Sea of Okhotsk – 1.583 million km2
- Gulf of Mexico – 1.550 million km2
- Gulf of Alaska – 1.533 million km2
- Barents Sea – 1.4 million km2
- Norwegian Sea – 1.383 million km2
- East China Sea – 1.249 million km2
- Hudson Bay – 1.23 million km2
- Greenland Sea – 1.205 million km2
- Somov Sea – 1.15 million km2
- Mar de Grau – 1.14 million km2
- Riiser-Larsen Sea – 1.138 million km2
- Sea of Japan – 1.05 million km2
- Argentine Sea – 1 million km2
- East Siberian Sea – 987,000 km2
- Lazarev Sea – 929,000 km2
- Kara Sea – 926,000 km2
- Scotia Sea – 900,000 km2
- Labrador Sea – 841,000 km2
- Andaman Sea – 797,700 km2
- Laccadive Sea – 786,000 km2
- Irminger Sea – 780,000 km2
- Solomon Sea – 720,000 km2
- Mozambique Channel – 700,000 km2
- Cosmonauts Sea – 699,000 km2
- Banda Sea – 695,000 km2
- Baffin Bay – 689,000 km2
- Laptev Sea – 662,000 km2
- Arafura Sea – 650,000 km2
- Ross Sea – 637,000 km2
- Chukchi Sea – 620,000 km2
- Timor Sea – 610,000 km2
- North Sea – 575,000 km2
- Bellingshausen Sea – 487,000 km2
- Beaufort Sea – 476,000 km2
- Red Sea – 438,000 km2
- Black Sea – 436,000 km2
- Gulf of Aden – 410,000 km2
- Yellow Sea – 380,000 km2
- Baltic Sea – 377,000 km2
- Caspian Sea – 371,000 km2
- Libyan Sea – 350,000 km2
- Mawson Sea – 333,000 km2
- Levantine Sea – 320,000 km2
- Java Sea – 320,000 km2
- Gulf of Thailand – 320,000 km2
- Celtic Sea – 300,000 km2
- Gulf of Carpentaria – 300,000 km2
- Celebes Sea – 280,000 km2
- Tyrrhenian Sea – 275,000 km2
- Sulu Sea – 260,000 km2
- Cooperation Sea – 258,000 km2
- Persian Gulf – 251,000 km2
- Flores Sea – 240,000 km2
- Gulf of St. Lawrence – 226,000 km2
- Bay of Biscay – 223,000 km2
- Aegean Sea – 214,000 km2
- Gulf of Anadyr – 200,000 km2
- Molucca Sea – 200,000 km2
- Oman Sea – 181,000 km2
- Ionian Sea – 169,000 km2
- Gulf of California – 160,000 km2
- Balearic Sea – 150,000 km2
- Adriatic Sea – 138,000 km2
Marginal seas by ocean
Seas may be considered marginal between ocean and land, or between oceans in which case they may be treated as marginal parts of either. There is no single ultimate authority on the matter.[13]
Arctic Ocean
(clockwise from 180°)
- Chukchi Sea
- East Siberian Sea
- Laptev Sea
- Kara Sea
- Barents Sea (connected to the Kara Sea by the Kara Strait)
- Pechora Sea
- White Sea
- Queen Victoria Sea
- Wandel Sea
- Greenland Sea
- Lincoln Sea (recognized by the IHO but not the IMO)
- Baffin Bay
- The Northwest Passages
- Prince Gustaf Adolf Sea
- Amundsen Gulf
- (more to be listed)
- Hudson Bay
- Foxe Basin
- Bowman Bay
- Wager Bay
- Roes Welcome Sound
- Foxe Channel
- Bay of Gods Mercy
- Hudson Strait
- Ungava Bay
- Native Bay
- Evans Strait
- Fisher Strait
- James Bay
- Foxe Basin
- Beaufort Sea
Atlantic Ocean
In addition to the marginal seas listed in the three subsections below, the Arctic Ocean itself is sometimes also considered a marginal sea of the Atlantic.[14][15]
Africa and Eurasia
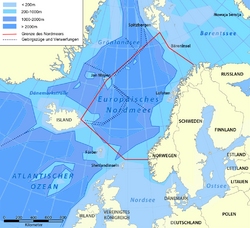
- Norwegian Sea
- North Sea
- Kattegat
- Skagerrak
- Wadden Sea
- Dogger Bank
- Baltic Sea
- Gulf of Bothnia
- Kvarken
- Bothnian Sea
- South Kvarken
- Sea of Åland
- Archipelago Sea
- Gulf of Finland
- Vyborg Bay
- Neva Bay
- Koporye Bay
- Luga Bay
- Narva Bay
- Väinameri Sea
- Gulf of Riga
- Curonian Lagoon
- Vistula Lagoon
- Gdańsk Bay
- Bay of Pomerania
- Szczecin Lagoon
- Bay of Greifswald
- Rügischer Bodden
- Strelasund
- Bay of Lübeck
- Bay of Kiel
- Kalmar Strait
- Bight of Hanö
- Danish straits
- Oresund Strait
- Fehmarn Belt
- Great Belt
- Little Belt
- English Channel
- Strait of Dover
- Irish Sea
- Celtic Sea
- Iroise Sea
- Bay of Biscay
- Cantabrian Sea
- Gulf of Cádiz
- Mediterranean Sea
- Alboran Sea
- Mar Menor
- Balearic (Catalan) Sea
- Gulf of Valencia
- Gulf of Lion
- Étang de Thau
- Ligurian Sea
- Gulf of Genoa
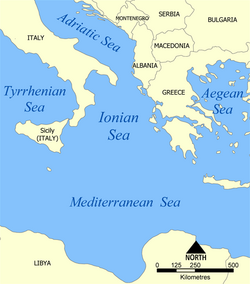
- Tyrrhenian Sea
- Gulf of Naples
- Gulf of Salerno
- Gulf of Cagliari
- Adriatic Sea
- Bay of Kotor
- Gulf of Venice
- Gulf of Trieste
- Venetian Lagoon
- Kvarner Gulf
- Ionian Sea
- Gulf of Taranto
- Gulf of Corinth
- Messenian Gulf
- Laconian Gulf
- Aegean Sea
- Myrtoan Sea
- Argolic Gulf
- Saronic Gulf
- Petalioi Gulf
- South Euboean Gulf
- North Euboean Gulf
- Malian Gulf
- Pagasetic Gulf
- Thermaic Gulf
- Thracian Sea
- Strymonian Gulf
- Gulf of Saros
- Edremit Gulf
- Gulf of İzmir
- Icarian Sea
- Gulf of Gökova
- Sea of Crete
- Sea of Marmara[16]
- Gulf of İzmit[16]
- Levantine Sea
- Gulf of Antalya
- Gulf of Alexandretta
- Libyan Sea
- Gulf of Sidra
- Gulf of Gabès
- Strait of Sicily
- Gulf of Tunis
- Inland Sea, Gozo
- Sea of Sardinia
- Gulf of Asinara
- Black Sea[16]
- Gulf of Burgas[16]
- Karkinit Bay[16]
- Kalamita Bay[16]
- Sea of Azov[16]
- Syvash[16]
- Taganrog Bay[16]
- Bay of Arguin
- Dakhlet Nouadhibou
- Yawri Bay
- Gulf of Guinea
- Bight of Benin
- Bight of Bonny
- Corisco Bay
- Luanda Bay
- Walvis Bay
- Saldanha Bay
- Table Bay
- False Bay
Americas
(coast-wise from north to south)
- North Water Polynya
- Baffin Bay
- Davis Strait
- Home Bay
- Labrador Sea
- Cumberland Sound
- Frobisher Bay
- Gulf of St. Lawrence
- Gulf of Maine
- Bay of Fundy
- Massachusetts Bay
- Cape Cod Bay
- Nantucket Sound
- Vineyard Sound
- Buzzards Bay
- Narragansett Bay
- Rhode Island Sound
- Block Island Sound
- Fishers Island Sound
- Long Island Sound
- Shelter Island Sound
- Noyack Bay
- Peconic Bay
- Gardiners Bay
- Tobaccolot Bay
- Sag Harbor Bay
- Three Mile Harbor
- Long Beach Bay
- Pipes Cove
- Southold Bay
- Flanders Bay
- Napeague Bay
- Fort Pond Bay
- North Sea Harbor
- New York Bay
- Upper New York Bay
- Lower New York Bay
- Jamaica Bay
- Raritan Bay
- Sandy Hook Bay
- Delaware Bay
- Chesapeake Bay
- Albemarle Sound
- Pamlico Sound
- American Mediterranean Sea
- Gulf of Mexico
- Florida Bay
- Tampa Bay
- Charlotte Harbor Estuary
- Pensacola Bay
- Mobile Bay
- Vermilion Bay
- Galveston Bay
- Bay of Campeche
- Caribbean Sea
- Gulf of Gonâve (Haiti)
- Gulf of Honduras
- Golfo de los Mosquitos
- Gulf of Venezuela
- Lake Maracaibo
- Gulf of Paria
- Gulf of Darién
- Gulf of Mexico
- Bay of All Saints
- Guanabara Bay
- Lagoa dos Patos
- Argentine Sea
- Samborombón Bay
- San Matías Gulf
- Golfo Nuevo
- San Jorge Gulf
Northern islands
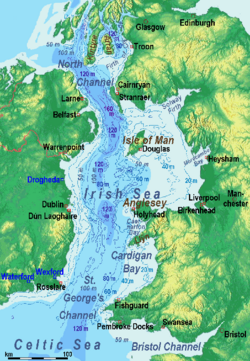
(from east to west)
- Irish Sea (between Great Britain and Ireland)
- Inner Seas off the West Coast of Scotland
- Sea of the Hebrides (Great Britain)
- Denmark Strait (between Greenland and Iceland)
- Irminger Sea
Indian Ocean
- Andaman Sea
- Gulf of Martaban – an arm of the Andaman Sea in the southern part of Myanmar
- Arabian Sea
- Gulf of Kutch
- Gulf of Khambhat
- Bay of Bengal
- Gulf of Aden
- Gulf of Oman
- Laccadive Sea
- Mozambique Channel
- Persian Gulf
- Red Sea
- Sea of Zanj
- Timor Sea
- Palk Strait
- Palk Bay
- Gulf of Mannar
Pacific Ocean
Americas
- Bering Sea
- Bristol Bay
- Norton Sound
- Chilean Sea
- Gulf of Corcovado
- Gulf of Penas
- Moraleda Channel
- Reloncaví Sound
- Sea of Chiloé
- Gulf of Alaska
- Cook Inlet
- Glacier Bay
- Prince William Sound
- Salish Sea
- Gulf of California (also known as the Sea of Cortés)
- Gulf of the Farallones
- Gulf of Fonseca
- Gulf of Guayaquil
- Gulf of Nicoya
- Gulf of Panama
- Bay of San Miguel
- Gulf of Parita
- Panama Bay
- Grau Sea
- San Francisco Bay
- San Pablo Bay
Australia and Eurasia
- Arafura Sea
- Bali Sea
- Banda Sea
- Bay of Kampong Som
- Bay of Plenty
- Bismarck Sea
- Bohai Sea
- Bohol Sea (also known as the Mindanao Sea)
- Camotes Sea
- Celebes Sea
- Ceram Sea
- Coral Sea
- Devil's/Dragon's Sea
- East China Sea
- Ariake Sea
- Hangzhou Bay
- Kagoshima Bay
- Flores Sea
- Gulf of Carpentaria
- Gulf of Thailand
- Bandon Bay
- Bay of Bangkok
- Halmahera Sea
- Hauraki Gulf
- Hawke's Bay
- Java Sea
- Koro Sea
- Molucca Sea
- Philippine Sea
- Ise Bay
- Mikawa Bay
- Suruga Bay
- Ise Bay
- Poverty Bay
- Sagami Bay
- Savu Sea
- Sea of Japan
- Peter the Great Gulf
- Toyama Bay
- Wakasa Bay
- Sea of Okhotsk
- Shelikhov Gulf
- Seto Inland Sea
- Osaka Bay
- Sibuyan Sea
- Solomon Sea
- South China Sea
- Gulf of Tonkin
- Qiongzhou Strait
- Natuna Sea
- North Natuna Sea
- West Philippine Sea
- South Seas
- Gulf of Tonkin
- Sulu Sea
- Tasman Sea
- Tokyo Bay
- Visayan Sea
- Waihau Bay
- Yellow Sea
- Bohai Sea
- Bohai Bay
- Laizhou Bay
- Liaodong Bay
- Jiaozhou Bay
- Korea Sea
- Bohai Sea
Southern Ocean
- Amundsen Sea
- Bellingshausen Sea
- Cooperation Sea[lower-alpha 3]
- Cosmonauts Sea[lower-alpha 3]
- Davis Sea
- D'Urville Sea
- Drake Passage
- King Haakon VII Sea[lower-alpha 3]
- Lazarev Sea[lower-alpha 3]
- Mawson Sea[lower-alpha 3]
- McMurdo Sound
- Polynyas in McMurdo Sound
- Riiser-Larsen Sea
- Ross Sea
- Scotia Sea
- Somov Sea[lower-alpha 3]
- Spencer Gulf
- Weddell Sea
- Weddell Polynya/Maud Rise Polynya
Defined by ocean currents
While all other seas in the world are defined at least in part by land boundaries, there is only one sea which is defined only by ocean currents:[20]
- Sargasso Sea – a sea defined by the four ocean currents which create the North Atlantic Gyre
Not included
Entities called "seas" which are not divisions of the World Ocean are not included in this list. Excluded are:
- Salt lakes with "Sea" in the name: Aral Sea, Dead Sea, Salton Sea
- Freshwater lakes with "Sea" in the name: Sea of Galilee
- Extraterrestrial oceans: list of largest lakes and seas in the Solar System
- Gulfs, bays, straits, and other bodies of water in lakes
Other items not included:
- Coral reefs
- Glaciers
- Ice shelves
- Marshes
- Ocean banks
- Ocean gyres
- Oceans
- Reefs
- River deltas
- Rivers
- Swamps
- Swimming pools / water parks
- Wetlands
See also
- Inland sea (geology)
- Mediterranean sea (oceanography)
- Oceanography
- Atlantic Ocean
- Indian Ocean
- List of largest lakes and seas in the Solar System
Notes
- ↑ There is no accepted technical definition of sea among oceanographers. A rather weak definition is that a sea is a subdivision of an ocean, which means that it must have oceanic basin crust on its floor. This definition, for example, accepts the Caspian Sea, which was once part of an ancient ocean, as a sea.[3] The Introduction to Marine Biology defines a sea as a "landlocked" body of water, adding that the term "sea" is only one of convenience, but the book is written by marine biologists, not oceanographers.[4] The Glossary of Mapping Sciences similarly states that the boundaries between seas and other bodies of water are arbitrary.[5]
- ↑ According to this definition, the Caspian would be excluded as it is legally an "international lake".[11]
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 Proposed names to the IHO 2002 draft. This draft was never approved by the IHO (or any other organization), and the 1953 IHO document (which does not contain these names which mostly originated from 1962 onward) remains currently in force.[17] Leading geographic authorities and atlases do not use these names, including the 2014 10th edition World Atlas from the National Geographic Society and the 2014 12th edition of the Times Atlas of the World. But Soviet and Russian-issued state maps do include them.[18][19]
References
- ↑ INTERNATIONAL HYDROGRAPHIC ORGANIZATION – LIMITS OF OCEANS AND SEAS]
- ↑ OCEANS & SEAS OF THE WORLD
- ↑ Conforti, B; Bravo, Luigi Ferrari (2005). The Italian Yearbook of International Law 2004. ISBN 9789004150270. https://books.google.com/books?id=tLcin2NyJQgC&pg=PA237.
- ↑ Karleskint, George; Turner, Richard L; Small, James W (2009). Introduction to Marine Biology. ISBN 9780495561972. https://books.google.com/books?id=0JkKOFIj5pgC&pg=PA47.
- ↑ The Glossary of the Mapping Sciences – Google Books. 1994. ISBN 9780784475706. https://books.google.com/books?id=jPVxSDzVRP0C&pg=PA365. Retrieved 2013-04-19.
- ↑ "What's the difference between an ocean and a sea?". Oceanservice.noaa.gov. 11 January 2013. http://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/oceanorsea.html.
- ↑ American Congress on Surveying and Mapping (1994). Glossary of the mapping sciences. ASCE Publications. p. 469. ISBN 978-0-7844-0050-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=jPVxSDzVRP0C&pg=PA469. Retrieved 9 December 2010.
- ↑ Vukas, B (2004). The Law of the Sea: Selected Writings. ISBN 9789004138636. https://books.google.com/books?id=sbqBvQy04XwC&pg=PA271.
- ↑ Gupta, Manoj (2010). Indian Ocean Region: Maritime Regimes for Regional Cooperation. ISBN 9781441959898. https://books.google.com/books?id=5zpbN8I2ZR4C&pg=PA57.
- ↑ "Discover The Seven Seas of the Earth". Geography.about.com. http://geography.about.com/od/waterandice/a/sevenseas.htm.
- ↑ Gokay, Bulent (2001). The Politics of Caspian Oil. ISBN 9780333739730. https://books.google.com/books?id=uxmInSrE9vQC&pg=PA74.
- ↑ "gulf – coastal feature". https://www.britannica.com/science/gulf-coastal-feature.
- ↑ Wang, James C. F. (1992). Handbook on Ocean Politics & Law. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 14. ISBN 978-0-313-26434-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=GrEOofrVra4C.
- ↑ James C. F. Wang (1992). Handbook on ocean politics & law. Greenwood Publishing Group. pp. 14–. ISBN 9780313264344. https://books.google.com/books?id=GrEOofrVra4C&pg=PA14. Retrieved 9 December 2010.
- ↑ Longhurst, Alan R. (2007). Ecological Geography of the Sea. Academic Press. p. 104. ISBN 978-0-12-455521-1. https://books.google.com/books?id=QdJZezzrCfQC&pg=PA104.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 16.3 16.4 16.5 16.6 16.7 16.8 Often treated as a part of the Mediterranean Sea.
- ↑ "Limits of Oceans and Seas, 3rd (currently in-force) edition". International Hydrographic Organization. 1953. https://iho.int/uploads/user/pubs/standards/s-23/S-23_Ed3_1953_EN.pdf.
- ↑ Антарктида, rubricon.com/ (map)
- ↑ "Антарктида". gturs.com. http://gturs.com/Maps/pic/ant_fiz.jpg. (map)
- ↑ National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration – What is the Sargasso Sea?
External links
 |
Categories: [Oceanography]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 06/07/2024 04:30:28 | 8 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Earth:List_of_seas | License: CC BY-SA 3.0


 KSF
KSF