African, Caribbean And Pacific Group Of States
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 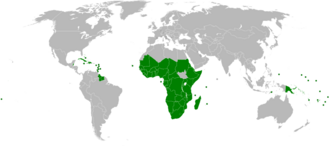
The African, Caribbean and Pacific Group of States (ACP) is a group of countries in Africa, the Caribbean, and the Pacific that was created by the Georgetown Agreement in 1975. In December 2019, the ACP's Council of Ministers endorsed a revision of the Georgetown Agreement that will transform the current ACP Group of States into the Organisation of African, Caribbean Pacific States (OACPS).[1] The group's main objectives are sustainable development and poverty reduction within its member states, as well as their greater integration into the world's economy. All of the member states, except Cuba, are signatories to the Cotonou Agreement with the European Union.
The Cotonou Agreement (signed in Cotonou, Benin in June 2000) is the successor to the Lomé Conventions. One of the major differences from the Lomé Convention is that the partnership is extended to new actors such as civil society, private sector, trade unions and local authorities. These will be involved in consultations and planning of national development strategies, provided with access to financial resources and involved in the implementation of programmes.
Many small island developing states are ACP states; the fourth Lomé Convention was revised in 1995 in Mauritius and gives special attention to island countries in this agreement.
States
Africa
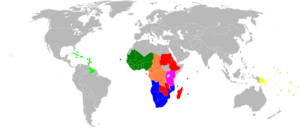
The African ACP countries negotiate in five Economic Partnership Agreements groups[2] (West Africa, CEMAC, Southern Africa Development Community, East African Community, Eastern and Southern Africa) with the EU.
"West Africa group" (ECOWAS plus Mauritania)
|
EAC group
• South Sudan[3]
|
Caribbean
|
|
All countries of the Caribbean Community plus Dominican Republic group negotiate in the CARIFORUM Economic Partnership Agreement (EPA) with the European Union (EU).
Pacific
|
|
All developing member states of the Pacific Islands Forum group[4] and Timor Leste negotiate in the Pacific EPA with the EU.
North Atlantic
In this region are located the EU overseas countries and territories (OCTs) of Greenland and Saint Pierre and Miquelon, but there are no ACP states.[5]
South Atlantic
In this region are located the EU OCTs of Saint Helena and Falkland Islands, but there are no ACP states.[5] Nevertheless, Saint Helena is developing links with the SADC EPA group.[6]
Uninhabited territories
The uninhabited EU OCTs do not participate in regional integration and do not receive development funding from the EU.
- British Indian Ocean Territory, located in the Indian Ocean[5][7]
- French Southern and Antarctic Territories, located in the Indian Ocean[8]
- South Georgia and South Sandwich Islands, located in the South Atlantic, thus in a group with the inhabited OCTs there[5]
- British Antarctic Territory, located near the South Atlantic, thus in a group with the inhabited OCTs there[5]
Special designations
The Cotonou agreement recognises the specific challenges faced by less developed countries, land-locked countries, and islands in their economic development. Therefore, those countries are granted a more favourable treatment than other ACP member countries. The text of the Cotonou agreement has been updated in 2005 and 2010, but the lists have not, despite the fact that the actual list of LDCs as defined by the United Nations has changed: Cape Verde has graduated from LDC status in December 2007, while Senegal has acquired the status in 2001 and Timor-Leste in 2003. The following lists should thus not be considered as the actual lists of ACP LDCs and islands (a few islands are also not listed).
Annex VI of the Cotonou agreement lists the following designations:
Least-developed ACP states
- Angola
- Benin
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cape Verde
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Comoros
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Djibouti
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Ethiopia
- Gambia
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Haiti
- Kiribati
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mozambique
- Niger
- Rwanda
- Samoa
- Sâo Tome and Principe
- Sierra Leone
- Solomon Islands
- Somalia
- Sudan
- Tanzania
- Tuvalu
- Togo
- Uganda
- Vanuatu
- Zambia
The Least developed OCTs are the following: Anguilla, Mayotte, Montserrat, Saint Helena, Turks and Caicos Islands, Wallis and Futuna, Saint Pierre and Miquelon.[9]
Landlocked ACP states
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Ethiopia
- Lesotho
- Malawi
- Mali
- Niger
- Rwanda
- Eswatini
- Uganda
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
Island ACP states
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Bahamas
- Barbados
- Cape Verde
- Comoros
- Cuba
- Dominica
- Dominican Republic
- Fiji
- Grenada
- Haiti
- Jamaica
- Kiribati
- Madagascar
- Mauritius
- Nauru
- Papua New Guinea
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Samoa
- São Tomé and Principe
- Seychelles
- Solomon Islands
- Tonga
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Tuvalu
- Vanuatu
See also
- ACP-EU Development Cooperation
- EU-ACP Economic Partnership Agreements
- ACP-EU Joint Parliamentary Assembly
- Economic Partnership Agreements (EPA) with the ACP countries
- The Courier (ACP-EU) : The magazine of Africa-Caribbean-Pacific and European Union cooperation and relations
- Technical Centre for Agricultural and Rural Cooperation ACP-EU (CTA)
- Everything but Arms
- European Centre for Development Policy Management
References
- ↑ Seychelles at the 110th ACP Council of Ministers, Nairobi, Kenya
- ↑ EPA Groups
- ↑ Economic and technical cooperation : agreement between the United States of America and South Sudan, signed at Juba, September 11, 2012.. U.S. Dept. of State. c. 2012. OCLC 815531434.
- ↑ That is: all member states except Australia and New Zealand.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 OCT regional groups
- ↑ Saint Helena
- ↑ Because of forced population relocation the BIOT it is commonly associated with Mauritius that is currently in the Eastern and Southern Africa EPA group."Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2008-12-29. https://web.archive.org/web/20081229033328/http://ec.europa.eu/development/geographical/regionscountries/countries/country_profile.cfm?cid=io&type=short&lng=en. Retrieved 2009-09-16.
- ↑ TAAF The islands of the TAAF are located in the southern Indian Ocean and thus if applicable would be associated with the SADC EPA group. The antarctic territory is also located near the south-eastern edge of the Indian Ocean
- ↑ Overseas Association Decision, Annex I B
External links
- Secretariat of the African, Caribbean and Pacific Group of States
- ACP-EU Joint Parliamentary Assembly
- ACP-EU cooperation dossier of Euforic
- African Voices: About EC Aid to Africa
- The Courier - The Magazine of Africa, Caribbean, Pacific and European Union cooperation and relations
- CTA's magazine on agriculture in ACP countries, Spore
- Website on EU cooperation for ACP countries
Categories: [International economic organizations] [International trade organizations] [Trade blocs]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 08/26/2024 13:07:35 | 2 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Organization:African,_Caribbean_and_Pacific_Group_of_States | License: CC BY-SA 3.0

 KSF
KSF