High-voltage direct current interconnections in western Europe in 2008 - red are existing links, green are under construction, and blue are proposed.
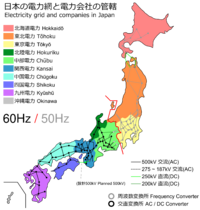
Map of Japan's electricity transmission network, showing differing systems between regions. Unusually for a national grid, different regions run at completely different frequencies.
An electrical interconnector is a high power AC or DC connection, typically across national borders[1] or between different electrical grids.[2] They can be formed of submarine power cables or underground power cables or overhead power lines.
The longest interconnection at 2016 was the undersea NorNed link between Norway and the Netherlands, spanning nearly 600 km and delivering 700 MW of high voltage direct current power.[3]
See also
- List of HVDC projects
- Asian Super Grid
- Super grid
References
- ↑ Electricity interconnectors ofgem
- ↑ LARGE-SCALE ELECTRICITY INTERCONNECTION 2016
- ↑ IEA/OECD (2016) Large-Scale Electricity Interconnection: Technology and prospects for cross-regional networks, (IEA, Paris)
Electricity delivery |
|---|
| Concepts |
- Availability factor
- Automatic Generation Control
- Backfeeding
- Base load
- Capacity factor
- Demand factor
- Droop speed control
- Economic dispatch
- Electric power
- Demand management
- EROEI
- Fault
- Home energy storage
- Grid storage
- Grid code
- Load factor
- Load following
- Merit order
- Nameplate capacity
- Peak demand
- Power quality
- Power-flow study
- Repowering
- Utility frequency
- Variability
|
|---|
| Sources | | Nonrenewable |
- Coal
- Fossil fuel power station
- Natural gas
- Petroleum
- Nuclear
- Oil shale
|
|---|
| Renewable |
- Biomass
- Biofuel
- Geothermal
- Hydro
- Marine
- Current
- Osmotic
- Thermal
- Tidal
- Wave
- Solar
- Wind
|
|---|
|
|---|
| Generation |
- AC power
- Cogeneration
- Combined cycle
- Cooling tower
- Induction generator
- Micro CHP
- Microgeneration
- Rankine cycle
- Three-phase electric power
- Virtual power plant
|
|---|
Transmission
and distribution |
- Demand response
- Distributed generation
- Dynamic demand
- Electric power distribution
- Electrical busbar system
- Electric power system
- Electric power transmission
- Electrical grid
- Electrical interconnector
- High-voltage direct current
- High-voltage shore connection
- Load management
- Mains electricity by country
- Power line
- Power station
- Power storage
- Pumped hydro
- Smart grid
- Substation
- Super grid
- Transformer
- Transmission system operator (TSO)
- Transmission tower
- Utility pole
|
|---|
| Failure modes |
- Blackout (Rolling blackout)
- Brownout
- Black start
- Cascading failure
|
|---|
Protective
devices |
- Arc-fault circuit interrupter
- Earth leakage circuit breaker
- Residual-current device (GFI)
- Power-system protection
- Protective relay
- Digital protective relay
- Sulfur hexafluoride circuit breaker
|
|---|
Economics
and policies |
- Carbon offset
- Cost of electricity by source
- Ecotax
- Energy subsidies
- Feed-in tariff
- Fossil-fuel phase-out
- Net metering
- Pigovian tax
- Renewable Energy Certificates
- Renewable energy payments
- Renewable energy policy
- Spark/Dark/Quark/Bark spread
|
|---|
| Statistics and Production |
- List of electricity sectors
- Electric energy consumption
|
|---|
- Categories
- Electric power distribution
- Electricity economics
- Power station technology
- Portals
- Energy
- Renewable energy
|
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 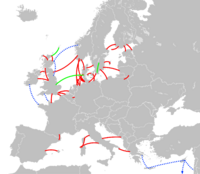

 KSF
KSF