Atlantica
 From Handwiki
From Handwiki 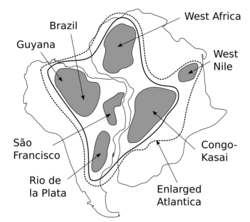
Atlantica (Greek: Ατλαντικα; Atlantika) is an ancient continent that formed during the Proterozoic about 2,000 million years ago (two billion years ago, Ga) from various 2 Ga cratons located in what are now West Africa and eastern South America.[1] The name, introduced by Rogers 1996, was chosen because the parts of the ancient continent are now located on opposite sides of the South Atlantic Ocean.[2]
Formation
Atlantica formed simultaneously with Nena at about 1.9 Ga from Archaean cratons, including Amazonia in present-day South America, and the Congo, West Africa and North Africa Cratons in Africa.[3]
Breakup
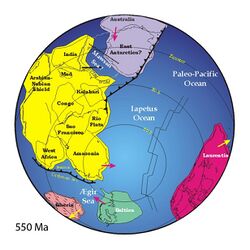
Atlantica separated from Nena between 1.6–1.4 Ga when Columbia — a supercontinent composed of Ur, Nena, and Atlantica — fragmented.[2] Atlantica and continents Nena and Ur and some minor plates formed the supercontinent Rodinia about 1 Ga ago. Between 1–0.5 Ga Rodinia split into three new continents: Laurasia and East and West Gondwana; Atlantica became the nucleus of West Gondwana.[1] During this later stage, the Neoproterozoic era, a Brasiliano-Pan African orogenic system developed. The central part of this system, the Araçuaí-West Congo orogen, has left a distinct pattern of deformations, still present on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean.[4][5]
See also
- Plate tectonics
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Rogers 1996
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Sankaran 2003, p. 1122
- ↑ Yoshida, Windley & Dasgupta 2003, p. 16
- ↑ Alkmim et al. 2006, Abstract
- ↑ Noce et al. 2007, p. 60
References
- Alkmim, Fernando F.; Marshak, Stephen; Pedrosa-Soares, Antônio Carlos; Peres, Guilherme Gravina; Cruz, Simone Cerqueira Pereira; Whittington, Alan (September 1, 2006). "Kinematic evolution of the Araçuaí-West Congo orogen in Brazil and Africa: Nutcracker tectonics during the Neoproterozoic assembly of Gondwana". Precambrian Research 149 (1–2): 43–64. doi:10.1016/j.precamres.2006.06.007. Bibcode: 2006PreR..149...43A. http://www.repositorio.ufop.br/handle/123456789/1981.
- Noce, Carlos M.; Pedrosa-Soares, Antônio Carlos; da Silva, Luiz Carlos; Armstrong, Richard; Piuzana, Danielle (2007). "Evolution of polycyclic basement complexes in the Aracuaí Orogen, based on U–Pb SHRIMP data: Implications for Brazil–Africa links in Paleoproterozoic time". Precambrian Research 159 (1-2): 60–78. doi:10.1016/j.precamres.2007.06.001. Bibcode: 2007PreR..159...60N. http://www.cprm.gov.br/publique/media/paleop_MG.pdf.
- Rogers, John J. W. (January 1996). "A History of Continents in the Past Three Billion Years". The Journal of Geology 104 (1): 91–107. doi:10.1086/629803. Bibcode: 1996JG....104...91R.
- Sankaran, A. V. (2003). "The supercontinent medley: Recent views". Current Science 85 (8): 1121–1123. http://www.iisc.ernet.in/currsci/oct252003/1121.pdf.
- Yoshida, Masaru; Windley, Brian F.; Dasgupta, Somnath, eds (2003). Proterozoic East Gondwana: supercontinent assembly and breakup. 206. Geological Society of London. ISBN 1-86239-125-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=4B8nrDVjaCgC&pg=PA16.
 |
Categories: [Historical continents] [Proterozoic]
↧ Download as ZWI file | Last modified: 08/25/2025 11:36:34 | 2 views
☰ Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Earth:Atlantica | License: CC BY-SA 3.0
.svg.png)
.svg.png)
.svg.png)
.svg.png)
.svg.png)
_political.svg.png)
.svg.png)
.svg.png)
.svg.png)

 KSF
KSF