GSK-189,254
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 3 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 3 min
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
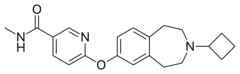
| Formula | C21H25N3O2 |
| Molar mass | 351.441 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
GSK-189,254 is a potent and selective H3 histamine receptor inverse agonist developed by GlaxoSmithKline. It has subnanomolar affinity for the H3 receptor (Ki = 0.2nM) and selectivity of over 10,000x for H3 over other histamine receptor subtypes.[1] Animal studies have shown it to possess not only stimulant and nootropic effects,[2] but also analgesic action suggesting a role for H3 receptors in pain processing in the spinal cord.[3] GSK-189,254 and several other related drugs are currently being investigated as a treatment for Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia,[4] as well as possible use in the treatment of conditions such as narcolepsy,[5] or neuropathic pain which do not respond well to conventional analgesic drugs.[6]
References
- ↑ "GSK189254, a novel H3 receptor antagonist that binds to histamine H3 receptors in Alzheimer's disease brain and improves cognitive performance in preclinical models". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 321 (3): 1032–45. June 2007. doi:10.1124/jpet.107.120311. PMID 17327487.
- ↑ "Correlation between ex vivo receptor occupancy and wake-promoting activity of selective H3 receptor antagonists". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 325 (3): 902–9. June 2008. doi:10.1124/jpet.107.135343. PMID 18305012.
- ↑ "Novel histamine H3 receptor antagonists GSK189254 and GSK334429 are efficacious in surgically-induced and virally-induced rat models of neuropathic pain". Pain 138 (1): 61–9. August 2008. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2007.11.006. PMID 18164820.
- ↑ "The histamine H3 receptor: an attractive target for the treatment of cognitive disorders". British Journal of Pharmacology 154 (6): 1166–81. July 2008. doi:10.1038/bjp.2008.147. PMID 18469850.
- ↑ "Differential effects of acute and repeat dosing with the H3 antagonist GSK189254 on the sleep-wake cycle and narcoleptic episodes in Ox-/- mice". British Journal of Pharmacology 157 (1): 104–17. May 2009. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00205.x. PMID 19413575.
- ↑ "Structurally novel histamine H3 receptor antagonists GSK207040 and GSK334429 improve scopolamine-induced memory impairment and capsaicin-induced secondary allodynia in rats". Biochemical Pharmacology 73 (8): 1182–94. April 2007. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2007.01.007. PMID 17276409.
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:GSK-189,2544 views | Status: cached on October 12 2024 23:06:10↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF