Historical public education information in Texas, 2011-2015
 From Ballotpedia - Reading time: 10 min
From Ballotpedia - Reading time: 10 min
![]() This article does not contain the most recently published data on this subject. If you would like to help our coverage grow, consider donating to Ballotpedia.
This article does not contain the most recently published data on this subject. If you would like to help our coverage grow, consider donating to Ballotpedia.
| Education policy in the U.S. |
| Public education in the U.S. |
| School choice in the U.S. |
| Charter schools in the U.S. |
| Higher education in the U.S. |
| Glossary of education terms |
| Education statistics |
- This page contains archived information on Texas' public education system, primarily from 2011-2012, but also from other years due to the availability of data at the time it was written. For more recent information, view Texas' public education page.
The Texas public school system (prekindergarten through grade 12) operates within districts governed by locally elected school boards and superintendents. In 2012 Texas had 5,000,470 students enrolled in a total of 8,697 schools in 1,262 school districts. There were 324,282 teachers in the public schools, or roughly one teacher for every 15 students, compared to the national average of 1:16. There was roughly one administrator for every 232 students, compared to the national average of one administrator for every 295 students.[1] On average Texas spent $8,671 per pupil in 2011, which ranked it 43rd highest in the nation. The state's graduation rate was 88 percent in 2012.[2]
State agencies[edit]
- See also: Texas Department of Education
The mission statement of the Texas Education Agency reads:[3]
| “ | The mission of the Texas Education Agency (TEA) is to provide leadership, guidance, and resources to help schools meet the educational needs of all students and prepare them for success in the global economy.[4] | ” |
The Texas Education Agency is led by the Commissioner of Education. The Commissioner of Education is appointed by the governor with the consent of the senate. As of June 2015, the officeholder for this position was Michael Williams.[5]
The Texas State Board of Education is responsible for overseeing the state's public education system. The board is composed of 15 members elected from districts. Members serve four-year terms.[6]
Regional comparison[edit]
- See also: General comparison table for education statistics in the 50 states and Education spending per pupil in all 50 states
The following chart shows how Texas compared to three neighboring states in school year 2011-2012 with respect to number of students, schools, the number of teachers per pupil, and the number of administrators per pupil. Further comparisons between these states with respect to performance and financial information are given in other sections of this page.
| Regional comparison, 2011-2012 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | Schools | Districts | Students | Teachers | Teacher/pupil ratio | Administrator/pupil ratio | Per pupil spending |
| Texas | 8,697 | 1,262 | 5,000,470 | 324,282 | 1:15.4 | 1:232.4 | $8,671 |
| Louisiana | 1,437 | 132 | 703,390 | 48,657 | 1:14.5 | 1:244.3 | $10,723 |
| New Mexico | 866 | 135 | 337,225 | 21,957 | 1:15.4 | 1:253.4 | $9,070 |
| Oklahoma | 1,774 | 575 | 666,120 | 41,349 | 1:16.1 | 1:303.6 | $7,587 |
| United States | 98,328 | 17,992 | 49,521,669 | 3,103,263 | 16 | 295.2 | $10,994 |
| Sources: U.S. Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics, Common Core of Data (CCD), "State Nonfiscal Public Elementary/Secondary Education Survey", 2011-12 v.1a. National Center for Education Statistics, "Table 2. Number of operating public schools and districts, state enrollment, teacher and pupil/teacher ratio by state: School year 2011–12" | |||||||
Demographics[edit]
The following table displays the ethnic distribution of students in Texas as reported in the National Center for Education Statistics Common Core of Data for 2011-2012.[7]
| Demographic information for Texas' K-12 public school system, 2011-2012 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethnicity | Students | State percentage | United States percentage** | |
| American Indian | 22,390 | 0.45% | 1.10% | |
| Asian | 177,203 | 3.54% | 4.68% | |
| African American | 640,723 | 12.81% | 15.68% | |
| Hawaiian Nat./Pacific Isl. | 6,258 | 0.13% | 0.42% | |
| Hispanic | 2,541,966 | 50.83% | 24.37% | |
| White | 1,527,763 | 30.55% | 51.21% | |
| Two or more | 84,167 | 1.68% | 2.54% | |
| **Note: This is the percentage of all students in the United States that are reported to be of this ethnicity. | ||||
Enrollments by region type[edit]
A plurality of students in Texas attended city schools during school year 2011-2012. Approximately 64 percent of the state's students attended city or suburban schools, compared to approximately 36 percent who attended rural or town schools.
| Student distribution by region type, 2011-2012 (as percents) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | City schools | Suburban schools | Town schools | Rural schools | |||
| Texas | 39.7% | 24.5% | 9.8% | 26% | |||
| Louisiana | 20.7% | 24.5% | 19.6% | 35.2% | |||
| New Mexico | 32.6% | 11.9% | 27.4% | 28.1% | |||
| Oklahoma | 21.9% | 19.4% | 22.9% | 35.8% | |||
| U.S. average | 28.9% | 34% | 11.6% | 25.4% | |||
| Source: U.S. Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics, Common Core of Data (CCD) | |||||||
Academic performance[edit]
| Education terms |
|---|
| |
| For more information on education policy terms, see this article. |
NAEP scores[edit]
- See also: NAEP scores by state
The National Center for Education Statistics provides state-by-state data on student achievement levels in mathematics and reading in the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP). Compared to three neighboring states (Louisiana, New Mexico, and Oklahoma), Texas had the highest share of fourth and eighth grade students who scored at or above proficient in math in school year 2012-2013.[8]
| Percent of students scoring at or above proficient, 2012-2013 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Math - Grade 4 | Math - Grade 8 | Reading - Grade 4 | Reading - Grade 8 | |
| Texas | 41% | 38% | 28% | 31% |
| Louisiana | 26% | 21% | 23% | 24% |
| New Mexico | 31% | 23% | 21% | 22% |
| Oklahoma | 36% | 25% | 30% | 29% |
| U.S. average | 41% | 34% | 34% | 34% |
| Source: United States Department of Education, ED Data Express, "State Tables," accessed May 13, 2014 | ||||
Graduation, ACT and SAT scores[edit]
- See also: Graduation rates by groups in state
- See also: ACT and SAT scores in the U.S.
The following table shows the graduation rates and average composite ACT and SAT scores for Texas and surrounding states for 2012 and 2013.[8][9][10]
| Comparison table for graduation rates and test scores* | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | Graduation rate, 2012 | Average ACT composite, 2012 | Average SAT composite, 2013 | ||||
| Percent | Quintile ranking** | Score | Participation rate | Score | Participation rate | ||
| Texas | 88% | First | 20.8 | 39% | 1,437 | 59% | |
| Louisiana | 72% | Fourth | 20.3 | 100% | 1,655 | 5% | |
| New Mexico | 70% | Fifth | 19.9 | 75% | 1,626 | 12% | |
| Oklahoma | 78% | Fifth | 20.7 | 80% | 1,689 | 5% | |
| U.S. average | 80% | 21.1 | 1,498 | ||||
| *Regulatory Adjusted Cohort Rate (except for Idaho, Kentucky, Oklahoma, which did not report “Regulatory Adjusted Cohort Graduation Rate,” but instead used their own method of calculation). **Graduation rates for states in the first quintile ranked in the top 20 percent nationally. Similarly, graduation rates for states in the fifth quintile ranked in the bottom 20 percent nationally. Source: United States Department of Education, ED Data Express | |||||||
Dropout rate[edit]
- See also: Public high school dropout rates by state for a full comparison of dropout rates by group in all states
The high school event dropout rate indicates the proportion of students who were enrolled at some time during the school year and were expected to be enrolled in grades 9–12 in the following school year but were not enrolled by October 1 of the following school year. Students who have graduated, transferred to another school, died, moved to another country, or who are out of school due to illness are not considered dropouts. The average public high school event dropout rate for the United States remained constant at 3.3 percent for both school year 2010–2011 and school year 2011–2012. The event dropout rate for Texas was lower than the national average at 2.4 percent in the 2010-2011 school year, and 2.5 percent in the 2011-2012 school year.[11]
Educational choice options[edit]
- See also: School choice in Texas
As of June 2015 school choice options in Texas include: charter schools, inter-district and intra-district open enrollment policies and online learning programs. In addition, about 5.14 percent of school-age children in the state attended private schools in the 2011-2012 academic year, and an estimated 2.67 percent were homeschooled in 2012-2013.
Education funding and expenditures[edit]
- See also: Texas state budget and finances
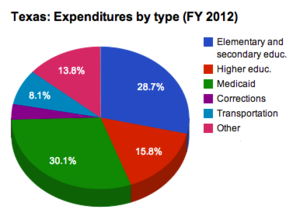
Source: National Association of State Budget Officers
According to the National Association of State Budget Officers (NASBO), Texas spent approximately 28.7 percent of its fiscal year 2012 budget on elementary and secondary education. As a share of the budget, this was down 0.10 percentage points, or 0.35 percent, from fiscal year 2008, when the state spent 28.8 percent of its budget on elementary and secondary education.[12][13][14][15][16]
| Comparison of financial figures for school systems | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State | Percent of budget (2012) | Per pupil spending (2011) | Revenue sources (2011) | ||||
| Percent federal funds | Percent state funds | Percent local funds | |||||
| Texas | 28.7% | $8,671 | 15.34% | 39.65% | 45.01% | ||
| Louisiana | 18.4% | $10,723 | 19.11% | 41.43% | 39.46% | ||
| New Mexico | 24.7% | $9,070 | 17.66% | 65.78% | 16.55% | ||
| Oklahoma | 16.5% | $7,587 | 16.62% | 47.01% | 36.37% | ||
| Sources: NASBO, "State Expenditure Report," Table 8: Elementary and Secondary Education Expenditures As a Percent of Total Expenditures U.S. Census Bureau, "Public Education Finances: 2011,Governments Division Reports," issued May 2013 | |||||||
Revenue breakdowns[edit]
According to the National Center for Education Statistics, public school system revenues in Texas totaled approximately $52.2 billion in fiscal year 2011. The table and chart below present further detail, including revenue sources, for Texas and surrounding states.[17]
| Revenues by source, fiscal year 2011 (amounts in thousands) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Federal revenue | State revenue | Local revenue | Total revenue | |
| Texas | $8,009,703 | $20,699,461 | $23,502,535 | $52,211,699 |
| Louisiana | $1,570,393 | $3,404,656 | $3,242,171 | $8,217,220 |
| New Mexico | $641,925 | $2,390,635 | $601,508 | $3,634,068 |
| Oklahoma | $970,577 | $2,745,748 | $2,124,039 | $5,840,364 |
| U.S. total | $74,943,767 | $267,762,416 | $264,550,594 | $607,256,777 |
| Source: National Center for Education Statistics | ||||
| Public school revenues by source, fiscal year 2011 (as percents) |
|---|
Expenditure breakdowns[edit]
According to the National Center for Education Statistics, public school system expenditures in Texas totaled approximately $53.7 billion in fiscal year 2011. The table and chart below present further detail, including expenditure types, for Texas and surrounding states.[17]
| Expenditures by type, fiscal year 2011 (amounts in thousands) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General expenditures** | Capital outlay | Other*** | Total expenditures | |
| Texas | $42,782,827 | $6,556,210 | $4,358,069 | $53,697,106 |
| Louisiana | $7,440,499 | $812,768 | $149,430 | $8,402,697 |
| New Mexico | $3,045,075 | $621,504 | $66,091 | $3,732,670 |
| Oklahoma | $5,001,641 | $510,611 | $91,371 | $5,603,623 |
| U.S. total | $520,577,893 | $52,984,139 | $29,581,293 | $603,143,325 |
| **Funds spent operating local public schools and local education agencies, including such expenses as salaries for school personnel, student transportation, school books and materials, and energy costs, but excluding capital outlay, interest on school debt, payments to private schools, and payments to public charter schools. ***Includes payments to state and local governments, payments to private schools, interest on school system indebtedness, and nonelementary-secondary expenditures, such as adult education and community services expenditures. Source: National Center for Education Statistics | ||||
| Public school expenditures, fiscal year 2011 (as percents) |
|---|
Personnel salaries[edit]
According to the National Center for Education Statistics, the average national salary for classroom teachers in public elementary and secondary schools declined by 1.3 percent from the 1999-2000 school year to the 2012-2013 school year. During the same period in Texas, the average salary decreased by 6.3 percent.[19]
| Estimated average salaries for teachers (in constant dollars**) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1999-2000 | 2009-2010 | 2011-2012 | 2012-2013 | Percent difference | |
| Texas | $51,339 | $51,516 | $49,178 | $48,110 | -6.3% |
| Louisiana | $45,246 | $52,201 | $51,014 | $51,381 | 13.6% |
| New Mexico | $44,488 | $49,378 | $46,381 | $46,573 | 4.7% |
| Oklahoma | $42,772 | $50,907 | $45,130 | $44,128 | 3.2% |
| U.S. average | $57,133 | $58,925 | $56,340 | $56,383 | -1.3% |
| **"Constant dollars based on the Consumer Price Index (CPI), prepared by the Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor, adjusted to a school-year basis. The CPI does not account for differences in inflation rates from state to state." | |||||
Organizations[edit]
Unions[edit]
In 2012 the Fordham Institute and Education Reform Now assessed the power and influence of state teacher unions in all 50 states and the District of Columbia. Their rankings were based on 37 different variables in five broad areas, including: resources and membership, involvement in politics, scope of bargaining, state policies and perceived influence. Texas ranked 44th overall, or "weakest," which was in the fifth of five tiers.[20]
Government sector lobbying[edit]
- See also: Texas government sector lobbying
Taxpayer-funded lobbyists for the state public schools include:
School official lobbyists include the Texas Association of School Business Officials and Texas Association of Secondary School Principals.
Lobbies concerned with school administrators and school boards include the Texas Association of School Boards and Texas Association of School Administrators.
Transparency[edit]
The state's official spending transparency database, which includes information pertaining to public schools, can be accessed here.[21]
Studies and reports[edit]
State Budget Solutions education study[edit]
State Budget Solutions examined national trends in education from 2009 to 2011, including state-by-state analysis of education spending, graduation rates and average ACT scores. The study showed that the states that spent the most did not have the highest average ACT test scores, nor did they have the highest average graduation rates. A summary of the study is available here. The full report can be accessed here.
See also[edit]
Footnotes[edit]
- ↑ United States Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics, "Common Core of Data (CCD); Table 2.—Number of operating public schools and districts, state enrollment, teacher and pupil/teacher ratio by state: School year 2011-12," accessed May 12, 2014
- ↑ United States Department of Education, "ED Data Express," accessed May 12, 2014
- ↑ Texas Education Agency, "TEA Mission and Responsibilities," accessed June 5, 2014
- ↑ Note: This text is quoted verbatim from the original source. Any inconsistencies are attributable to the original source.
- ↑ Texas Education Agency, "Commissioner of Education," accessed June 5, 2014
- ↑ Texas Education Agency, "SBOE History and Duties," accessed June 5, 2014
- ↑ United States Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics, "Common Core of Data (CCD), State Nonfiscal Public Elementary/Secondary Education Survey, 2011-2012," accessed May 7, 2014
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 United States Department of Education, ED Data Express, "State Tables," accessed May 13, 2014
- ↑ ACT, "2012 ACT National and State Scores," accessed May 13, 2014
- ↑ Commonwealth Foundation, "SAT Scores by State 2013," October 10, 2013
- ↑ United States Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics, "Common Core of Data (CCD), State Dropout and Graduation Rate Data File, School Year 2010-11, Provision Version 1a and School Year 2011-12, Preliminary Version 1a," accessed May 13, 2014
- ↑ National Association of State Budget Officers, "State Expenditure Report, 2011-2013," accessed February 21, 2014
- ↑ National Association of State Budget Officers, "State Expenditure Report, 2009-2011," accessed February 24, 2014
- ↑ National Association of State Budget Officers, "State Expenditures Report, 2010-2012," accessed February 24, 2014
- ↑ National Association of State Budget Officers, "State Expenditure Report, 2009," accessed February 24, 2014
- ↑ National Association of State Budget Officers, "State Expenditure Report, 2008," accessed February 24, 2014
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 United States Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics, "Revenues and Expenditures for Public Elementary and Secondary School Districts: School Year 2010–11," accessed May 13, 2014
- ↑ Maciver Institute, "REPORT: How much are teachers really paid?" accessed October 29, 2014
- ↑ United States Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics, "Table 211.60. Estimated average annual salary of teachers in public elementary and secondary schools, by state: Selected years, 1969-70 through 2012-13," accessed May 13, 2014
- ↑ Thomas E Fordham Institute, " How Strong Are U.S. Teacher Unions? A State-By-State Comparison," October 29, 2012
- ↑ Texas Transparency, "Home page," accessed June 5, 2014
| |||||
 |
State of Texas Austin (capital) |
|---|---|
| Elections |
What's on my ballot? | Elections in 2025 | How to vote | How to run for office | Ballot measures |
| Government |
Who represents me? | U.S. President | U.S. Congress | Federal courts | State executives | State legislature | State and local courts | Counties | Cities | School districts | Public policy |
 KSF
KSF

