Autonomic nervous system
 From Citizendium - Reading time: 1 min
From Citizendium - Reading time: 1 min
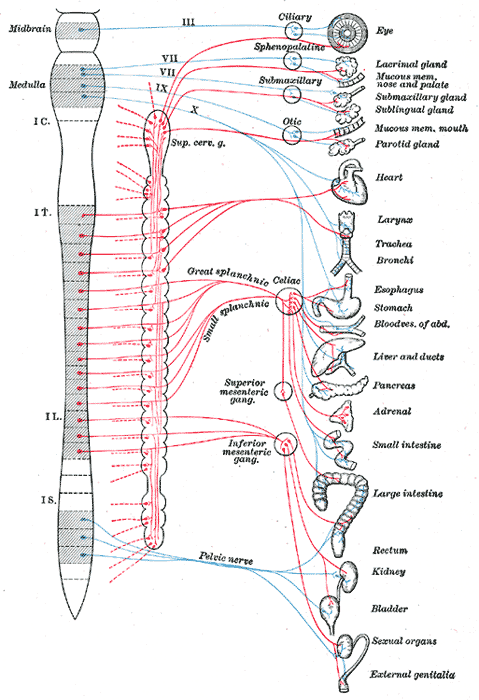
Blue = parasympathetic
Red = sympathetic
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) (or visceral nervous system) is the part of the peripheral nervous system that acts as a control system, maintaining homeostasis in the body. These maintenance activities are primarily performed without conscious control or sensation. The ANS has far reaching effects, including: heart rate, digestion, respiration rate, salivation, perspiration, diameter of the pupils, micturition (the discharge of urine), and sexual arousal. Whereas most of its actions are involuntary, some ANS functions work in tandem with the conscious mind, such as breathing. Its main components are its sensory system, motor system (comprised of the parasympathetic nervous system and sympathetic nervous system), and the enteric nervous system.
Components[edit]
Sympathetic nervous system[edit]
Promotes a "fight or flight" response, corresponds with arousal and energy generation, inhibits digestion.
Parasympathetic nervous system[edit]
Promotes a "rest and digest" response; promotes calming of the nerves return to regular function, and enhances digestion.
 KSF
KSF