Honshu
 From Citizendium - Reading time: 2 min
From Citizendium - Reading time: 2 min
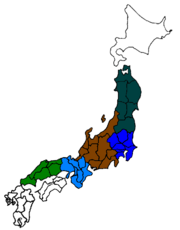
Honshu is the largest of the four main islands, and is divided into five regions.
Honshu (本州 Honshuu) is the largest of the thousands of islands that make up Japan. Many of the most important cultural and economic centres of Japan lie within Honshu, which is also home to most of the country's population.
Honshu is divided into five regions, each with its own dialects, traditions and local character. Northernmost is snowy Tohoku; neighbouring Kanto includes the Japanese capital Tokyo within its borders; Chubu and Kansai[1] occupy the centre; and southernmost Chugoku marks the end of the island. 34 of Japan's 47 prefectures are located in Honshu. The total population was 103,423,000 in 2006;[2] only about 23 million people live on other islands.

Photo © by Sonny Santos, used by permission.
Honshu's urban areas are particularly densely populated. Of Japan's eleven cities with a population exceeding one million, nine are on Honshu, and four of these - Tokyo, Yokohama, Saitama and Kawasaki - lie within the Greater Tokyo Area, the most populous urban region in the world. Tokyo itself includes over 12 million people within its municipal borders, making it the top city in Japan for population. Honshu is also host to other large urban regions centred around Nagoya and Osaka; with Tokyo, these three areas now include half the country's population for the first time ever.[3]
Footnotes[edit]
- ↑ Also known as Kinki.
- ↑ Japan Statistical Yearbook: 'Population by Prefecture 1920-2006'. Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications. .xls document.
- ↑ Japan Times: 'Population shrinks again despite increase in births'. 3rd August 2007.
 KSF
KSF