Life/Citable Version
 From Citizendium - Reading time: 68 min
From Citizendium - Reading time: 68 min

Buzz of Life: One aspect of the interrelations among living entities. Researchers begin to understand the mechanisms governing the complex network interactions between plants and pollinators, such as hummingbirds, shown in this illustration from Ernst Haeckel's Kunstformen der Natur (1904).[1]
The definition of life, the determination of the fundamental nature of living things, and the explanation of life's origin and evolution, have engendered much thought, debate and research throughout history. The perspective on life at any given moment in history, even today, qualifies as realistic and fruitful only to the extent of human knowledge at the time. In this article we focus defining the activity of living. We focus on what essential activities living entities perform that enable their living — specifically, we focus on the fundamental processes of living, those that constitute the system that counts as a living thing, the "common denominator that allows for the discrimination of the living from the non-living",[2] as inferred from the study of Earth's living things in the light of science.[3] This article takes, as its theme, “Life is what is common to all living things on Earth” (Christian De Duve).[4] Those include the basic working unit of life, the biological cell, and the many molecular structures and processes cells have in common, including a boundary; the importation of energy and exportation of entropy; metabolism; information processing and communication; self-organization and self-defense; adaptation; death; (re)production from parents; and, cognition of self and the outside world.
What is Life?[edit]
Biologists use the word life in several of its many senses: to refer to:
- the biography of a living thing (— the life of a mountain gorilla — its life history), sometimes even after it/she/he has died (— the life of Albert Einstein);
- living things in the aggregate (— plant life);
- the relationships among living things (— the life of the forest);
- biology-related sciences (— she became a life scientist, specializing in plant physiology);
- intellectual or imaginative activity (— the life of the mind);
- all of the living things past and present (— evolution of life); and,
- the fundamental processes that characterize living things that distinguish them from non-living matter (— life as a unique self-fabricating material system).
Biologists use the latter sense of ‘life’ when asking "what is life?" and "what is the origin of life?"
Perhaps elsewhere in the universe we might find the same kinds of processes that characterize living things on Earth, or, foregoing geoanthropocentrism, we might find different kinds of processes generating entities that we might recognize as living. In this article, only for life on Earth can we make observations and draw a few provisional conclusions to ask "what is life?".
Can we conceive that non-living matter could acquire naturally those processes that characterize living things? If living things developed from inanimate things, as science postulates, can we discover how that happened? We leave that question for an origin of life article. Here we focus on discovering the fundamental processes that uniquely characterize living things (on Earth), processes which origin-of-life researchers would need to know in order to target their search for the mechanisms that led to the transition of the non-living to the living.
The fundamental units and processes of living things: the sine qua non[edit]
Building blocks[edit]
On Earth, everything living teems with vibrant molecules of myriad types and sizes, too small for the naked human eye to see, but numerous enough to come into view as a flea or a giant sequoia tree (up to 4.5 million pounds of molecules).[5][6] It inspires wonder that particular collections of molecules, we humans, can generate words in the form of metaphors, in an attempt to explain the very activity of living that enables that feeling of wonder. Notwithstanding the molecular foundation of living things, the atoms and molecules must first aggregate and organize as biological cells before anything living can emerge.
Cells are considered the unit of life and living organisms can be either a single cell or a community of interacting cells. In living nucleated cells, organic molecules exist in heterogeneous pools of colloidal aqueous solutions bounded by lipid-protein membranes (e.g., nuclei, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum (see Cell). Each pool can have a different composition with distinct properties (e.g., transmembrane electrical potential difference; density; viscosity; osmotic pressure; acidity; ionic strength) and different architectures. This heterogeneity provides the basis for the physiology that can cause electric fields, fluid shifts, energy transfers, and the transport of molecules into and out of the pools.
Although organic molecules contain a variety of atomic elements (especially hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur), they always have a predominant structure of carbon atoms, typically linked as carbon-to-carbon bonds in diverse topologies. All cells share a common set of carbon-containing molecules - organic molecules, dissolved or dispersed in water as a common medium of housing and interaction — water comprises ~60-70% of the mature human organism. Those molecules include relatively small molecules, like amino acids, nucleotides, monosaccharides, and esters, and large macromolecules made up of sequences of smaller organic molecules. Organic macromolecules include proteins (sequences of amino acids), lipids, nucleic acids (sequences of nucleotides), polysaccharide (sequences of monosaccharides), and many other molecular genera.
The 'stuff' of life, then, is carbon-to-carbon chains, studded with other atomic elements, arranged in aqueous lagoons containing a variety of organic and inorganic molecules, interacting in accord with physico-chemical principles.
— Molecules[edit]
- See related topics: Chemistry, Biochemistry, and Organic Chemistry
|
From Molecule to Metaphor |
Why do carbon atoms play a central role in the chemistry of living things? Carbon has four electrons in its eight-electron-capacity outer shell, and it behaves as if it seeks four additional electrons to fill its outer shell to capacity (see accompanying figure and caption). Metaphorically speaking, it usually achieves its goal by forming "covalent bonds" with other atoms. The physical chemistry of carbon enables it to bond with many other elements with unfilled outer shells. Those include hydrogen, which can share one electron with carbon to fill its [hydrogen's] outer shell, allowing carbon to covalently bond to four hydrogen atoms, as in methane (CH4) [=natural gas]; oxygen, which can share two electrons with carbon to fill its [oxygen's] outer shell, allowing carbon to double-covalently bond with two oxygen atoms, as in carbon dioxide (CO2, or O=C=O; and nitrogen, which can share three electrons with carbon to fill its [nitrogen's] outer shell, allowing carbon to triple-covalently bond with one nitrogen atom, as in hydrocyanic acid (HCN). Most importantly, carbon can share electrons with itself, allowing the formation of C-C bonds, including double bonds (C=C) and triple bonds. The avidity for carbon to bond to itself allows carbon atoms to join into long chains, sometimes with C-C side chains, or even closed rings of C-C bonds, with or without side chains. Rings and chains and branches of linked carbons can combine into almost any imaginable shape. The particular covalent bonding capacity of carbon thus enables it to combine with hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and itself in multi-varied ways that generate small carbon-based molecules such as sugars, amino acids and nucleotides, which can join to become huge macromolecules with remarkable stability. The sequences of the varied subunits of such macromolecules give them the informational content required for self-constructing the dynamic organization of cells and for constructing copies of themselves.
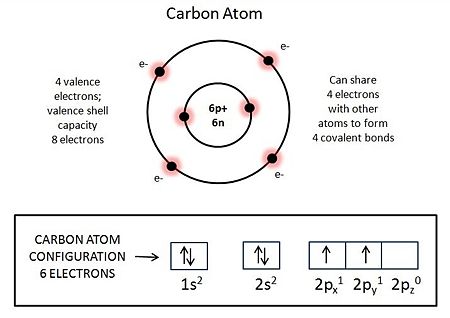
Atomic structure of the predominant isotope of a carbon atom: atomic number, Z=6; atomic mass = 12. Nucleus contains six protons (6p+) and six neutrons (6n). Electron configuration shown in rectangle. Outer shell (=valence shell) contains four electrons, has a capacity for eight electrons. The atom behaves as if it wants to fully fill its valence shell. With its valence shell fully occupied the atom achieves greatest stability as it has its least ability to react with other atoms. It usually achieves its valence shell octet of electrons by 'covalent' bonding, sharing electrons with other atoms, often with one or more other carbon atoms and one or more atoms of different elements also behaving as if they wanted to fill their own valence shells. See text.
The variety of carbon bonds vary in strength as well as in 3-D conformation. The simplest set of bonds that carbon can form is that of a tetrahedron, or pyramid, but the capacity of carbon for single, double and triple covalent bonding allows for many different geometries. Changing from one type of C-C bond to another type, as when a double bond is reduced to a single bond, will cause energy changes but without destroying the molecule. Such changes not only affect the molecule's energy state, but also affect the shape of the molecule and the particular side groups attached to it. One might say that the 'pulse of life' is represented at an atomic level.
The properties of carbon mean that organic macromolecules can contain huge 'banks' of information coded in their structure. Not only can each of the constituent molecules be huge, but several categories of chemicals, like nucleotides or amino acids, that contain several different species, can be ordered so that the possible combinations are effectively limitless. All of these molecules are involved in the molecular-interaction networks of cells.
Amongst those networks of molecular interactions are those that enable cells to import and transform energy and energy-rich matter from the environment and that ultimately enable cells to grow, survive and reproduce. Matter needs energy to vitalize it. D'Arcy Thompson, a pioneering biologist in the early 20th century, considered talking about molecules (or matter generally) only provides convenience in that enables us to abbreviate the nomenclature and description of the energies and their forces that give the molecular assembly living status.[7]
Elsewhere in the universe, elements other than carbon and Earth-life's carbon-associated elements might give structure to living systems. Silicon, carbon's close columnar relative on the periodic table, also forms bond-chains with itself, forms covalent bonds with other elements, and supplies the basis for extraterrestrial living systems in fantasies by science fiction writers. Scientists conclude that silicon-silicon bonds do not stabilize under an Earth-like physico-chemical environment compatible with life as we know it.[8] Living systems, whether carbon-based or not, may not even require water to support the organization's chemistry.[9]
For the possibility of extraterrestrial life based on inorganic matter see novel proposal of physicists Tsytovich et al.[10][11] A mass of charged particles — like a swarm of bees — exhibiting features similar to Earth-type living systems
The possibility of non-molecular life, or life consisting of no matter at all (e.g., made up of energy fields), also interests science fiction writers. We science non-fiction writers consider energized molecules as the structural basis of living things on Earth.
— Cells[edit]
- See Related Topics: Cell, Microbiology, Systems biology
|
"Omnis cellula e cellula" (Every cell out of a cell) |
In recognizing a living thing, biologists recognize it as a unity within an environment, yet apart from it — a compartment of a larger whole, structurally distinguishable though not functionally completely isolated from or closed to its surroundings. Every entity that biologists acknowledge as living — bacteria, trees, fish, chimpanzees — has a structurally compartmentalized building block, the biological cell. All cells extend themselves to (and include) an enclosing boundary that consists of a lipid-protein molecular membrane known as the cytoplasmic membrane, which structurally separates the interior of the cell from the external environment while allowing certain exchanges of energy and matter. The lipid molecules form the backbone of the cell membrane. [12]
Many organisms live as isolated cells, others as cooperative colonies of cells, and still others as complex multicellular systems that include diverse cell types, each specializing in different functions.[13] Nature has produced an enormous variety of cell types that span three vast ‘domains’ of living systems: Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya,[14] yet cells in all three domains have many features in common. In particular, as described above, they have a surrounding membrane, a physical boundary that separates them from their environment. (Yet that generally accepted commonality may oversimplify: see[15])
The detailed composition of cell membranes differ among cell types, with differing protein types and auxiliary lipid species, enabling specific kinds of functional exchanges with the surroundings. Pores, receptor molecules and protective walls are often features of the cell surface, in both unicellular and multicellular entities.[16]
Current evidence indicates that only pre-existing cells can ‘manufacture’ cells, so how did the first cell(s) arise? Examining what all cells have in common may provide insight to the origin of life. All extract energy from energy-rich molecules by simple oxidation reactions, and convert it into other, chemical forms of energy useful for cell function. The molecule ATP universally serves as the cell's main energy 'currency'. All cells inherit digitally stored information in the form of molecules of DNA, and with minor exceptions the DNA of all cells use the same universal genetic code to guide production of a myriad of distinct protein structures. Cells use those proteins to carry out diverse activities, including energy processing and conversion of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorous-containing materials into cellular structures. In the human genome, perhaps as few as 22,000 different protein-coding genes[17] lead to the production of many times more distinct protein structures that make up the variety and quantity of protein molecules needed for the structures and functions of a cell. Numerous molecular mechanisms account for that quantitative gene-to-protein amplification.[18]
Nature has produced a huge diversity of single-celled organisms and complex animals and plants. These can contain vast numbers of cells, each part of a specialized subpopulation (cell types) — in a mammal, the cells that make up bone differ in numerous structural and functional properties from those that make up muscle, and differ again from those that make up skin, for example. Humans contain approximately 200 different cell types as classified by microscopic anatomy.[13] In multicellular organisms, cells combine to make organs, the functional and structural components of the single larger organism.
What makes a single celled organism 'alive', and does the answer apply also when we call a large complex multicellular animal or plant 'alive'? What exactly do we mean by 'living'? We turn to those considerations next.
The thermodynamics of 'living'[edit]
|
"A deterministic emergence of life would reflect an essential continuity between physics, chemistry, and biology." |
|
"We propose that the only absolute requirements [for life] are a thermodynamic disequilibrium |
|
"Organisms do not maintain their complexity, and become more complex, in a vacuum. |
Biologists have learned the importance of viewing living things from the perspective of thermodynamics — the science of interactions among energy, heat, work, and entropy (the degree of disorder of a system) and information (the degree of order of a system).[20] These interactions define what a system can and cannot do when interconverting energy and work. For example, by the First Law of Thermodynamics, when a process converts one form of energy (e.g., light) to another (e.g., electricity), no net loss of energy and no net gain results, when the byproduct, heat, is taken into account.[21] Once heat gets generated in an energy conversion, it becomes difficult to reverse the conversion. We can use sunlight to generate light back having a solar cell power a lightbulb, but do not get all the light back because some of the energy of sunshine converts to heat — i.e., it gets degraded to a lower 'quality' form of energy, less organized.
Scientists developed the laws of thermodynamics through experiment, debate, mathematical formulation and conceptual refinement; Albert Einstein believed that they stood as an edifice of physical theory that would never topple.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics has fundamental pertinence to the understanding of living systems:

Energy emitted by our sun provides the great bulk of the energy gradient that living systems on earth exploit, either directly or indirectly, to maintain a state far from the equilibrium state of randomness. The photograph shows a handle-shaped cloud of plasma (hot ions) erupting from the Sun.
- Heat flows spontaneously — i.e., without help from an external agency — from a region of higher temperature to one of lower temperature, and never spontaneously in the reverse direction. That also holds for other forms of energy, including electromagnetic and chemical energy: concentrations of energy disperse, down-flow, to lower energy levels, flowing, so to speak, "into the cool", and in the process, capable of doing work.[22][23]
- When heat, as input to a system, causes it to perform work (e.g., as in a steam engine), it never converts the energy input entirely to work. Some of the heat always dissipates as ‘exhaust’, lower quality heat energy unusable by the system for further work. That also holds for other forms of energy doing work; some of the energy always turns into exhaust, typically heat. As empirical fact, conversion of energy to work in a system can never proceed at 100% efficiency.
- Consequences arise because work can produce order in a system, but always exports some of the energy input as a less organized form of energy, heat. Experiments reveal the balance sheet of order: the degree of order of a system (e.g., a living cell) and its surroundings together never increases when energy input causes the system to perform work; the 'net' order always decreases — disorder increases. Scientists have learned how to quantify the degree of disorder, and they refer to that quantity as entropy. Water vapor, with its molecules distributed nearly randomly, has a higher entropy (the molecules show a less ordered arrangement) than liquid water, with its molecules distributed less randomly, and a much higher entropy than ice, with its molecules distributed in a more ordered crystal-like array. Left to itself in an isolated system, ice tends to spontaneously melt and liquid water to evaporate. Order tends to disorder, with the Universe as a whole tending to exhaust itself into an ‘equilibrium’ state of randomness.
Water vapor in a glass jar, with its higher degree of disorder than it would have if it were liquid water in the jar, will, at room temperature, eventually settle at the bottom of the jar into a puddle of the more ordered liquid water. That decrease in disorder (entropy) of the jar-system can occur only because the water-vapor-filled jar-system is not an isolated system, closed off from energy exchange with its surroundings. The water-vapor-filled jar can export heat to the lower-temperature room as the water vapor condenses into liquid water, releasing the heat energy that maintained the water as vapor instead of liquid — an instance of energy flowing downhill, dissipating itself from a more to a less concentrated state. The exported heat, no longer a concentrated source of energy in the water vapor, becomes a less concentrated source of energy, distributed throughout the room, the jar-system's surroundings. Because experience has established that a system and its surroundings can statistically never spontaneously increase its degree of order — according to the Second Law of Thermodynamics, the room then becomes more, or minimally as much, disordered as the jar-system became more ordered. Thus, an open system can become more ordered spontaneously without conflict with the Second Law of Thermodynamics.
The above three expressions of the Second Law of Thermodynamics reflect the fact that energy and order spontaneously flow downhill — down a ‘gradient’— toward eliminating the gradient of energy.[22] Upon eliminating the gradient by flowing downhill, no energy flows, all work production ceases, all order dissipates, and an equilibrium state of maximal disorder, entropy, ensues.
So, how do living entities, those manifestly energized organisms, come into existence — to develop from an embryonic state to one of more order and less entropy — and perpetuate their order? How do they thwart the Second Law of Thermodynamics?
They don’t: they only seem to do so. We saw, in the jar-filled water vapor example, that an 'open' system — one that can exchange energy with its surroundings — can order itself within the constraints of the Second Law of Thermodynamics. Living systems exploit the Universe’s gradients of energy and order. Like a steam engine, they 'import' energy and order, convert it to the work of building internal order in the form of a dynamic organization of constituent elements, which they fabricate themselves, and so fabricate a system of decreasing internal (within-system) entropy.[24] But, all along, they emit enough 'exhaust' to increase the disorder and entropy of their surroundings, so that the total entropy of the living system and its surroundings increases. Thereby the Second Law receives its due. The living system skims off a portion of the order flowing past it; it ingests order.
Biological cells qualify as non-equilibrium thermodynamic open systems. They ingest some of the energy that flows through them, and use it to keep away from the equilibrium state of randomness dictated by the Second Law. By exporting unusable energy as heat, they actually export more disorder (entropy) than they produce within themselves, thereby increasing the total entropy. They hasten the dissipation of the energy gradient they are in, as if nature's abhorrence of energy gradients 'favored' the origin, development and persistence of living systems to maximize the rate of entropy gain of the Universe as a whole.
Importantly, living things can store energy.
Recognition of the need for energy, as defined by the physicists, to enable life, has a long history.[7] [25]
A living system always works far from the 'equilibrium' state of activity that would ensue if no energy could be imported, and energy from outside keeps the system far from equilibrium. Non-equilibrium thermodynamic open systems, including living things, can exhibit unexpectedly complex behaviors because of their far-from-equilibrium state, and one very remarkable behavior that can result is self-organization.[26]
The sun (Sol) supplies much of the energy gradient that sources thermodynamic disequilibrium for living systems on earth. However, as Benner et al.[27] point out,
...heavier atomic nuclei, left from a supernova, are not at thermodynamic equilibrium. Decay of these nuclei is a powerful source of planetary not-at-equilibrium environments. Radioactive decay [deep in Earth] drives tectonics and volcanism on Earth. These create non-equilibrium environment in many areas such as black smokers on the ocean floor. The consequent energetic disequilibrium supports life [near them] despite the absence of direct solar energy.
Some biophysicists propose that the production of order by matter in an energy gradient, as in living things, tends to develop inevitably and proceed inexorably. They give two reasons: (1) the production of order through work, by exporting more than counterbalancing degrees of disorder, increases total entropy production (i.e., dissipates the energy gradient and renders the dissipated energy unusable) beyond that which would otherwise occur, and (2) energy sources dissipate their gradient to produce disorder at the fastest rate possible — to reach random thermal equilibrium as fast as they can. In other words, the physical principles governing energy gradient dissipation and energy degradation not only allows the development of living systems, but, in effect, tends to select for them — or urges their emergence — in particular, when no constraints are present disallowing their development (e.g., excess heat, poverty of appropriate resources. See additional argument in:[28]
Thermodynamic principles thus contribute not only to answering the question “what is life?” but also to “why is there life?”.[29] [30] Sir Arthur Eddington, the astronomer who first confirmed Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity, remarked:
The law that entropy always increases--the second law of thermodynamics--holds, I think, the supreme position among the laws of Nature. If someone points out to you that your pet theory of the universe is in disagreement with Maxwell's equations--then so much the worse for Maxwell's equations. If it is found to be contradicted by observation--well, these experimentalists do bungle things sometimes. But if your theory is found to be against the second law of thermodynamics I can give you no hope; there is nothing for it but to collapse in deepest humiliation.[31]
Harold Morowitz and Eric Smith begin their essay on that perspective as follows:[19]
Life is universally understood to require a source of free energy and mechanisms with which to harness it. Remarkably, the converse may also be true: the continuous generation of sources of free energy by abiotic processes [e.g., energy from radioactive decay deep in the Earth] may have forced life into existence as a means to alleviate the buildup of free energy stresses. This assertion — for which there is precedent in non-equilibrium statistical mechanics and growing empirical evidence from chemistry — would imply that life had to emerge on the earth, that at least the early steps would occur in the same way on any similar planet, and that we should be able to predict many of these steps from first principles of chemistry and physics together with an accurate understanding of geochemical conditions on the early earth. A deterministic emergence of life would reflect an essential continuity between physics, chemistry, and biology. It would show that a part of the order we recognize as living is thermodynamic order inherent in the geosphere, and that some aspects of Darwinian selection are expressions of the likely simpler statistical mechanics of physical and chemical self-organization.
See also commentary on Professors Morowitz and Smith's article.[32]
Morowitz and Smith think that such order happens because it is a better 'lightning conductor' for discharging excess energy.[32]
High energy (low entropy) cannot contain itself. When it has a channel to a lower energy (higher entropy) source, it discharges itself through the channel, causing patterns in space-time. Living systems provide such a channel for free energy from the sun and hydrothermal vents, because they actively consume energy and use it, in part to lower their own entropy, through growth and development and maintaining the living state. The system's surroundings receives the fruits of its labors, waste, translated as less usable energy than it would have without part of it already used up, and more entropy than without the lowering of entropy in the living organization because lowering entropy through incomplete conversion of energy to work generates entropy as waste. Living systems help relieve solar and vocanic pent-up energy, hastening its dissipation, justifying their cognomen as "dissipative structures".
We can, then, view a living system as a state of organizational activity maintained by importing, storing and transforming energy and matter — into the work of fabricating structures needed to sustain that state. They can only do so by producing waste and exporting it, and this lowers the ordered state of the environment. A living system maintains its organization at the expense of its external environment, leaving the environment more disordered than the gain in order of the living system — in keeping with the Second Law of Thermodynamics. Thus, from a thermodynamic perspective:
A living system:
|
However, as physicist Philip Nelson writes: "The pleasure, the depth, the craft of our subject lie in the details of how living organisms work out the solution to their challenges within the framework of physical law."[33] [Emphasis in original] To discuss those details would require invoking the facts and theories of biological physics, molecular and cell physiology, and systems biology, beyond the scope of this article if not the scope yet of those disciplines.
Evolutionary aspects of 'living'[edit]
|
Last Paragraph of Charles Darwin’s Origin of Species (1859) "It is interesting to contemplate an entangled bank, clothed with many plants of many kinds, with birds singing on the bushes, with various insects flitting about, and with worms crawling through the damp earth, and to reflect that these elaborately constructed forms, so different from each other, and dependent on each other in so complex a manner, have all been produced by laws acting around us. These laws, taken in the largest sense, being Growth with Reproduction; Inheritance which is almost implied by reproduction; Variability from the indirect and direct action of the external conditions of life, and from use and disuse; a Ratio of Increase so high as to lead to a Struggle for Life, and as a consequence to Natural Selection, entailing Divergence of Character and the Extinction of less-improved forms. Thus, from the war of nature, from famine and death, the most exalted object which we are capable of conceiving, namely, the production of the higher animals, directly follows. There is grandeur in this view of life, with its several powers, having been originally breathed into a few forms or into one; and that, whilst this planet has gone cycling on according to the fixed law of gravity, from so simple a beginning endless forms most beautiful and most wonderful have been, and are being, evolved." |
Fires and storms have achieved status as living entities in human 'poetic/animistic' imagination, but although some non-living entities, such as tornadoes or the flames of candles, exist as non-equilibrium open thermodynamic systems, they lack essential qualities of Earth's living things. Tornadoes and candle flames cannot 'reproduce' themselves. Fire may spread and tornadoes may split, but the system that comprises each phenomenon does not self-replicate. Living systems have the capability of reproducing themselves.
When a living system reproduces itself, its offspring inherit its properties, but with variations introduced by random events (mutations). Some variations offer some of the offspring[34] less opportunity to reproduce than others, and other offspring better opportunity, sometimes better even than their parents. Accordingly, new groups with different properties arise that may supplant older groups because of their greater reproductive fitness.[35]Biologists call this "evolution by natural selection", and many, but not all,[36] [37] [38] regard it as the most important way whereby living systems evolve over geological time.
Therefore, biologists recognize the ability to produce offspring that inherit some of its features, but with some variation, as an essential characteristic of living systems. They refer to it as descent with modification.[36] [38] [37] Evolution by natural selection will occur if heritable variations produce offspring that differ in their reproductive fitness and if circumstances induce competition among conspecifics. The variations occur due to chance variations (e.g., mutations) in the inherited genetic database (genome) that the organism draws upon to the help it self-construct and self-maintain its organismic traits (phenotype), and also to various natural experiments (e.g., symbiogenesis) that lead to emergent genotype-phenotypes.[36]
In all living systems, DNA primarily provides the database for the construction of their protein constituents. All living things descended with modification from an ancestral community of microorganisms with a partially shareable gene pool. (But see:[39] To glimpse beyond that horizon, we will need to take heed of the findings of intense current research on early cellular evolution -- see Evolution of cells).
Viruses have few of these characteristics, but they do have a genotype and phenotype, making them subject to natural selection and evolution. Accordingly, descent with modification is not uniquely a characteristic of living systems. Beyond the scope of this article, we find descent with modification in memes and the artificial life of computer software, such as self-modifying computer viruses and programs created through genetic programming. Descent with modification has also been proposed to account for the evolution of the universe.[40]
When it comes to the fundamental structures and processes of living, however, some biologists argue against the requirement for reproduction.[41] NASA defines 'life' as a "chemical system capable of Darwinian evolution", without specification of reproduction per se (for discussion, see Benner et al.[42]).
Adding to the thermodynamic perspective, we might say that:
A living system:
|
Self-organization[edit]
| As the wind of time blows into the sails of space, the unfolding of the universe nurtures the evolution of matter under the pressure of information. From divided to condensed and on to organized, living, and thinking matter, |
In living systems, self-organization 'emerges' as a spontaneous manifestation of the interactions among the systems' components. In cells, self-organization emerges in part from so-called supramolecular (non-covalent) interactions of proteins-with-proteins and proteins with other molecules.[43] [44] The proteins make their appearance through a genetic transcription-translation machinery, which itself represents a self-organized molecular machine that emerges in part from the non-covalent interactions of proteins with nucleic acids and other molecules.
Molecules interact by forming and breaking strong or weak covalent bonds, and also through weaker intermolecular interactions, like hydrogen bonding and Van der Waals forces. Those supramolecular interactions self-assemble aggregates of molecules (e.g., organelles, networks), giving them the properties that enable many biological processes.[44][45] To quote Reinhout and Crego-Calama:[46]
In chemistry, noncovalent interactions are now exploited for the synthesis in solution of large supramolecular aggregates. The aim of these syntheses is not only the creation of a particular structure, but also the introduction of specific chemical functions in these supramolecules.
And JM Lehn:[47]
Starting with the investigation of the basis of molecular recognition, [supramolecular chemistry] has explored the implementation of molecular information in the programming of chemical systems towards self-organisation processes, that may occur either on the basis of design [by the chemist] or with selection of their components.
The qualifier that self-organization emerges in part from supramolecular interactions of proteins with proteins and other molecules reflects the need to invoke not only supramolecular self-assembly but also evolutionary mechanisms that produce and select genes that tend to optimize functional self-organization — in other words, adaptation. One must also invoke local real-time selective processes that confer stability and appropriate functionality to self-assembly, called homeostasis or adaptability. [48]
Professor of Microbiology, Franklin M. Harold, offers the following definition of self-organization:
...let me define self-organization as the emergence of supramolecular order from the interactions among numerous molecules that obey only local rules, without reference to an external template or global plan...The definition explicitly excludes order imposed by an external template, whether physical (as in a photocopier) or genetic (as in the specification of an amino acid sequence by a sequence of nucleotides)...The structure of the self-assembled complex is wholly specified by the structures of its parts and is therefore implicit in the genes that specify those parts: natural selection crafted those genes to specify parts that assemble into a functional complex.[49]
Information resides in proteins and other molecules in virtue of their structure, and through them, information flows through cells, just as energy does, and determines their organizational nature.[50]
One way to understand this self-organization is to view a living system as a 'computing device'. The inherited and acquired information base specifies components which arrange themselves in accord with their physico-chemical properties — i.e., they 'compute' the system in a complex chemical reaction. Yet that description under-characterizes the complexity of the system. In a multicellular organism, each cell retrieves only its own particular pieces of information from the total information base, and the selection varies with time. Each cell must perform specific computations to effect that dynamic activity. The behavior of the system's functional networks constitute those specific dynamic computations. The apparent circularity begat by adding that further characterization of the system as a 'computing device' exemplifies two-way nature of the 'computations' self-organizing the living system. With the tinkering and discovering comprising local trial-and-error and evolution’s handiwork, that 'circularity' carries out ('computes') integrative functions not explicitly encoded in the inherited and acquired information base of the system.[51]
The molecular biologist Sidney Brenner[52] expressed the 'computing device' metaphor this way:
...biological systems can be viewed as special computing devices. This view emerges from considerations of how information is stored in and retrieved from the genes. Genes can only specify the properties of the proteins they code for, and any integrative properties of the system must be 'computed' by their interactions. This provides a framework for analysis by simulation and sets practical bounds on what can be achieved by reductionist models.[53]
The structure and behavior of self-organized systems need no behind-the-scene 'master controller', and no prepared blueprints that specify the structure and dynamics of the system. Instead, they emerge from interactions among the naturally generated and naturally selected components of a system, dictated by their physico-chemical properties, and dynamically modified by the emergent organization, which is itself modified by the environment. The single-celled zygote self-organizes into a multicellular living system as genetically encoded proteins interact, responding to changing influences from the changing environment generated by growing multicellularity — becoming a network of many cell-types working cooperatively.
That biological systems self-organize has led one prominent biologist to say they are products of a "blind watchmaker".[54]
Self-organization tends to breed greater complexity of self-organization. One important aspect of self-organization in cells rests on the tendency for lipid molecules with polar (water-loving) and non-polar (water-shunning) ends to form bilayers in an aqueous solution, each unit of the bilayer with two lipid non-polar ends mutually attracted in the center and the polar ends surrounded by water. Protein molecules can span the bilayer membrane, or selectively straddle only one or the other side of the membrane and its aqueous surrounding, according to their specific amino-acid sequence and side-groups. Those lipid-protein membranes allow cells to communicate with other cells, either in free-living cellular communities or in multicellular organisms, and those communication activities self-organize by virtue of the properties of the cells, generated by natural experiments and selected for fitness by evolutionary mechanisms, and subject to downward effects by the systems' organization and environmental influences on the systems.
Self-organization occurs at all levels of living systems. For example, the dynamics of communities, such as the feeding relationships within communities of large mammals, also reflect self-organization. The animals and components of the ecosystem embedding them self-organize, resulting in "...unitary structures with coherent properties...[that] can operate in an integrated way, which allows for the acceptance of their changes on large time-scales as evolutionary."[55]
Further elaborating the descriptions of living systems beyond the thermodynamic and evolutionary perspectives, we might say that:
A living system:
|
Autonomous agents[edit]
Views of a Foetus in the Womb (c. 1510 - 1512) by Leonardo da Vinci. Although this near term fetus is a symbol of a new human life, the drawing is of a cadaver specimen.
Stuart Kauffman uses the concept of 'autonomous agents' to explain living systems.[56] [57] He gives the hypothetical example of an enzyme that catalyzes the binding of two smaller sub-component molecules into a copy of itself — self-replication by auto-catalysis. The energy to produce the enzyme comes from a neighboring molecule, which, by breaking an energy-rich bond, serves as a 'motor' to produce excess enzyme. The self-replication stops after using all duplicates of the motor, so external energy — perhaps from light impinging on the system — must drive the repair of the broken chemical bond, re-establishing a supply of that energy-supplying molecule, thereby re-energizing the motor. A new cycle of auto-catalytic self-replication can then begin, given an influx of external energy and 'food' (sub-components of the auto-catalytic enzyme). As an essential feature, interactions among the components of a system have effects (technically 'allosteric' effects) that help organize and coordinate its processes, allowing the self-replication to proceed.[56]
Kauffman conceives, then, of an autocatalytic molecule in a network of molecules that has cycles of self-replication driven by external energy and materials. Such a network is a 'molecular autonomous agent' because, given external energy and ample materials, the network perpetuates its existence;. The network is autonomous because it is not controlled by outside forces even though it depends on outside energy and materials. The 'agent' is the system doing work autonomously; in this case, the work of self-replication. (That's what 'agents' do; they do work.) In this example, the agent survives by ‘eating’ outside materials and energy. Work gets done because the system remains far-from-equilibrium: as energy flows through the system, the system does its work, and in so doing dissipates the energy gradient, but it temporarily constrains the rate of dissipation by storing energy in its internal organization. The agent continues to "live" only while that far-from-equilibrium state exists, and it can be starved to 'death' by stopping the matter and energy from flowing through the system. Kauffman argues that cells, and indeed all living systems, qualify as autonomous agents, constructed from molecular autonomous agents.[56]
Autonomous agents also interest scientists in the fields of artificial intelligence and artificial life. One careful description of autonomous agents from some members of that group adds further insight to this view of living systems:
An autonomous agent is a system situated within and a part of an environment that senses that environment and acts on it, over time, in pursuit of its own agenda and so as to effect what it senses in the future. It has the properties of reactivity (timely response to environmental changes; autonomy (controls its own actions); goal-orientation (pursues its own agenda); continuous processing. Some autonomous agents may also have the properties of communicability (with other agents); adaptability (based on previous experience); unscripted flexibility.[58]
For Kauffman, the property of pursuing its own agenda includes contributing to its own survival and reproduction: "...an autonomous agent is something that can both reproduce itself and do at least one thermodynamic work cycle. It turns out that this is true of all free-living cells, excepting weird special cases. They all do work cycles, just like the bacterium spinning its flagellum as it swims up the glucose gradient. The cells in your body are busy doing work cycles all the time."[59] There is only one escape from work, and that is death.
If the descriptions of living systems from thermodynamic, evolutionary, self-organizational and autonomous agent perspectives are considered, we might add that:
A living system:
|
Networks[edit]

The modular organization of a cellular network. Yeast Transcriptional Regulatory Modules. Nodes represent modules, and boxes around the modules represent module groups. Directed edges represent regulatory relationship. The functional categories of the modules are color-coded.[60]
The science of networks[61] provides another useful perspective on living things. Networks ‘re-present’ a system as 'nodes’ and ‘interactions’ among the nodes (also referred to as ‘edges’ or ‘arrows’ or ‘links’). For example, in a spoken sentence, words and phrases make up the nodes, and the interconnections of syntax (subject-to-predicate, preposition-to-object of preposition, etc.) make up the links. Intracellular molecular networks represent specific functions in the cell; molecules make up the nodes, and their interactions with other nodes make up the edges or arrows. Some networks accept inputs of one kind and return outputs of a different kind.
One finds networks everywhere in biology, from intracellular signaling pathways, to intraspecies networks, to ecosystems. Humans deliberately construct social networks of individuals working (more or less) to a common purpose, such as the U.S. Congress; they also construct networks of electronic parts to produce, for example, mobile phones; and networks of sentences and paragraphs to express messages, including this very article. Researchers view the World Wide Web as a network, and study its characteristics and dynamics.[61] [62]
According to Alon, "The cell can be viewed as an overlay of at least three types of networks, which describes protein-protein, protein-DNA, and protein-metabolite interactions."[63] Alon notes that cellular networks are like many human engineered networks in that they show 'modularity', 'robustness', and 'motifs':
- Modules comprise subnetworks with specific functions differing from those of other modules, and which typically but not invariably connect with other modules, often only at one input node and one output node. An individual module achieves its status as a distinct entity not only by its functional specificity but also by spatial specificity (e.g., ribosomes) or by chemical specificity (e.g., signal transduction networks). Modularity helps to facilitate real-time system adaptability to environmental change, as the organization of modules in the system contributes to the emergent properties of the system.[64] It also facilitates evolutionary adaption, as, to select an adaptation, evolution may need tinker with just a few modules rather than with the whole system. Evolution can sometimes 'exapt' existing modules for new functions that contribute to reproductive fitness. For example, Darwin surmised that the swim bladder of skeletally heavy fish evolved as an adaptation for control of buoyancy but was exapted as a respiratory organ in certain fish and in land vertebrates. [65] [66]
- Robustness describes how a network is able to maintain its functionality despite environmental perturbations that affect the components. Robustness also reduces the range of network types that researchers must consider, because only certain types of networks are robust.[67]
- Network motifs offer economy of network design, as the same circuit can have many different uses in cellular regulation, as in the case of autoregulatory circuits and feedforward loops. Nature selects motifs in part for their ability to make networks robust, so systems use motifs that work well over and over again in many different networks.[68] In several well-studied biological networks, the abundance of network motifs — small subnetworks — correlates with the degree of robustness.[69] Networks, like those in cells and those in neural networks in the brain,[70] use motifs as basic building blocks, like multicellular organisms use cells as basic building blocks. Motifs offer biologists a level of simplicity of biological functionality for their efforts to model the dynamics of organized hierarchies of networks.[68]
The view of the cell as an overlay of mathematically-definable dynamic networks can reveal how a living system can exist as an improbable, intricate, self-orchestrated dance of molecules.[71] The 'overlay of networks' view also suggests how the concept of self-organized networks can extend to all higher levels of living systems.
Further elaborating the descriptions of living systems beyond the thermodynamic, evolutionary, self-organizational and autonomous agent perspectives we might add that:
A living system:
|
Information processing[edit]
| I shall argue that this information flow, not energy per se, is the prime mover of life-- that molecular information flowing in circles brings forth the organization we call "organism" |
Bioscientists study biological systems for many different reasons, hence biology has many subdisciplines (see Biology and List of biology topics). But in every subdiscipline, bioscientists study biological systems for the proximate reason of gaining information about the system to satisfy their however-motivated curiosity and to apply that information to human agendas (e.g., to prevent disease, to develop treatments, to enhance health and longevity, to conserve the environment, etc.). Those realities attest that biological systems harbor information, at least as people usually understand the term. To appreciate how that perspective can contribute to understanding living systems, the following questions need answers:
- What do we mean by information?
- How does information apply to biological systems?
- How does information emerge in biological systems?
- How do the answers to those questions add to explaining living systems?
The word 'information' comes from the verb 'to inform', originally meaning to put form into something: the seal in-forms the wax, and the wax now contains in-formation. A random collection of particles or other entities has no form, nothing has given it form, and it contains no in-formation. The more randomness in the structure of the collection, the fewer improbable arrangements or interactions it has among its parts.

Information processing from DNA to a living system. Genes, composed of DNA, contain the information used by other cellular components to create proteins. A cell is tightly packed with tens of thousands of proteins and other molecules, often working as multi-molecular 'machines' to perform essential cellular activities.
A drinking glass falls onto the sidewalk, it falls apart into a random collection of bits of glass. Notice it doesn’t regroup into the drinking glass — you could watch it for a lifetime. Our experience shows us that the drinking glass is more improbable than the glass smithereens. The more improbable the arrangements, the more in-formation a collection of parts has received and therefore contains. An observer will conclude that something has happened to form the parts into a more improbable state — an in-formation has occurred, and that the collection of parts contains that in-formation. By that reasoning, biological systems contain in-formation: something has happened to 'form' the parts into an improbable state.[72]
An ordered desktop soon becomes disordered. The ordered desktop has message value, or 'information', in that something must have happened to give it form. The more unlikely the arrangement of the parts, the more information it contains. Biological systems have information content in that they are unlikely (non-random) arrangements of parts, non-random collections of interactions of parts, and non-random collections of functional activities.
The above-discussed thermodynamic and autonomous agent perspectives viewed cells as interposed between a higher-to-lower degrees of usable (free) energy — embedded in downward sloping free energy gradient. The flow of energy through the cell fuels it, enabling it to perform the work that leads it to gain form, or order, or organization, and to gain functionalities, which raises its information content.[73]
Thus a living system emerges as an information processing system. It can receive information from energy[74] and energy-rich materials in its environment, which fuels and supplies the self-organizing machinery that builds and sustains an information-rich organization; it can generate new information inside itself, as in embryonic development; and it can transmit information within and outside itself, as in transcription regulation and exporting pheromones. From its parent(s), it inherits information (genetic) that provides a database to help it realize its developmental potential — including information critical for its self-reproduction, though it also inherits information in non-genetic forms (epigenetic, behavioral, symbolic) that contribute to its development.[37][36] [75] [38]
Physiologist and Director of the Laboratory of Cell Communication at the Marine Biological Laboratory, Woods Hole, Massachusetts, Werner R. Loewenstein[50] emphasizes the reciprocal relationship between changes in information and changes in entropy: “…we may regard the two entities as related by a simple conservation law: the sum of (macroscopic) information change and entropy change in a given system is zero. This is the law which every system in the universe…must obey.” He elaborates:
"Living beings continuously lose information and would sink to thermodynamic equilibrium just as surely as nonliving systems do. There is only one way to keep a system from sinking to equilibrium: to infuse new information…[T]o maintain its high order, an organism must continuously pump in information. Now, this is precisely what the protein demons do inside an organism. They take information from the environment and funnel it into the organism. By virtue of the conservation law, this means that the environment must undergo an equivalent increase in thermodynamic entropy; for every bit of information the organism gains, the entropy in the demon's environment must rise by a certain amount. There is thus a trade-off here, an information-for-entropy barter; and it is this curious trade which the protein demons ply. Indeed, they know it from the ground up and have honed it to perfection. Bartering nonstop, they draw in huge information amounts, and so manage to maintain the organism above equilibrium and locally to turn the thermodynamic arrow around."
Combined with other perspectives, viewing living systems as information processors, as inheritors, receivers, generators and transmitters of information, and as reproducers of inherited information, enables one to see living systems and their interactions with other living systems as a vast, complex, emergent, naturally-selected, self-sustaining, evolving communications network. Recently, on the timescale of evolving living systems, that evolving communications network emerged as the human brain, capable of communicating with itself and other humans using networks of symbols.[76] That led to the emergence of cultural evolution, a whole new domain of self-reproducing entities ('culturgens', 'memes') and a whole new domain of descent with modification. That in turn led to the emergence of other vast communications network: books, wikis, and other technologies of information generation and exchange.
We might now consider another closely related perspective, a ‘cognitive’ perspective.[77] Given that networks resist common perturbations (e.g., by their robustness, and by ‘homeostasis’), one might think of them as containing a representation of themselves and of their environment, and of how they might vary. As networks self-organize through interactions among proteins, any network-like 'representation’ of of the living system embedding it, and its environment, must derive from the information that determines those proteins. The genetic information comprises a molecular code, and the process that transforms that information into proteins describes an algorithm — the transcription-translation algorithm, including its regulatory circuits. Inasmuch as those algorithms evolved through natural experiment and selection, one can view evolution as selecting for cognitive functionality in the genome — the ability to ‘represent’ the cell’s state and environment and, more generally, to remember and anticipate.
Genetic information has the form of a digital code, one whose execution jump-starts self-organizing cellular processes, including the processes that lead to self-organization of networks that regulate execution of the genetic digital code — the gene regulatory networks. A separate digital code also has a central role in the operation of those gene regulatory networks: the code adjacent to a gene determines which transcription regulating factors can bind there, and thereby controls gene activity. In other words, a digital code, separate from the code that specifies the proteins of the gene regulatory networks, gives specificity to the behavior of those networks and to their regulation of the execution of the genetic digital code.[78] Eventually, digital codes surrender to decipherment, offering the hope that we might someday read the message they contain and find ways to edit it.
Further elaborating beyond the thermodynamic, evolutionary, self-organizational, autonomous agent and network perspectives we might add that:
A living system:
|
Living systems as self-fabricating autonomous homeostatic cognitive machines[edit]
|
In its broadest sense a living unit or entity is one that can direct chemical changes by catalysis, |
In this section we consider living systems, as distinct from non-living systems, from the perspective of the concept of ‘autopoiesis’ — autonomous self-fabrication — introduced in the 1970s by Humberto Maturana (b. 1928) and Francesco Varela (1946-2001),[79] though first enunciated, as pointed out in 2007 by J-H S. Hofmeyr,[80] by the philosopher Immanuel Kant (1724–1804),[81] and adumbrated by twentieth century biologists before Maturana and Varela.[82].
Microbiologist Harold Frank elaborates on Kant's view:
In a machine, [the German philosopher, Immanuel] Kant said, the parts exist for each other but not by each other; they work together to accomplish the machine's purpose, but their operation has nothing to do with building the machine. It is quite otherwise with organisms, whose parts not only work together but also produce the organism and all its parts. Each part is at once cause and effect, a means and an end. In consequence, while a machine implies a machine maker, an organism is a self-organizing entity. Unlike machines, which reflect their maker's intentions, organisms are “natural purposes.” Kant's vision was eminently sensible and remains true, but even he was stymied by the next stage: How can we ever discover the cause of that purposeful organization that is the hallmark of organisms?[83]
Any entity we recognize as living we recognize also as a ‘system’, an assemblage of components, interrelated structurally, interacting in a coordinated, dynamic, hierarchical way such as to self-construct an autonomously working organization characterizable as a ‘whole’ or ‘operational unit’ in virtue of a boundary selectively separating it from its environment — a kind of universe unto itself. We can hold that view of living systems regardless of the nature of the components that self-construct it, but on Earth we recognize those components as matter in the form of atoms and molecules, importing, converting, storing, releasing free energy, and actuated by it.
The precise description of the organization of living things differs widely among species. Think of an ant and an anteater. We can, however, specify characteristics of the ‘kind’ of organization that all species share here on Earth. For one thing, we can say a living system’s complexity exceeds current human cognitive ability to comprehend it, even with the aid of a powerful computer exo-cortexes. Arguably, in the future that characteristic of the organization in living things may prove non-constitutive.
We can say also that the organizational state of living systems resembles that of a man-made machine, like a super-jet airplane or a super-computer, though not made by man and not obviously having a purpose except to perpetuate its activity of living. We can think of a living system as a different ‘kind’ of machine than man-made machines. We can see that living machines exhibit a natural, or non-contrived ability to keep many of its internal variables constant, or within narrow bounds — it qualifies as a homeostasis machine.
A living system’s homeostatic ability plays a critical role in defining its uniqueness, as it enables it to homeostatically regulate the most important variable required for its continued living: an organization, whatever its description, that perpetuates its existence as a living system. Through the activity of its organization, the living system produces those components that provide the structural basis for the self-construction of its state as an autonomously working organization. If a living system cannot self-maintain its organization, it cannot produce the structure whose self-constructed coordinated interactions enable it to remain a living machine.
Autopoiesis co-founder Francisco Varela summarizes thusly:
Autopoiesis attempts to define the uniqueness of the emergence that produces life in its fundamental cellular form. It's specific to the cellular level. There's a circular or network process that engenders a paradox: a self-organizing network of biochemical reactions produces molecules, which do something specific and unique: they create a boundary, a membrane, which constrains the network that has produced the constituents of the membrane. This is a logical bootstrap, a loop: a network produces entities that create a boundary, which constrains the network that produced the boundary. This bootstrap is precisely what's unique about cells. A self-distinguishing entity exists when the bootstrap is completed. This entity has produced its own boundary. It doesn't require an external agent to notice it, or to say, "I'm here." It is, by itself, a self- distinction. It bootstraps itself out of a soup of chemistry and physics.” [84]
We can view a living system then as:
- A self-constructed machine organized as a network of interactions that fabricate, cyclically, the components whose self-organized interactions self-construct the system’s self-perpetuating network of interactions.
- A self-constructed machine organized as a network of interactions that can respond to perturbations either by self-correction of its disturbed organization (homeostasis), or by reorganizing itself into a different self-perpetuating network of interactions (adaptability; reproduction).
We can encapsulate that view of living systems preliminarily as ‘self-constructed self-perpetuating homeostatic machines’. Maturana and Varela[79] introduced the term ‘autopoiesis’ and ‘autopoietic organization’ to encapsulate that view of living machines as self-constructed self-perpetuating homeostatic machines as we have characterized them. Bitbol and Luisi expressed the definition of autopoiesis as follows:[85]
The theory of autopoiesis...captures the essence of cellular life by recognizing that life is a cyclic process that produces the components that in turn self-organize in the process itself, and all within a boundary of its own making.
That view of a living system reveals a special property of homeostasis in living machines: adaptability. A human, to take an example mammal, self-perpetuates a life-sustaining organization despite enormous perturbations of its organization during embryonic and fetal ‘development’. It does it by self-reorganizing — the homeostatic property of adaptability. If we think a fetus or a child an immature adult, we must think of adults as aged fetuses or children. As one individual or identity, fetus and adult represent a single self-constructing self-perpetuating homeostatically adaptable machine.
Ontogeny highlights the living system’s unique property of homeostasis in targeting with highest priority the maintenance of an organization that produces components that self-organize a network of interactions that perpetuates that organization — including its networks of interactions that retain its homeostatic property of adaptability. Homeostatic reorganization goes on continuously. The living machine maintains networks of interactions that define it as a self-constructing self-sustaining machine.
The self-constructed self-perpetuating homeostatic machine also produces its own boundary, as without that it could not maintain its organization against all the chaos outside.
A man-made, non-living machine yields products other than itself, products for human use. A living machine yields itself as its product, a product in continuous production, no matter how much it must modify itself in the process.
Therein defines the living machine’s autonomy —- it works in its own behalf to construct and sustain itself. So central to a living machine's uniqueness, its homeostatic organizational ability to produce components whose interactions self-organize a self-perpetuating organization, that, before accumulated perturbations of its organization overwhelms its homeostatic ability, the machine self-reproduces.
By this view, neither growth nor reproduction necessarily constitute ‘primary’ abilities of living machines, as both occur, in life on Earth, as the consequence of the homeostatic adaptable activities of the self-constructing organization that fabricates components whose interactions realize that organization, along with its homeostatic adaptability. On other worlds, living systems need not necessarily grow or reproduce, so long as they can, in some way, fabricate the components that can self-organize to construct the organization that can fabricate those components, including the system’s own boundary whose character enables its individuality and access to resources and waste disposal.[86]
Scientists can model and even synthesize experimental living machines that satisfy the basic criteria of a self-constructing self-perpetuating homeostatic machine (see[85]).
Access to resources alone cannot carry the day for a self-constructing homeostatic machine. It must have the ability, as part of its self-constructed organization, to recognize the resources it needs in order to sustain its organization. Recognition, however mediated, implies a type of ‘cognition’. In that case, for living machines to have an organization that produces the components that self-construct their-own component-producing organization, that organization must devote some of its activities to a type of cognition that enables it to recognize resources and import them and dispose of waste.
Those considerations dictate that a full description, or definition, of a living machine include the following:
- An organization of components capable of producing and reproducing, cyclically, the components that self-organize to construct the organization of components that produces those components;
- The components produced self-construct a boundary between the machine and the environment, of a nature that enables the machine to trade with the environment, acquiring the materials and/or energy required to sustain its self-perpetuating organization;
- The components produced self-construct an organization that has the cognitive ability to recognize the resources it needs to import and the wastes it needs to export.
- The components produced self-construct an organization that has the homeostatic ability to ‘correct’/’accommodate’ perturbations of the organization, or to reorganize appropriately to sustain a self-perpetuating organization;[87]
With those conditions realized, we can then ask about the details of the mechanisms or conditions that effect that realization in Earth’s living machines, whose components are molecules that self-construct networks comprising an organization that recursively constructs its components of such nature that the organization they produce can operate autonomously with homeostatic adaptability to sustain or reorganize itself as a cognizing compartmented system capable of escaping thermodynamic equilibrium through repeated self-reproduction.
Further elaborating beyond the thermodynamic, evolutionary, self-organizational, autonomous agent, network and information-processing perspectives we might add that:
A living system:
|
A living system as a hierarchy of emergent systems[edit]
(See Systems biology)
|
Every object that biology studies is a system of systems. |
A systems perspective of 'living' recalls Aristotle's four components of causality,[88] [89] (see also Some modern views of the four Aristotelian causes of living) in that a living thing comprises:
- A list of organic and inorganic parts (molecules and ions; cells, organelles, organs and organisms) — Aristotle’s 'material' cause;
- How the parts relate to each other to form structures (e.g., networks), how they interact with each other (e.g., network dynamics), and how the structures interact with each other in a coordinated dynamic and hierarchical manner — Aristotle’s 'formal' (form-like) cause;
- How the parts and structures became dynamically coordinated (e.g., gene expression; self-organization; competition) — Aristotle’s 'efficient' (effect-producing) cause; and
- How the living system as-a-whole functions and behaves, and the properties that characterize it (e.g., reproduction; locomotion; cognition) — Aristotle’s 'final' cause
The analysis of all of those components together forms part of the new discipline of Systems Biology.
Systems biologists study, among other things, the phenomenon of 'emergence', whereby properties, functions and behaviors of living systems arise though not exhibited by any individual component of the system, and not explainable or predictable from complete understanding the components' properties/behaviors considered in isolation from the system that embeds them. Every cellular system exhibits emergent behaviors. Emergent behaviors of living systems include such things as locomotion, sexual display, flocking, and conscious experiencing. Even the biological components of living cells, such as mitochondria and other organelles, exhibit emergent properties.
Some biologists might find it tempting to see a type of 'vitalism', or 'life force', in living systems, given that some whole-system properties/behaviors of organisms, including even the activity of living itself, exemplify such emergent phenomena. One could not explain, for example, the action of an organism fleeing from a predator from a study of the properties of an organism's component subsystems. The properties of the component parts depend on the organization of those parts in the whole system. Because biologists and their co-scientists can explain emergent properties/phenomena, if only sometimes in principle, by mechanisms that do not transcend interactions of matter and energy, any such ‘vitalism’ properly qualifies only as a ‘materialistic vitalism’.
One example of emergence: When components of a signaling pathway, which enable between-cell communication, interact to form the signaling system, properties can emerge — such as a self-sustaining feedback loop and generation of the signals themselves — that one cannot explain from the individuated properties of the separate components of the system.[90]
For another example, in studying a protein separated from the system it belongs to, one can observe many of its properties, but in so studying the protein one cannot explain any of the properties it has only in the context of the system that embeds it, such as the property of catalyzing a biochemical reaction, or of binding to other proteins to form a functional protein complex. Those properties of the protein emerge in the context of the protein’s environment — how it interacts in the context of the system as a whole. Moreover, those emergent properties may result in effects within the system that, in a feedback way, further alters the properties of the protein in the system, as when a reaction product alters the catalytic properties of the protein.
Why do not all of the properties/behaviors of a system predictably result from the properties of its components? After all, the reductionist paradigm that dominated the Scientific method in the 20th century operated on the exactly opposite assumption. For one thing, the intrinsic properties of a system’s components themselves do not determine those of the whole system; rather, their 'organizational dynamics' does — how the components interact coordinately in time and space. Those organizational dynamics include not only the interrelations among the components themselves, but also interactions among the many different organizational units in the system. [91] Secondly, the living system always operates in a certain context (its external environment, or surroundings), and those surroundings, in turn, always affect the properties of the system-as-a-whole. For example, nutrient gradients in its environment influence the direction a bacterium’s locomotion. The impact of environmental context affects the dynamic organization of the components within the system — a 'downward causation'. [92] For another example, environmental signals can activate or suppress a metabolic pathway, reorganizing cellular activity[93] One cannot simply take a living system apart and predict how it will behave in its natural environment.
As Gilbert and Sarkar puts it: “Thus, when we try to explain how the whole system behaves, we have to talk about its parts the context of the whole and cannot get away talking only about the parts.”
Philosopher of science D.M. Walsh puts it this way: "The constituent parts and processes of a living thing are related to the organism as a whole by a kind of 'reciprocal causation'."[94] In other words, the organization of the components determine the behavior of the system, but that organization arises from more than the set of its internal components. How the whole system behaves as it interacts with its environment determines how those components organize themselves, and so novel properties of the system 'emerge' that characterize neither the environment nor that set of internal components. For example, the behavior of a human kidney cell depends not only on its cellular physiology, but also on all the properties of the organ (kidney) which constitutes its environment. The kidney's overall structure and function influence the cell’s structure and behavior (e.g., by physical confinement and by cell-to-cell signaling), which in turn influence the organization of its intracellular components. The kidney in turn responds to its environment, namely the individual body that it lives in, and that body responds to its environment, which includes such factors as the availability of particular food items, fresh water, and ambient temperature and humidity. Systems biologists regard emergent properties as arising from a combination of bottom-up and top-down effects — Walsh's 'reciprocal causation'.
Emergent processes have been recognised as, for example, contributing to understanding:
Emergent phenomena appear even in non-biological physical systems. [101] Emergent phenomena attract the attention of cellular neuroscientists; [102] and cognitive scientists [103]. At still higher systems levels, emergent properties appear for example in the behaviour of ant colonies and the concept of swarm intelligence, [104] Systems scientists have simulated emergent phenomena [105] Emergent phenomena in human societies has also received attention. [106]. Biologists even explain the biosphere itself as emergent. [107]
Emergent systems always display what we recognize as ‘complexity’, a feature we have a difficult time precisely defining. Complex systems appear to require more bits of information (words, sentences, lines of computer code, etc.) to describe than the bits of information in the system itself. [108] The operation of the system itself supplies its own most economical model.
According the paleontologist and origin of life researcher, Robert Hazen, four basic complexity elements underpin emergence in a system: [109]
- A sufficiently large ‘density’ of components, with increasing complexity as the concentration increases, up to a point;
- Sufficient interconnectivity of the components, with increasing complexity with greater and more varied types of interconnectivity, up to a point;
- A sufficient energy flow through the system to enable the system’s components to perform the work of interacting in the self-organized way characteristic of the energized system;
- Flow of energy through the system in a cyclic manner, presumably facilitating the spatiotemporal patterning characteristic of organized systems.
Living systems thus generate complexity and emergent properties as a hierarchy of emergent subsystems embedded in even more complex emergent systems, as in the case of an organism living in an environment of other organisms.
Further elaborating on the several perspectives described above, we may say that:
A living system:
|
Fundamental underpinning of living systems[edit]
Different scientific perspectives[edit]
The different perspectives biologists use in viewing living systems can be identified as follows:
- Living systems import free energy, energy-rich matter, order and information from their environment, and export waste in the form of degraded energy, unusable materials, and more disorder (entropy) than the order they generate within themselves. The downhill flow of free energy enables living systems to organize themselves and sustain that organization, and thus to delay (for their lifetime) the dictate of the Second Law of Thermodynamics, which states that organized systems ultimately degrade to a state of randomness;
- The basic building blocks and working units of all living systems are cells, separated from their surroundings by a boundary membrane that allows energy, material and information exchange with their surroundings;
- The basic (genetic) database that cells draw upon for self-organization comes as part of their starting materials. This source of information, in the form of nucleic acid macromolecules, encodes many different types of proteins that interact according to their natural physico-chemical properties to self-assemble an organization of hierarchically arranged subsystems that can import energy and export waste.
- Cells inherit genetic and other forms of heritable information from ‘parent’ cells, raising as yet unanswered questions: how did cells arise in the first place? and how did they acquire stores of information?;[110] (see Origin of life and Evolution of cells)
- The molecular interactions that self-assemble and sustain the living organization are governed by the universal laws of physics and chemistry; those laws, together with the inherited information, enable a self-organizing system that can work autonomously in its own behalf for persistence of the living state and for reproduction, and allow properties and physiological functions to emerge that could not be anticipated from those of the system's components alone.
- The activities of a living system have no 'master controller'; they need only a type of organization that maintains the system far-from-equilibrium, which can yield improbable self-organized structures and activities.
- Living things cannot escape from real-time changes in external conditions, so they must maintain homeostasis, exhibit robustness in their organization, and must be adaptable enough to reorganize to sustain their living state. Robustness and adaptability derive from the properties of a hierarchical network of subnetworks of molecular circuits;
- Living systems generate complexity and emergent properties as a hierarchy of emergent subsystems embedded in even more complex emergent systems, as in the case of an organism living in an environment of other organisms.
- Living systems produce enough reproductive variability to allow evolution through natural selection, which guides the continuation of a 3.5 billion year history of Earth’s living world. By evolution, living systems generate increasing varieties of living systems, occupy an extreme spectrum of environments, create their own environments,[111] and permit sufficient complexity to enable them to process information in a way that allows them to ‘experience’ themselves.
Synthesis of perspectives[edit]
|
The eternal mystery of the world is its comprehensibility... |
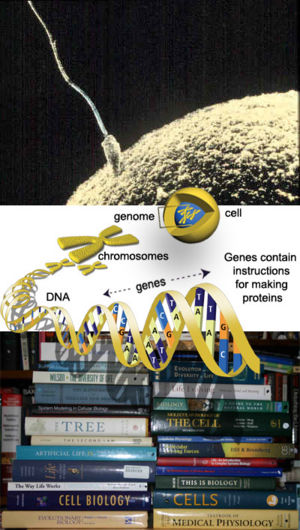
Signs of life. Top: Spermatozoon and oocyte merge to begin a new building block for a living system. Middle: DNA, the database for the construction of life's protein components. Bottom: Life as humans describe it in books.
The activity of living, for a cell-based system, depends on its ability to generate and sustain quasi-steady-states of self-organized functioning far from the state of randomness, and its ability to respond to internally and externally derived conditions that perturb its current quasi-steady-state by making adjustive responses, including self-reorganization (as in growth and development) and self-reproduction. The system attains those abilities partly and critically because of its location in the path of a downhill gradient of flowing free energy, including that stored in energy-rich molecules. It can draw off some of that downflow of energy by importing it, and it can export the inevitable wastes of degraded energy and materials it generates in performing the activities that keep it alive. It thereby generates, sustains and increases its own highly ordered and improbable state at the expense of a more than counterbalancing, more probable disordered state of its surroundings.
- An organism lives by importing and utilizing free energy and by generating and exporting entropy.
Those principles seem to apply to all living systems: single cells, multicellular organs and organisms, and to biological systems whose parts are living systems: multi-organism demes and ecosystems. The fundamental challenges to staying alive do not differ greatly for an amoeba from those of a human. Neuroscientist Antonio Damasio[112] puts it this way:
"All living organisms from the humble amoeba to the human are born with devices designed to solve automatically, no proper reasoning required, the basic problems of life. Those problems are: finding sources of energy; incorporating and transforming energy; maintaining a chemical balance of the interior compatible with the life process; maintaining the organism's structure by repairing its wear and tear; and fending off external agents of disease and physical injury."
Professor Damasio neglected to stress the critical feature of the organism's ability to generate and export entropy — to a greater extent than it reduces its internal entropy. Without that ability, an internal entropy build-up would randomize it to premature death, though without that ability it would never have come to exist in the first place.
Steven Benner, Alonso Ricardo and Matthew Carrigan boil life down to this:
”We propose that the only absolute requirements [for life] are a thermodynamic disequilibrium and temperatures consistent with chemical bonding.”[27]
With those requirements met, living things can emerge.
The building block and working unit of all living systems is the cell. For cells to utilize available external energy or energy-rich matter to achieve and maintain a state of complex organization (order), they must have, from the outset, a basic informational content, a database. That database enables the cell to self-produce components that can, by natural molecular interactions, respond to the imported energy and material to self-organize. That organization comprises modular networks of molecular interactions, and a hierarchy of interacting networks — self-organized and coordinated functional interactions. The properties of the networks and those of the hierarchy of networks enable the system to perpetuate itself, and to maintain its steady-state despite fluctuations in environmental factors. That principle, too, applies to all living systems. Any organism, plant or animal, comprises a network of organs working autonomously, maintaining its steady-state functioning far from equilibrium in response to environmental perturbations — physiologists refer to that as homeostasis, adaptability and robustness.
One can view any living organism as an autonomous cognitive living machine functioning in its own behalf, i.e., without a master controller. It comprises an organization of components capable of producing and reproducing, cyclically, the components that self-organize to construct the organization of components that produces those components. The components self-construct a boundary between the machine and the environment, of a nature that enables the machine to trade with self-interest with the environment, acquiring the materials and/or energy required to sustain its self-perpetuating organization. The components self-construct an organization that has the cognitive ability to recognize the resources it needs to import and the wastes it needs to export. The components self-construct an organization that has the homeostatic ability to ‘correct’/’accommodate’ perturbations of the organization, or to reorganize appropriately to sustain a self-perpetuating organization, including reproducing itself.
The networks that regulate the flow of information through the cell resulted from natural experiments refined and preserved by natural selection and other evolutionary processes. The databases it inherits, that evolved by natural experiment and selection, do not program living, but enable the living thing to self-produce the molecules that can interact in the very ways that contribute to self-organization of those networks that enable a cell to sustain and reproduce itself.
The collaboration of natural selection and physico-chemical laws perpetuates living systems not only in real-time but also in geological, or ‘evolutionary’, time. From common ancestors — however they may have arisen (see Evolution of cells) — informationally-guided, self-organizing, autonomous network dynamics enabled generation of the diversity of all living systems on the planet, over nearly four billion years. Living systems perpetuate living systems, exploiting free energy on its inexorable path to dissipation and degradation, and harvesting energy in developing organized systems by a more than counterbalancing dis-organizing of the larger system in which it is embedded.
Supplementary text[edit]
- See Life/Addendum for supplementary text pertaining to this article.
Selected definitions of life[edit]
Published collections of definitions of life[edit]
The exobiologists view[edit]
The gray zone[edit]
Some modern views of the four Aristotelian causes of living things[edit]
References[edit]
Citations and notes[edit]
|
Most citations to articles listed here include links to full-text. Accessing full-text may require personal or institutional subscription. Nevertheless, usually the links will show the abstracts of the articles, free without subscription. Links to books variously may open to full-text, or to the publishers' description of the book with or without downloadable selected chapters, reviews, and table of contents. Books with links to Google Books often offer extensive previews of the books' text. |
Footnotes[edit]
- ↑ From: Robinson R. (2007) Both barriers and trait complementarity govern pollination network structure. PLoS Biol 5(2): e54.
- ↑ Luisi PL (2003) Autopoiesis: a review and a reappraisal Naturwissenschaften 90:49-59 PMID 12590297.
- Abstract: The aim of the paper is to review critically the notion of autopoiesis as presented by Maturana and Varela. In particular, recognizing that there are difficulties in obtaining a complete and clear picture from the primary literature, an effort is made to present a coherent view--also based on many years of personal contact with Francisco Varela. The paper begins with a few historical notes to highlight the cultural background from which the notion of autopoiesis arose. The basic principles of autopoiesis as a theory of cellular life are then described, emphasizing also what autopoiesis is not: not an abstract theory, not a concept of artificial life, not a theory about the origin of life--but rather a pragmatic blueprint of life based on cellular life. It shown how this view leads to a conceptually clear definition of minimal life and to a logical link with related notions, such as self-organization, emergence, biological autonomy, auto-referentiality, and interactions with the environment. The perturbations brought about by the environment are seen as changes selected and triggered by the inner organization of the living. These selective coupling interactions impart meaning to the minimal life and are thus defined by Maturana and Varela with the arguable term of "cognition". This particular view on the mutual interactions between living organism and environment leads these authors to the notion of "enaction", and to the surprising view that autopoiesis and cognition are two complementary, and in a way equivalent, aspects of life. It is then shown how cognition, so defined, permits us to build a bridge between biology and cognitive science. Autopoiesis also allows one to conceive chemical models of minimal cellular life that can be implemented experimentally. The corresponding work on "chemical autopoiesis" is then reviewed. The surprising impact of autopoiesis in the social sciences ("social autopoiesis") is also briefly discussed. This review also comments on why the theory of autopoiesis had, and still has, a difficult time being accepted into the mainstream of life-science research. Finally, it is pointed out that the new interest in system biology and complexity theories may lead to a reappraisal of autopoiesis and related notions, as outlined also by other authors, such as Tibor Ganti and Stuart Kauffmann.
- ↑ Note: Some words, so-called ‘semantic primes’ have distinct meanings not definable in terms of other words. Ultimately, all definitions converge on about 70 semantic primes that occur universally among the languages humans speak, the descendants of the original human lexicon. Semantic primes include the verb ‘live’ but not the noun ‘life’.
Wierzbicka A.(1996) Semantics: Primes and Universals. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0198700024. Publisher’s website’s description of book Professor Wierzbicka’s faculty webpage Excepts from Chapters 1 and 2
- Carol Cleland of NASA’s Astrobiology Institute suggests that scientists are not really interested in what the word 'life' happens to mean in our language. "What we really need to focus on is coming up with an adequately general theory of living systems, as opposed to a definition of 'life'." Carol Cleland on "What is Life?"
- ↑ De Duve C (2004) Life Evolving: Molecules, Mind, and Meaning. Oxford University Press. New York ISBN 0195156056 Full-Text Online
- ↑ Grant MC. (1993)
The Trembling Giant Discover Magazine, October 1st
- From the article: "Yet even the majestic giant sequoia is not the record holder. That honor goes to a tree that my co-workers and I have studied for years: the quaking aspen, a common tree that dapples many mountains of North America. Unlike giant sequoias, each of which is a genetically separate individual, a group of thousands of aspens can actually be a single organism, sharing a root system and a unique set of genes. We therefore recently nominated one particular aspen individual growing just south of the Wasatch Mountains of Utah as the most massive living organism in the world. We nicknamed it Pando, a Latin word meaning "I spread". Made up of 47,000 tree trunks, each with an ordinary tree’s usual complement of leaves and branches, Pando covers 106 acres and, conservatively, weighs in excess of 13 million pounds…".
- ↑ Zax D (2007) Champs. Smithsonian, Fall 2007. The General Sherman Tree
- According to Smithsonian author David Zax, as of 2006 a California sequoia, the General Sherman Tree, ranks as the world's largest living organism (52,500 cubic feet, 2.7 million pounds). The world's oldest, a California bristlecone pine, Methuselah, >4,800 years old.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Thompson D(‘Arcy)W(entworth). (1992 reprint; original published 1917). On Growth and Form. Edited by John Tyler Bonner. Foreword by Stephen Jay Gould. Reprinted in abridged edition by: Cambridge University Press. ISBN -13: 9780521437769; ISBN -10: 0521437768. Google Books Preview Foreword, Introduction, Chapters 1 and 2
- Excerpt: "Morphology is not only a study of material things and of the forms of material things, but has its dynamical aspect, under which we deal with the interpretation, in terms of force, of the operations of Energy...And here it is well worth while to remark that, in dealing with the facts of embryology or the phenomena of inheritance, the common language of the books seems to deal too much with the material elements concerned, as the causes of development, of variation or of hereditary transmission. Matter as such produces nothing, changes nothing, does nothing; and however convenient it may afterwards be to abbreviate our nomenclature and our descriptions, we must most carefully realise in the outset that the spermatozoon, the nucleus, the chromosomes or the germ-plasma can never act as matter alone, but only as seats of energy and as centres of force."
- ↑ Bains W. (2004) Many Chemistries Could Be Used to Build Living Systems. Astrobiology 4(2):137-167.
- In places in the universe where physical conditions might favor silicon-based macromolecules, silicon-based life might exist.
- ↑ Ball P. (2005) Water and life: Seeking the solution. Nature 436:1084-5]
- ↑ Tsytovich VN et al. (2007) From plasma crystals and helical structures towards inorganic living matter. New J Phys 9:263]
- Note: From the Abstract: “Complex plasmas [a state of matter common in outer space consisting of a mass of charged particles] may naturally self-organize themselves into stable interacting helical structures that exhibit features normally attributed to organic living matter. The self-organization is based on non-trivial physical mechanisms of plasma interactions involving over-screening of plasma polarization. As a result, each helical string composed of solid microparticles is topologically and dynamically controlled by plasma fluxes leading to particle charging and over-screening, the latter providing attraction even among helical strings of the same charge sign. These interacting complex structures exhibit thermodynamic and evolutionary features thought to be peculiar only to living matter such as bifurcations that serve as `memory marks', self-duplication, metabolic rates in a thermodynamically open system, and non-Hamiltonian dynamics. We examine the salient features of this new complex `state of soft matter' in light of the autonomy, evolution, progenity and autopoiesis principles used to define life. It is concluded that complex self-organized plasma structures exhibit all the necessary properties to qualify them as candidates for inorganic living matter that may exist in space provided certain conditions allow them to evolve naturally."
- ↑ Editors (2007) 'It might be life, Jim...' Astrobiology Magazine Online, August 21, 2007.
- Astrobiology Magazine’s report for the general reader on the findings of Tsytovich et al. of self-organizing structures in plasma from inorganic dust. Remarkable images.
- ↑ Interestingly, among the three domains of living systems , the predominant lipid species differs. In most types of cells the predominant lipid species consist of molecules based on esters of glycerol combined with straight chain fatty acids, but in the Archaea domain it consists of ethers of glycerol combined with isoprene fatty components. That lack of membrane structural universality has implications for the origin of life.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Valentine JW et al. (1994) Morphological complexity increase in metazoans. Paleobiology 20:131-42
- ↑ Woese CR et al. (1990) Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains archaea, bacteria, and eucarya. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:4576-9
- ↑ Baluska F et al. (2004) Eukaryotic cells and their cell bodies: cell theory revised. Ann Bot 94:9-32]
- Note: “…those who are aware of the most recent advances in plant cell biology…are convinced that Cell Theory, as it now stands, is absolutely incompatible with a cell-based organization of higher plants…and requires an update....Indeed, formulation of organismal theory of plant development, in which it is stated that it is not the cell but the whole multicellular organism that is the primary unit of plant life....has precipitated a crisis for Cell Theory as applied to plants. A consequence of the fact that the cytoplasms of plant cells are interconnected via plasmodesmata is that the individuality of the cell is given up in favour of an integrated and corporate cytoplasm that benefits the whole organism. This supracellular, or organismal, approach towards multicellularity seems to have allowed sessile plants to adapt to life on land and to evolve even within hostile environments.
- ↑ Note: Other boundaries of living systems include bark, shells, cell walls, skin, fur, and structures of the physical environment.
- ↑ How Many Genes Are in the Human Genome? at the Human Genome Project Information website hosted by the U.S. Department of Energy
- ↑ (a) The UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot Human Proteome Initiative; (b) Norregaard Jensen O (2004) Modification-specific proteomics: characterization of post-translational modifications by mass spectrometry. Curr Opin Chem Biol 8:33-41]
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 Morowitz H, Smith E (2006) Energy flow and the organization of life Working Paper, Santa Fe Institue
- "Energy flow embeds life within the geosphere not just mechanistically but conceptually as an inevitable form of driven geochemical order."
- ↑ Note: A random pattern of parts has no order (it has maximal entropy) and no information. A living system has order in its organized state; it has computationally-rich informational content, and low entropy.
- ↑ Note: At birth — the big bang — the Universe received an energy account. The amount of energy remains forever constant, although it can distribute itself into many smaller accounts in a process in which the more organized forms of energy — the 'higher quality' energy — degrades to a 'lower quality' energy, heat, or thermal energy. When the starting account finally becomes completely dispersed throughout the Universe in the form of randomly distributed colliding particles, (thermal energy, heat — energy's most degraded and least useful form) no work will be possible, because no energy gradients (downward slopes) exist down which energy can flow to perform any work. At that point, the Universe will be at an equilibrium, characterized by a random distribution of the initial energy.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 Schneider ED, Sagan D (2005) Into the Cool: Energy Flow, Thermodynamics, and Life. Chicago: The University of Chicago Press. ISBN 0-226-73937-6 Chapter Excerpts and Reviews
- ↑ Carnot S. (1825) Reflections On The Motive Power Of Heat And On Machines Fitted To Develop That Power
- Sadi Carnot (1796-1832), one of the founders of thermodynamics, understood that the capacity to do work by heat energy required a difference in temperature, an energy gradient. He wrote:
- ”The production of motive power is then due in steam-engines not to an actual consumption of caloric [quantity of heat], but to its transportation from a warm body to a cold body, that is, to its re-establishment of equilibrium…. According to this principle, the production of heat alone is not sufficient to give birth to the impelling power: it is necessary that there should also be cold; without it, the heat would be useless. And in fact, if we should find about us only bodies as hot as our furnaces, how can we condense steam? What should we do with it if once produced? We should not presume that we might discharge it into the atmosphere, as is done in some engines; the atmosphere would not receive it. It does receive it under the actual condition of things, only because it fulfils the office of a vast condenser, because it is at a lower temperature; otherwise it would soon become fully charged, or rather would be already saturated…. Wherever there exists a difference of temperature, wherever it has been possible for the equilibrium of the caloric to be re-established, it is possible to have also the production of impelling power.
- ↑ Note:
- The words 'organize' and 'organization' appear often in this article, and so merit special note. When one organizes a collection of entities, one puts them in some kind of order, typically for some function. Functionality serves as the criterion for organization, or for an organized state of the entities. To organize, then, implies to structure parts in relation to one another for functionality.
- For living systems, nature inclines to organization. Often she structures the parts in 'dynamic' relation, such that the parts 'interact' temporally. The parts work together in a 'coordinated' and 'hierarchical' way that achieves a functionality that contributes to the naturally selected goals of a living system to survive in the living state and to manufacture new living systems like itself. 'Dynamic', 'coordinated', 'hierarchical', and 'goal-directed functionality' characterize 'organization' in biological systems. The words 'organize' and 'organization' should invoke those properties. Thus 'organization' connotes more than 'order' when it comes to living systems — a special kind of order that achieves not only life-preserving functionality, but also unpredictable novelty, or emergent behavior. As we shall see, nature enables living systems to organize themselves.
- ↑ Lotka AJ. (1922) Contribution to the Energetics of Evolution. PNAS 8: 147-151.
- Excerpt: "Evolution, in these circumstances, proceeds in such direction as to make the total energy flux through the system a maximum compatible with the constraints….We have thus derived, upon a deductive basis, at least a preliminary answer to a question proposed by the writer in a previous publication.(cites: Lotka, A. J., Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci., 7, 1921, p. 172). It was there pointed out that the influence of man, as the most successful species in the competitive struggle, seems to have been to accelerate the circulation of matter through the life cycle, both by "enlarging the wheel," and by causing it to "spin faster." The question was raised whether, in this, man has been unconsciously fulfilling a law of nature, according to which some physical quantity in the system tends toward a maximum. This is now made to appear probable; and it is found that the physical quantity in question is of the dimensions of power, or energy per unit time, as was hinted by the writer on an earlier occasion."
- Note: Lotka invokes natural selection as facilitating energy dissipation (energy flow per unit time).
- ↑ Prigogine I, Stengers I (1997) The End of Certainty: Time, Chaos, and the New Laws of Nature. Free Press, New York. ISBN 0684837056 Excerpt from Chapter 1; Table of Contents
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 Benner SA, Ricardo A, Carrigan MA (2004) Is there a common chemical model for life in the universe? Curr Opin Chem Biol 8:672-89. PMID 15556414
- ↑ (a) Swenson R, Turvey MT. (1991) Thermodynamic reasons for perception-action cycles. Ecol Psychol 3:317-48. (b) Swenson R. (1997) Thermodynamics, Evolution, and Behavior. In The Encyclopedia of Comparative Psychology G. Greenberg and M. Haraway (Eds), New York: Garland Publishers, Inc.
- ↑ Schneider ED, Kay JJ (1994) Life as a manifestation of the second law of thermodynamics. Math Computer Modelling 19:25-48]
- ↑ Note: If an energy gradient promotes the origin of living systems for the reason that as the energy flows through them they hasten the rate of entropy production of the Universe as a whole, by exporting more entropy to their surroundings than they reduce their internal entropy, then the energy gradient might also promote the development of complexity in living systems, as complexity further reduces a living system’s internal entropy (as greater organization). With sufficient organization, living systems can attain a degree of intelligence enabling them to fabricate energy-utilizing artifacts, like electrical lighting systems, fossil-fuel-based transportation systems, and solar and geothermal energy conversion to work. Those artifacts then would further contribute to dissipation of the life-promoting energy gradient and further accelerate the rate of entropy production of the Universe as a whole. Such considerations make it seem likely, most speculatively, that Nature’s abhorrence of energy gradients throughout the Universe would promote the origin and complexity development of living systems wherever physico-chemical circumstances permit, as a means of maximizing the rate of entropy production of the Universe as a whole.
- ↑ Eddington AS. (1929)The Nature of the Physical World New York: The University Press, page 740. Full-Text, requires subscription.
- Also this passage and many excerpts of the book at: Google Books, page 74.
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 Ball P. (2006) Was life on Earth inevitable? Nature Published online 14 November in NatureNews.
- Commentary on article by Morowitz and Smith. “Life may be the ultimate in planetary stress relief…[Morowitz and Smith] argue that life was the necessary consequence of available energy built up by geological processes on the early Earth. Life sprang from this environment, they say, in the same way that lightning relieves the accumulation of electrical charge in thunderclouds." In other words, say biologist Harold Morowitz of George Mason University in Fairfax, Virginia, and physicist Eric Smith of New Mexico's Santa Fe Institute, the geological environment "forced life into existence".
- ↑ Nelson PC. (2004) W.H. Freeman and Company, New York ISBN 0-7167-4372—8
- ↑ Note: ....or the progeny of some conspecific living systems. Many living systems coexist with similar living systems, constituting a 'species', or group of 'conspecifics'.
- ↑ Charles Darwin (1859) The Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 36.2 36.3 Reid RGB. (2007) Biological Emergences: Evolution by Natural Experiment. (With Table of Contents and Sample Chapters) A Bradford Book, Cambridge ISBN 0-262-18257-2 Additional Chapter Excerpts
- ↑ 37.0 37.1 37.2 Jablonka E, Lamb MJ (2005) Evolution in Four Dimension: Genetic, Epigenetic, Behavioral, and Symbolic Variation in the History of Life. Cambridge: The MIT Press
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 38.2 Goodwin B. (1994) How The Leopard Changed Its Spots: The Evolution Of Complexity Princeton University Press, Princeton. ISBN 0-691-08809-8 Excerpts of Multiple Chapters
- ↑ Note: Some evidence supports the proposition that all extant living things (Archaea, Bacteria and Eukaya) descended from a common ancestor, though that common ancestor may have arisen from a proto-community of cells: "The common ancestor of eukaryotes, bacteria, and archaea may have been a community of organisms containing the following: autotrophs that produced organic compounds from CO2 either photosynthetically or by inorganic chemical reactions; heterotrophs that obtained organics by leakage from other organisms; saprotrophs that absorbed nutrients from decaying organisms; and phagotrophs that were sufficiently complex to envelop and digest prey." [italics added]. See—
- Kurland CG et al.(2006) Genomics and the irreducible nature of eukaryote cells. Science 312:1011-4 PMID 16709776
- Kurland CG et al.(2006) Genomics and the irreducible nature of eukaryote cells. Science 312:1011-4 PMID 16709776
- Woese CR (2002) On the evolution of cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:8742-7 PMID 12077305
- ↑ Smolin L (1997) The Life of the Cosmos. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 019510837X
- ↑ Varela FG, Maturana HR, Uribe R. (1974) Autopoiesis: the organization of living systems, its characterization and a model. Curr Mod Biol. 5:187-196 PMID 4407425
- "We assert that reproduction and evolution are not constitutive features of the living organization and that the properties of a unity cannot be accounted for only through ac¬counting for the properties of its components. In contrast, we claim that the living organization can only be characterized unambiguously by specifying the network of interactions of components which constitute a living system as a whole, that is, as a "unity"."
- "We also claim that all biological phenomenology, including reproduction and evolution, is secondary to the establishment of this unitary organization."
- "Thus, instead of asking "What are the neces¬sary properties of the components that make a living system possible?" we ask "What is the necessary and sufficient organization for a given system to be a living unity?" In other words, instead of asking what makes a living system reproduce, we ask what is the organi¬zation reproduced when a living system gives origin to another living unity?"
- ↑ Benner SA et al. (2004) Is there a common chemical model for life in the universe? Curr Opin Chem Biol 8:672-89. PMID 15556414
- ↑ Lehn JM. (2002) Toward complex matter: supramolecular chemistry and self-organization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:4763-4768 PMID 11929970
- From the article: "Supramolecular chemistry has paved the way toward apprehending chemistry as an information science through the implementation of the concept of molecular information with the aim of gaining progressive control over the spatial (structural) and temporal (dynamic) features of matter and over its complexification through self-organization, the drive to life [citations]...Supramolecular chemistry has developed as the chemistry of the entities generated by intermolecular noncovalent interactions [citations]."
- ↑ 44.0 44.1 Lehn JM (2002) Toward self-organization and complex matter Science 295:2400-3 PMID 11923524
- ↑ Percec V, Ungar G, Peterca M (2006) Self-assembly in action. Science 313:55-6 PMID 16825559
- ↑ Reinhoudt DN, Crego-Calama M (2002) Synthesis beyond the molecule Science 295:2403-7 PMID 11923525
- ↑ Lehn JM (2007) From supramolecular chemistry towards constitutional dynamic chemistry and adaptive chemistry. Chem Soc Rev 36:151-60 PMID 17264919
- ↑ Heylighen F (2001) The Science of Self-organization and Adaptivity. In: Kiel LD (ed.) Knowledge Management, Organizational Intelligence and Learning, and Complexity: The Encyclopedia of Life Support Systems EOLSS) Oxford: Eolss
- From the Abstract: "Self-organization can be defined as the spontaneous creation of a globally coherent pattern out of local interactions…Formally, the basic mechanism underlying self-organization is the (often noise-driven) variation which explores different regions in the system’s state space until it enters an attractor. This precludes further variation outside the attractor, and thus restricts the freedom of the system’s components to behave independently. This is equivalent to the increase of coherence, or decrease of statistical entropy, that defines self-organization."
- ↑ Harold FM. (2005) Molecules into cells: specifying spatial architecture. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 69:544-64 PMID 16339735
- ↑ 50.0 50.1 Loewenstein WR (1999) The Touchstone of Life: Molecular Information, Cell Communication, and the Foundations of Life. Oxford University Press, New York. ISBN 0-19-514057-5 Full-Text Online with Subscription
- ↑ Noble D (2002) Modeling the heart—from genes to cells to the whole organ. Science 295:1678-82]
- ↑ Sidney Brenner’s Nobel lecture (2002) “Nature’s Gift to Science”
- ↑ Brenner S (1998) Biological computation Novartis Found Symp 213:106-11 PMID 9653718
- ↑ Dawkins R (1988) The Blind Watchmaker: Why the Evidence of Evolution Reveals a Universe Without Design. New York: W.W. Norton & Company, Inc. ISBN 0393304485 Excerpt from Amazon.com review: “The title of this 1986 work, Dawkins's second book, refers to the Rev. William Paley's 1802 work, Natural Theology, which argued that, just as finding a watch would lead you to conclude that a watchmaker must exist, the complexity of living organisms proves that a Creator exists. Not so, says Dawkins: "the only watchmaker in nature is the blind forces of physics, albeit deployed in a very special way... it is the blind watchmaker." (Physics, of course, includes open-system non-equilibrium thermodynamics, pivotal to understanding how living systems fabricate and sustain themselves.)
- ↑ Mendoza M et al. (2004) Emergence of community structure in terrestrial mammal-dominated ecosystems. J Theor Biol :203-214] PMID 15302552.
- ↑ 56.0 56.1 56.2 Kauffman S (2003) Molecular autonomous agents. Philos Transact A Math Phys Eng Sci. 361:1089-99 PMI: 12816601
- ↑ Kauffman SA (2000) Investigations. Oxford University Press, Oxford. ISBN 019512104X Publisher’s description and reviews
- ↑ Franklin S, Graesser A (1996) Is it an Agent, or just a Program?: A Taxonomy for Autonomous Agents. Proc Third Int Workshop on Agent Theories, Architectures, and Languages, Springer-Verlag
- ↑ Kauffman S (2003) The Adjacent Possible
- ↑ From: Bar-Joseph Z et al. (2003) Computational discovery of gene modules and regulatory networks. Nat Biotechnol 21:1337–42, available online at http://www.nature.com/nbt/journal/v21/n11/abs/nbt890.html. And: Qi Y, Ge H (2006) Modularity and dynamics of cellular networks. PLoS Comp Biol 2(12):e174. Available online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.0020174
- ↑ 61.0 61.1 Barabási AL (2002) Linked: The New Science of Networks. Cambridge, Mass: Perseus Pub. ISBN 0-7382-0667-9
- ↑ Watts DJ. (2007) A twenty-first century science. Nature 445:489
- ↑ Alon U (2003) Biological networks: the tinkerer as an engineer. Science 301:1866-7 PMID 14512615
- ↑ Hartwell LH, Hopfield JJ, Leibler S, Murray AW. (1999) From molecular to modular cell biology. Nature 402:C47-C52] PMID 10591225
- ↑ Darwin C (1859) On the origin of species by means of natural selection, or the preservation of favoured races in the struggle for life. 1st edition. Chap. VI, p190 “Difficulties on Theory”
- Darwin wrote: “The illustration of the swimbladder in fishes is a good one, because it shows us clearly the highly important fact that an organ originally constructed for one purpose, namely flotation, may be converted into one for a wholly different purpose, namely respiration.”
- Stephen Jay Gould and others dispute Darwin on the direction of exaptation between swimbladder and lung, though not the rality of exaptation: Gould writes: “Darwin was wrong; ancestral vertebrates had lungs… The first vertebrates maintained a dual system for respiration: gills for extracting gases from seawater and lungs for gulping air at the surface. A few modern fishes, including the coelacanth, the African bichir Polypterus, and three genera of lungfishes, retained lungs… In two major lineages of derived bony fishes — the chondrosteans and the teleosts -- lungs evolved to swim bladders by atrophy of vascular tissue to create a more or less empty sac and, in some cases, by loss of the connecting tube to the esophagus (called the trachea in humans and other creatures with lungs). See: Gould SJ (1993) Eight Little Piggies: Reflections in Natural History. Norton, New York. ISBN 039303416X.
- ↑ See definition of ‘exapt’
- ↑ Lenski RE et al. (2006) Balancing robustness and evolvability. PLoS Biol 4(12):e428]
- ↑ 68.0 68.1 Alon U (2007) Simplicity in biology. Nature 446:497]
- ↑ Prill RJ et al. (2004) Dynamic properties of network motifs contribute to biological network organization. PLoS Biol 3:e343]
- ↑ Sporns O, Kotter R (2004) Motifs in brain networks. PLoS Biol 2:e369]
- ↑ Alon U (2007) An Introduction to Systems Biology: Design Principles of Biological Circuits. Boca Raton: Chapman and Hall/CRC
- ↑ Note: This article takes the view that a cell constitutes the unit ‘living systems’, and that cellular subsystems, like transcription networks and metabolic pathways, qualify as ‘biological systems’ but not as ‘living systems’.
- ↑ Note: That does not explain how living systems came to acquire the ability to utilize available energy in the first place. To explain that requires knowledge of the origin of living systems. See Origin of life
- ↑ Note: Usable energy, also called ‘free energy’, has all the attributes of information.
- ↑ Richardson PJ, Boyd R (2006) Not By Genes Alone. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago. ISBN 0-226-71212-5
- ↑ Deacon TW (1997) The Symbolic Species: The Co-Evolution of Language and the Brain. New York: W.W. Norton & Company, Inc. ISBN 0393038386
- ↑ Danchin A et al. (2007) The extant core bacterial proteome is an archive of the origin of life. Proteomics 7:875–89
- ↑ Hood L (2003) Systems biology: integrating technology, biology, and computation. Mechanisms of Ageing and Development 124:9-16]
- ↑ 79.0 79.1 Maturana HR, Varela FJ. (1973) Autopoiesis: The Origin of the Living. In: Autopoiesis and Cognition: The Realization of the Living. D. Reidel Publishing Company, Dordrect:Holland. ISBN 90-277-1015-5
- ↑ Hofmeyr JH (2007) "The biochemical factory that autonomously fabricates itself: A systems biological view of the living cell." In: Boogerd FC, Bruggeman FJ, Hofmeyr JH, and Westerhoff HV (editors). Systems Biology: Philosophical Foundations. Elsevier, Amsterdam. ISBN 13:978-0-444-52085-2 (see page 225)
- ↑ Immanuel Kant. Kant’s Critique of Judgement, translated with Introduction and Notes by J.H. Bernard (2nd ed. revised) (London: Macmillan, 1914).
- For a body then which is to be judged in itself and its internal possibility as a natural purpose, it is requisite that its parts mutually depend upon each other both as to their form and their combination, and so produce a whole by their own causality; while conversely the concept of the whole may be regarded as its cause according to a principle (in a being possessing a causality according to concepts adequate to such a product). In this case then the connexion of effective causes may be judged as an effect through final causes. In such a product of nature every part not only exists by means of the other parts, but is thought as existing for the sake of the others and the whole, that is as an (organic) instrument. Thus, however, it might be an artificial instrument, and so might be represented only as a purpose that is possible in general; but also its parts are all organs reciprocally producing each other. This can never be the case with artificial instruments, but only with nature which supplies all the material for instruments (even for those of art). Only a product of such a kind can be called a natural purpose, and this because it is an organised and self-organising being. [Emphases added]
- ↑ Alexander J. (1948) Life: Its Nature and Origin New York: Reinhold Pub. Corp.
- ↑ Harold FM (2003) The Way of the Cell: Molecules, Organisms, and the Order of Life New York: Oxford University Press. p220.
- ↑ Varela F. (2001) The Emergent Self. In: The Third Culture, by John Brockman. Chapter 12.
- ↑ 85.0 85.1 Bitbol M, Luisi PL (2004) Autopoiesis with or without cognition: defining life at its edge. PMID 16849156
- ↑ Varela FG, Maturana HR, Uribe R (1974) Autopoiesis: the organization of living systems, its characterization and a model. Curr Mod Biol 5:187-96 PMID 4407425
- "We assert that reproduction and evolution are not constitutive features of the living or¬ganization and that the properties of a unity cannot be accounted for only through ac¬counting for the properties of its components. In contrast, we claim that the living organiza¬tion can only be characterized unambiguously by specifying the network of interactions of components which constitute a living system as a whole, that is, as a "unity"."
- "We also claim that all biological phenomenology, including reproduction and evolution, is secondary to the establishment of this unitary organization."
- "Thus, instead of asking "What are the necessary properties of the components that make a living system possible?" we ask "What is the necessary and sufficient organization for a given system to be a living unity?" In other words, instead of asking what makes a living system reproduce, we ask what is the organization reproduced when a living system gives origin to another living unity?"
- ↑ Note: Taking homeostasis to mean stability of self-construction and self-sustenance, a living machine might achieve that by incorporating the perturbation (e.g., a foreign molecule) into its organization.
- ↑ Andrea Falcon (2006) Aristotle on Causality
- ↑ Bothwell JHF. (2006) The long past of systems biology. (Free Full-Text) New Phytologist 170:6-10.
Note: We might interpret Aristotle's four components of 'causality' as four components of 'explanation', for as Bothwell writes: “Aristotle (384-322 BCE) wanted to search for explanations of natural events that inspire wonder. His search led him to conclude that any question which might be asked about the behaviour of a complex, apparently designed, system might be answered if we knew four properties of that system. He called these the aitiai, a word which is usually rendered into English as 'causes', but which may be better translated as 'explanations' (Aristotle, APst 90a7-94b34; CA 715a1-17 [Aristotle. APst (Posterior Analytics), Trans: H. Tredennick (1960). Harvard University Press, Loeb Classical Library. (ISBN 0-674-99430-2)]).” - ↑ Bhalla US, Iyengar R (1999) Emergent properties of networks of biological signaling pathways. Science 283:381-7 PMID 9888852 Link-1 Link-2
- ↑ Note: For example, physical chemists cannot predict the properties of water from knowledge of its components, hydrogen and oxygen. The way hydrogen and water interact to form H2O, and the way H2O molecules interact, enables the properties of water to 'emerge'.
- ↑ Note: Following up on the example of water, the properties of its environment (e.g., temperature, pressure) affect the way the H2O molecules organize themselves, as ice, or liquid, or steam
- ↑ Note: In relation to downward causation, the environment’s effect can sometimes reach down to the genetic database with molecular signals, altering its expression and consequently the characteristics of the cells without altering the database itself — so-called 'epigenetic' effects. When epigenetic alterations of gene expression occur in the reproductive organs, the system changes can be transmitted to the next generation. See
- Jablonka E, Lamb MJ (2005) Evolution in Four Dimension: Genetic, Epigenetic, Behavioral, and Symbolic Variation in the History of Life. Cambridge: MIT Press
- Gorelick R (2004) Neo-Lamarckian medicine. Med Hypotheses 62:299-303 PMID 14962644.
- Abstract: "Darwinian medicine is the treatment of disease based on evolution. The underlying assumption of Darwinian medicine is that traits are coded by genes, which are often assumed to be sequences of DNA nucleotides. The quantitative genetic ramification of this perspective is that traits, including disease susceptibility, are either caused by genes or by the environment, with genotype-by-environment interactions usually considered statistical artefacts. I emphasize also examining those epigenetic signals that can be altered by environmental perturbations and then transmitted to subsequent generations. Although seldom studied, environmentally-alterable meiotically-heritable epigenetic signals exist and provide a mechanism underlying genotype-by-environment interactions. Environment of a parent can affect its descendants by heritably altering epigenetic signals. Neo-Lamarckian medicine is the application of these evolutionary epigenetic notions to diseases and could have enormous public health and environmental policy implications. If industrial contaminants adversely affect organisms by meiotically-heritably altering their epigenetic signals, then cleaning up these contaminants will not remedy the problem. Once contaminants have adversely altered an individual's epigenetic signals, this harm will be transmitted to future generations even if they are not exposed to the contaminant. Exposure to environmental shocks such as free radicals or other carcinogens can alter cytosine methylation patterns on regulatory genes. This can cause cancer by up-regulating genes for cell division or by down-regulating tumour suppressor genes. Environmentally-alterable meiotically-heritable epigenetic signals could also underlie other diseases, such as diabetes, Prader-Willi syndrome, and many complex diseases. If environmentally-altered meiotically-heritable epigenetic effects are widespread - which is an important open empirical question - they have the potential to alter paradigmatic views of evolutionary medicine and the putative dichotomy of nature versus nurture. Neo-Lamarckian medicine would thereby shift emphasis from cure to prevention of diseases."
- ↑ Walsh DM (2006) Organisms as natural purposes: the contemporary evolutionary perspective. Stud Hist Philos Biol Biomed Sci 37:771-91]
- ↑ Tabony J (2006) Microtubules viewed as molecular ant colonies. (Free Full-Text) Biol Cell 98:603-17 PMID 16968217.
- Abstract: "Populations of ants and other social insects self-organize and develop ‘emergent’ properties through stigmergy in which individual ants communicate with one another via chemical trails of pheromones that attract or repulse other ants. In this way, sophisticated properties and functions develop. Under appropriate conditions, in vitro microtubule preparations, initially comprised of only tubulin and GTP, behave in a similar manner. They self-organize and develop other higher-level emergent phenomena by a process where individual microtubules are coupled together by the chemical trails they produce by their own reactive growing and shrinking. This behaviour is described and compared with the behaviour of ant colonies. Viewing microtubules as populations of molecular ants may provide new insights as to how the cytoskeleton may spontaneously develop high-level functions. It is plausible that such processes occur during the early stages of embryogenesis and in cells."
- ↑ Theise ND, d'Inverno M. (2004) Understanding cell lineages as complex adaptive systems. Blood Cells Mol Dis 32:17-20 PMID 14757407.
- Abstract: "Stem cells may be considered complex reactive systems because of their vast number in a living system, their reactive nature, and the influence of local environmental factors (such as the state of neighboring cells, tissue matrix, stem cell physiological processes) on their behavior. In such systems, emergent global behavior arises through the multitude of local interactions among the cell agents. Approaching hematopoietic and other stem cell lineages from this perspective have critical ramifications on current thinking relating to the plasticity of these lineage systems, the modeling of stem cell systems, and the interpretation of clinical data regarding many diseases within such models."
- ↑ Ruiz i Altaba A et al. (2003) The emergent design of the neural tube: prepattern, SHH morphogen and GLI code. Curr Opin Genet Dev 13:513-21 PMID 14550418
- ↑ Jeong H et al.(2000) The large scale organisation of metabolic networks. Nature 407:651-4]
- ↑ e.g. Grindrod P, Kibble M (2004) Review of uses of network and graph theory concepts within proteomics. Expert Rev Proteomics 1:229-38 PMID 15966817
- ↑ Ye X et al.(2005) Multi-scale methodology: a key to deciphering systems biology. Front Biosci 10:961-5 PMID 15569634
- ↑ Cho YS et al. (2005) Self-organization of bidisperse colloids in water droplets. J Am Chem Soc 127:15968-75 PMID 16277541
- ↑ see e.g. Burak Y, Fiete I (2006) Do we understand the emergent dynamics of grid cell activity? J Neurosci 26:9352-4 PMID 16977716
- ↑ e.g. Courtney SM (2004) Attention and cognitive control as emergent properties of information representation in working memory. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 4:501-16 PMID 15849893
- ↑ Theraulaz G et al (2002) Spatial patterns in ant colonies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:9645-9 PMID 12114538
- ↑ Theraulaz G, Bonabeau E (1999) A brief history of stigmergy. Artif Life 5:97-116 PMID 10633572
- ↑ Bonabeau E, Meyer C (2001) Swarm intelligence. A whole new way to think about business. Harv Bus Rev 79:106-14 Download PDF of article -PMID 11345907
- ↑ Field CB et al.(1998) Primary Production of the Biosphere: Integrating Terrestrial and Oceanic Components. Science 81:237-40]
- ↑ (1991) Zurek WJ (ed) Complexity, Entropy, and the Physics of Information: The Proceedings of the Workshop on the Complexity, Entropy, and the Physics of Information May-June, 1989, Santa Fe, New Mexico. Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, The Advanced Book Program, Redwood City. Book preview by Google Books -ISBN 0201515091
- ↑ Hazen RM (2005) Genesis: The Scientific Quest for Life's Origin. Joseph Henry Press, Washington DC. Book description, reviews, and for-fee downloadable PDF of entire book or individual chapters -ISBN 0309094321.
- ↑ Note: We can arrive at a more-or-less empirically sound explanation of what constitutes living systems without having a good explanation for how they arose in the first place, because we can study the here-and-now and not the there-and-then.
- ↑ Odling-Smee FJ, Laland KN, Feldman MW (2003) Niche Construction; The Neglected Process in Evolution. Princeton: Princeton University Press. ISBN 0691044384. Google Books extensive excerpts. Website with bibliography on niche construction.
- ↑ Damasio A (2003) Looking for Spinoza: Joy, Sorrow, and the Feeling Brain. Orlando, Florida: Harcourt, Inc. Book synopsis, table of contents, excerpts, interview with author. -ISBN 978-0099421832, ISBN 978-0151005574
 KSF
KSF