Serine
 From Citizendium - Reading time: 1 min
From Citizendium - Reading time: 1 min
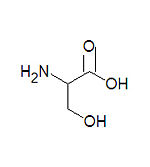
Serine, one of the twenty common amino acids.
Serine, abbreviated as Ser or S, is one of the twenty common amino acids used by living organisms to build proteins. It is one of the smallest amino acids, being larger than only glycine and alanine. It is subject to phosphorylation by kinases because it is one of the three amino acids, together with threonine and tyrosine, that contain a hydroxyl group (OH) on the side chain. It can be thought of as -hydroxylated alanine. The amino acids glycine and cysteine are synthesized from serine.
biosynthesis[edit]
The first step in the biosynthesis of serine begins with the oxidation of the hydroxyl group of 3-phosphoglycerate by NAD+ to produce 3-phosphohydroxy pyruvate. This reaction is followed by a transamination reaction in which glutamate transfers an amine group, becoming -ketoglutarate in the process, to 3-phosphohydroxypyruvate. Finally, hydrolysis and removal of the phosphate group yields serine.
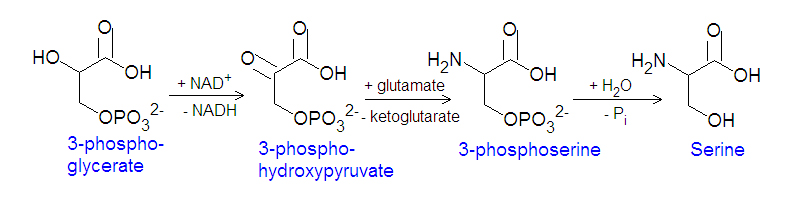
Biosynthesis of serine from 3-phosphoglycerate.
 KSF
KSF