Constants
 From Conservapedia - Reading time: 2 min
From Conservapedia - Reading time: 2 min
This page lists various constants used in physics and some useful conversions.
Contents
Physical constants[edit]
The number in brackets represents the uncertainty in the constant, so that  has an uncertainty of
has an uncertainty of  .
.
| Name | Symbol | Value | Meaning | Used in | Exact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Planck's constant | 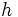
|

|
It relates the frequency of a photon to its energy | Quantum mechanics | Inexact[1] |
| Speed of light | 
|

|
This is the speed of light in a vacuum | Most of physics, such as optics and relativity | Exact[2] |
| Permittivity of free space | 
|

|
Related to the strength of an electric field produced by a charge | Electromagnetism | Exact[3] |
| Permeability of free space | 
|

|
Related to the strength of magnetic fields produced by a current | Electromagnetism | Exact[4] |
| Elementary charge | 
|

|
The magnitude of the electric charge on an electron | Determines the strength of electric and magnetic fields produced by protons, electrons etc. | Inexact[5] |
| Avogadro's number | 
|

|
The number of constituents in 1 mole of something | Chemistry, statistical mechanics, thermodynamics | Inexact[6] |
| Ideal gas constant | 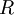
|

|
Relates the pressure, volume, temperature and number of moles of an ideal gas | Thermodynamics | Inexact[7] |
| Faraday Constant | 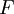
|

|
The electric charge on one mole of electrons (Avogadro's number times elementary charge) | Chemistry, physics | Inexact[8] |
| Gravitational constant | 
|

|
Constant related to the strength of Newtonian gravity | Newtonian gravity | Inexact[9] |
| Boltzmann constant | 
|

|
Thermodynamics | Inexact[10] | |
| Reduced Planck's constant | 
|

|
Quantum mechanics | It is Planck's constant divided by  . .
|
Inexact[11] |
| Wien displacement constant | 
|

|
Relates the temperature of a black body to the peak in its spectrum | Inexact[12] | |
| Standard acceleration due to gravity | 
|

|
This is the acceleration of any object near to the earth's surface when gravity is the only force acting (i.e., no air resistance). | Mechanics | Exact[13] |
| Proton mass | 
|

|
Rest mass of a proton | Inexact[14] | |
| Neutron mass | 
|

|
Rest mass of a neutron | Inexact[15] | |
| Electron mass | 
|

|
Rest mass of an electron | Inexact[16] |
Useful Conversions[edit]
Length[edit]
1 metre = 39.37 inches 1 metre = 3.281 feet 1 kilometre = 0.6213 miles
1 mile = 5280 feet 1 mile = 1760 yards
Weight[edit]
1 kilogram = 35.27 ounce 1 kilogram = 2.205 pounds
Pressure[edit]
1 atm = 101.1 kPa 1 atm = 760 torr 1 atm = 760 mm Hg
Other[edit]
Atomic mass unit: 1.00 amu = 1.67 x 10−27 kg
1.000 calorie = 4.184 Joules
Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP): temperature = 273 K and pressure = 1.00 atm
Relative mass and charge of subatomic particles found in atoms.
| Relative Mass | Relative Charge | |
|---|---|---|
| Proton | 1 | +1 |
| Neutron | 1 | 0 |
| Electron | 1/1837 | -1 |
Prefixes[edit]
Prefixes in front of a unit indicate that that unit should be multiplied by a multiple of ten, e.g. Giga is 109, so 1 GPa = 109 Pa.
| Name | Symbol | Power |
|---|---|---|
| Pico | p | 10−12 |
| nano | n | 10−9 |
| micro | μ | 10−6 |
| milli | m | 10−3 |
| centi | c | 10−2 |
| deci | d | 10−1 |
| deca | da | 101 |
| hecto | h | 102 |
| kilo | k | 103 |
| mega | M | 106 |
| giga | G | 109 |
| tera | T | 1012 |
References[edit]
- ↑ http://physics.nist.gov/cgi-bin/cuu/Value?h
- ↑ http://physics.nist.gov/cgi-bin/cuu/Value?c
- ↑ http://physics.nist.gov/cgi-bin/cuu/Value?ep0
- ↑ http://physics.nist.gov/cgi-bin/cuu/Value?mu0
- ↑ http://physics.nist.gov/cgi-bin/cuu/Value?e
- ↑ http://physics.nist.gov/cgi-bin/cuu/Value?na
- ↑ http://physics.nist.gov/cgi-bin/cuu/Value?r
- ↑ http://ch302.cm.utexas.edu/echem/echem-stoich/echem-stoich-all.php
- ↑ http://physics.nist.gov/cgi-bin/cuu/Value?bg
- ↑ http://physics.nist.gov/cgi-bin/cuu/Value?k
- ↑ http://physics.nist.gov/cgi-bin/cuu/Value?hbar
- ↑ http://physics.nist.gov/cgi-bin/cuu/Value?bwien
- ↑ http://physics.nist.gov/cgi-bin/cuu/Value?gn
- ↑ http://physics.nist.gov/cgi-bin/cuu/Value?mp
- ↑ http://physics.nist.gov/cgi-bin/cuu/Value?mn
- ↑ http://physics.nist.gov/cgi-bin/cuu/Value?me
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://www.conservapedia.com/Constants62 views | Status: cached on February 27 2023 17:50:57↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF