Fluid dynamics
 From Conservapedia - Reading time: 1 min
From Conservapedia - Reading time: 1 min
Fluid dynamics is the study of how fluids move. Fluids include water and gases (such as air).[1] Fluid dynamics is also known as continuum mechanics, as fluids cannot be treated as point objects; Newton's second law thus becomes Euler equation
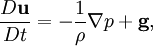
where  is the density of the fluid, u its velocity and g the gravitational acceleration. The operator
is the density of the fluid, u its velocity and g the gravitational acceleration. The operator  is the convective derivative, the rate of change of a certain quantity A(t) of the fluid as it is carried by the fluid (hence the presence of u). Euler equation is then a differential operation explicitly relating the effects of the gravity and the gradient of pressure on the velocity of the fluid.
is the convective derivative, the rate of change of a certain quantity A(t) of the fluid as it is carried by the fluid (hence the presence of u). Euler equation is then a differential operation explicitly relating the effects of the gravity and the gradient of pressure on the velocity of the fluid.
As long as the speed of sound is much larger than u, the density  of the fluid can assumed to be constant (incompressible) in most situations.
of the fluid can assumed to be constant (incompressible) in most situations.
References[edit]
10 views | Status: cached on February 18 2023 12:11:30
↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF