Latino
 From Conservapedia - Reading time: 21 min
From Conservapedia - Reading time: 21 min
Latino (in the US) is a new English word (Americanism) derived from a Spanish word that means a person of Latin languages-speaking descent. Latinos, in English, means descendents of the Conquistadors of the Spanish Conquest of North and South America (Spanish: La Conquista) living in the U.S.[1][2] Many descendants of the Spanish Conquest in the territories of the former Spanish Empire that are now part of the United States were never part of Mexico and find it highly offensive to be referred to as "Mexican-American."
Latino (female is "Latina", plural is "Latinos") is a broad geographic term referring to those who come from Latin American countries, regardless of whether he or she speaks Spanish. The term is not used universally across the United States and tends to be used regionally in the Eastern U.S. In the border states of Texas, New Mexico, Arizona, and California, people of Spanish and mixed Native American descent most often refer to themselves as Hispanic.
The term "Latin" is derived from Southern Europeans' ancient language, Latin, the language spoken by the Romans; descendant languages are Spanish, French, Italian, Portuguese (also spoken in Brazil in South America), and to a distance, Romanian in Romania and the Balkans.
Contents
- 1 Latinos in the US
- 2 19th century
- 3 20th century
- 4 World War II
- 5 Politics
- 6 Religion
- 7 Demography
- 8 Puerto Ricans
- 9 Chicago
- 10 Historiography
- 11 See also
- 12 External links
- 13 Further reading
- 14 Bibliography
- 15 Surveys and historiography
- 16 Pre 1965
- 17 Culture and politics, post 1965
- 18 Regional and Local
- 19 Related
- 20 Primary sources
Latinos in the US[edit]
Latinos are diverse: 60% are native-born and 40% foreign-born; 64% are of Mexican heritage, and the other 36% are from Cuba, Puerto Rico, Central America and beyond. They split their vote in 2004, when President Bush appealed for their votes, but voted 2–1 against McCain in 2008 when he made little appeal to them. Despite their diversity they were united in celebrating the nomination to the Supreme Court of Judge Sonia Sotomayor in May 2009. She was born to a poor family of migrants from Puerto Rico, and after attending Princeton and Yale Law School made it to the top through very hard work. Her nomination marked the national recognition and acceptance of all Latinos.
As a united whole, Hispanics make up more than 15% of the U.S. population and accounted for about half of the country's growth in the past decade.
By 2005, the Latino population in the US reached 41.3 million, of whom 64% were Mexican, 10% Puerto Rican, 3% Cuban, 3% Dominican, 3% Salvadoran, and the remaining 17% from smaller groups.[3] According to the Pew Research Center in 2008, 12,7 millions were of Mexican origin (32% of all immigrants living in this country).[4] About 30% of the Latinos—12 million—are illegal ("undocumented") immigrants to the U.S., a number that has grown since the 9-11 attacks of 2001. The illegal—and indeed the legal immigrants—have become targets of verbal and political criticism.
Culturally they are mostly conservative Catholics, with a strong evangelical element. They are known for very strong family ties, and high birth rates. They cluster at the bottom of the socio-economic scale, with low levels of education and high dropout rates from schools, and mostly hold unskilled or semi-skilled jobs. The "illegals" (undocumented) hold even lower-skilled jobs in agriculture, construction, landscaping, hotels and restaurants, while sending money back to their families. The Latino crime rate is about the national average. The illegals pay the same sales taxes as everyone, but usually have incomes too low to pay income taxes. Many of the illegals pay social security taxes into false accounts (which means they are not entitled to benefits). The legals include both citizens and legal residents who are not yet citizens; all children born in the U.S. have U.S. citizenship. In many families, some members are illegal and some are legal non-citizens and others are full citizens.
They have been politically rather inactive (except in New Mexico and Puerto Rico). Politically, the citizens have low turnout rates, but their rapid increase of numbers presages a major voting block. George W. Bush, and to a lesser extent John McCain have made major efforts to attract them to the Republican Party, but Democrats outnumber Republicans by about 65:35.
The assimilation rates of Latinos resembles that of Italians and Poles in the early 20th century, and is higher than the rate of immigrants who came from Germany in the 18th and 19th century. Latinos have assimilated smoothly into American religion, sports, jobs and popular culture. They cling to favorite foods, but have made Mexican cuisine as popular in the U.S. as pizza (which the Italians brought over). The first generation, who came to the U.S. as adults, mostly speak Spanish. Their children are usually bilingual; very few of the children attend Spanish language schools or read Spanish.
Many politically correct liberals and leftists[5] (most of whom are white), as well as many liberal media outlets, choose to use the made-up[6] misspelling Latinx[7] (pronounced "la-tinks", which they claim is "gender-neutral") to refer to Latinos as a whole; Wikipedia even has an article on the term. The term Latinx is not embraced by most Latinos, however,[8][9] and many find the term offensive.[10] Also, conservatives as a whole, regardless of ethnic or racial background, find the conscious use of the politically-correct term by white liberals to be ludicrous as well as condescending to Latinos.[11]
19th century[edit]
When Mexico took over control from Spain in the early 1820s, the new government ignored and isolated the "norteños" (inhabitants of Mexico's northern provinces), except to break up the mission system in California. The systematic Navajo and Apache raids on New Mexico villages and ranches were ignored, as was the vulnerability of California, as the central government pulled back its soldiers to use them in recurrent civil wars and factional battles. When Texas seemed too independent, Mexico's President Santa Anna led an army to massacre the villagers and destroy the American settlements. After initial victories and massacres at The Alamo and Goliad, Santa Anna was decisively defeated by the Texans, who declared independence. The Tejanos in Texas joined the revolution and supported the new Republic of Texas; The Hispanics in New Mexico and California were localistic and did not identify with the regime in Mexico City. The "norteños" played a minor role in the Mexican American War of 1846–48, and when offered the choice of repatriating to Mexico or remaining and becoming full citizens of the United States, the great majority remained. Only when large numbers of Americans arrived did they develop a sense of "lo mexicano," that is of "being Mexican," and that new identification had little to do with far-off Mexico.[12] American entrepreneurs often cultivated alliances and partnerships with the Mexican propertied elites in the states of Texas and California, and the territories of New Mexico and Arizona. The Californios—who only numbered 10,000 in 1848, remained in California but were soon overwhelmed by the immigration of hundreds of thousands of newcomers to California, and largely became invisible to Anglos. The Latino culture of the rest of the Southwest, especially New Mexico and southern Texas, called itself "Spanish" (rather than "Mexican") to distinguish themselves from "los norteamericanos". The Latinos emphasized their own religion, language, customs and kinship ties, and drew into enclaves, rural colonias and urban barrios, which norteamericanos seldom entered; intermarriage rates were low.
20th century[edit]
After 1911 the ferocious civil wars in Mexico led 600,000 to 1 million refugees to flee north across the border, which was generally open. Well educated middle-class families emigrated, as well as poor peons.In Texas a band of radicals based in Mexico issued the manifesto "Plan de San Diego" in 1915 in South Texas calling on Hispanics to reconquer the Southwest and kill all the Anglo men. These radicals assassinated opponents and killed several dozen people in attacks on railroads and ranches before the Texas Rangers smashed the insurrection. The vast majority of Tejanos strongly repudiated the Plan and affirmed their American loyalty by founding the League of United Latin American Citizens (LULAC). LULAC, headed by professionals, businessmen and modernizers, became the central Tejano organization promoting civic pride and civil rights.[13]
Over 500,000 returned after 1930, but many stayed. The consulates of the Mexican government in major cities in the Southwest organized a network of "juntas patrioticas" (patriotic councils) and "comisiónes honoríficos" (honorary committees) to celebrate Mexican national holidays such as the Cinco de Mayo; the target audience was the Latino middle class.[14]
In borderlands towns such as Brownsville, Corpus Christi, Laredo, San Antonio, El Paso, Tucson, Yuma, San Diego, and Los Angeles, local Latino leaders wanted to restrict the influx of immigrants, because the newcomers directly competed with resident Latinos for jobs and housing and because they reinforced negative stereotypes regarding a lazy and violent lifestyle. In 1929 the League of United Latin American Citizens (LULAC) was formed on the premise that full acceptance of American social, educational and political values was the only way Latinos could reasonably expect to improve their political, economic, and social position in American society. Some upwardly mobile families joined Protestant churches, but most remained devout, conservative Roman Catholics. From the early 1930s through the 1960s, LULAC's political agenda focused on citizenship training and naturalization of "foreign-born Mexicans," English-language training, active support of antidiscriminatory litigation and legislation (particularly regarding public schools), and strict control of further immigration from Mexico. LULAC promoted the liberal rhetoric of "equality" and "rights" and the mutual obligations of republican civic duty. However, voting levels were quite low, and especially in South Texas the Latino vote was controlled by local "bosses." There was little in the way of radical movements.
World War II[edit]
World War II was a watershed for all the Latino groups. Some 500,000 were drafted; even larger numbers of the women and older men worked in high paying munitions plants, ending the hardship years of the depression and inspiring demands for upward mobility and political rights. The League of United Latin American Citizens (LULAC) and El Congreso de Pueblos de Hablan Española (the Spanish-Speaking Peoples' Congress), founded before the war, expanded their membership and more successfully demanded full integration for their middle class constituents. Labor unions opened their membership rolls and Luisa Moreno became the first Latina to hold a national union office, as vice-president of the United Cannery, Agricultural, Packing, and Allied Workers of America (UCAPAWA), and affiliate of the Congress of Industrial Organizations (CIO).
Post 1945[edit]
From 1945 to the early 1970s, large numbers of Latinos moved out of dead-end, low-wage work into higher-paying and higher-status skilled blue-collar occupations.[15] They and their children experienced steady gains in virtually all major socioeconomic indicators, including income, occupational status, English-language proficiency, years of education, and geographic mobility. The opportunities were in the cities; there was little upward mobility for those who remained in the California farmland or in the chronically depressed lower Rio Grande Valley of Texas, and in the isolated rural hamlets of Colorado and New Mexico.[16]
Seasonal migration[edit]
A common pattern emerged after 1940 of men working summers in the U.S. and spending the winter season in the village back in Mexico. While this became illegal in 1965, the numbers involved kept growing. By 2007 there were 12 million or so undocumented workers in the U.S.; they had jobs, often using fake identity cards. They made money in the U.S. but returned to the villages to spend it, attend fiestas, tend to family business, and participate in extended kinship rituals such as baptisms, weddings, and funerals. After the increased border security following the 9-11 attacks in 2001, the back-and-forth pattern became dangerous. People kept coming north, but they stayed in the U.S. and sent money home every month. Locked into the American economy year-round, millions of these undocumented workers moved out of season agricultural jobs into year-round jobs in restaurants, hotels, construction, landscaping and semiskilled factory work, such as meat packing. Most paid federal social security taxes into imaginary accounts (and thus were not eligible for benefits.) Few had high enough incomes to pay federal or state income taxes, but all paid local and state sales taxes on their purchases as well as local property taxes (via their rent payments to landlords).
Politics[edit]
Latinos engaged in national politics for the first time in 1960 when hundreds of "Viva Kennedy" clubs were created. As a result of military service in World War II the slowly improving civil rights atmosphere of the 1950s, Mexican Americans had tasted some limited successes in access to employment, education (particularly through the benefits of the G.I. Bill), and the election of a few government officials at the state and local levels. Moreover, with the establishment of new, aggressive Mexican American advocacy organizations in the Southwest between 1947 and 1959, community activists symbolically announced that Mexican Americans would henceforth be a political force with which to reckon. About 85% of the Mexican American vote went to Kennedy, slightly higher than other Catholic ethnics. The Latinos took credit for carrying California and Texas by razor-thin margins. President Kennedy, however, made some symbolic appointments but showed minimal interest in Mexican American issues.
In 2000 and 2004 presidential elections, George W. Bush made a systematic effort to reach Latino voters, obtaining 40% of their vote. Most remained Democrats and in the 2008 presidential election, heavily favored Hillary Clinton over Barack Obama for the nomination.
Bill Richardson (1947) served as the Democratic Governor of the State of New Mexico from 2003 to 2011. He previously has served as a Congressman, United States Ambassadors to the United Nations, and U.S. Secretary of Energy. He was nominated as Secretary of Commerce in the Obama Administration. Three of his four grandparents were Mexican citizens.
Sonia Sotomayor (born in New York City, 1954) joined the U.S. Supreme Court in August 2009. Sotomayor, is a Catholic and the first Hispanic nominated to the high court.
Adolfo Carrion Jr. (b. 1961) is a Democratic politician of Hispanic ancestry. Carrion was appointed to the position of Director of the White House Office of Urban Affairs in the Obama Administration.
In September 2010, Obama declared: Long before America was even an idea, this land of plenty was home to many peoples, to British and French, to Dutch and Spanish, to Mexican, to countless Indian tribes. We all shared the same land. We didn't always get along.
In 2011, Brian Sandoval became Nevada's 30th governor; Sandoval is the first Hispanic in Nevada to win a statewide election as attorney general in 2002 and the former federal judge and chairman of the Gaming Commission will hold the same distinction as governor. At the same time Susana Martinez (1959), Republican, is the current Governor of New Mexico; She served as District Attorney for the 3rd Judicial District in Doña Ana County, New Mexico, having been elected in 1996 and reelected three times. She is the first Hispanic womam governor in U.S. history.
Another notable conservative Latino of Cuban origin is Marco Rubio, speaker of the house of Florida.
Religion[edit]
About 80% of Latinos are Roman Catholic, and typically follow traditional styles.
Pentecostals[edit]
Of the thirty-seven million Latinos living in the United States, nearly five million declare themselves to be either Pentecostal or Charismatic, and more convert every day. Latinos are not new to Pentecostalism; indeed, they have been becoming Pentecostal for more than a hundred years. Thus several generations have never belonged to any other faith. However, there is a common misperception of all of them as recent converts. The Latino Pentecostals participate in the spiritual and material culture of the larger evangelical Christian movement and imprints that movement with its own experiences. Diverse Latino faith communities—U.S. Chicano churches, pan–Latin American immigrant churches, and mixed Latin American and U.S. Latino churches—have carved out their own unique religious space.[17]
Demography[edit]

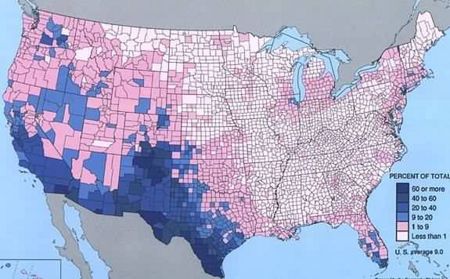
California in 2006 had the largest Hispanic population of any state as of 2006 (13.1 million), followed by Texas (8.4 million) and Florida (3.6 million). Texas had the largest numerical increase between 2005 and 2006 (305,000), with California (283,000) and Florida (161,000) following. In New Mexico, Hispanics comprised the highest proportion of the total population (44%), with California and Texas (36% each) next in line. The Hispanic population in 2006 was much younger, with a median age of 27.4 compared with the population as a whole at 36.4. About a third of the Hispanic population was younger than 18, compared with one-fourth of the total population.[18]
The rapid growth of the Hispanic population after 1972 began in the Southwest, but spread nationwide by 2000. The diffusion of Latinos across the country was dramatic by 2008, and became a major issue in the presidential election, with Republicans echoing nativist hostilities. In Georgia, for example, there were barely 60,000 Latinos in 1980, and 100,000 in 1990, less than 2%. By the 2000 Census the number had surged to 435,000, or 5%, with continuing rapid growth to 700,000 in 2006.[19]
In 1972 Hispanics comprised 6% of public school students, and more than tripled to 20% in 2005. However, despite fears that assimilation would be difficult, the proportion of students who spoke English with difficulty has been flat at 5%, according to graph 1.
Fernando Valenzuela, Salma Hayek, Eduardo 'Piolín' Sotelo and Andrés Bermúdez are examples of Latinos that succeeded in US.
Puerto Ricans[edit]
The U.S. acquired Puerto Rico from Spain in 1898, and engaged in a massive modernization program involving disease control, sanitation, transportation, internal improvements, and medical care, along with corporate investment in sugar plantations. The island was overpopulated, so a systematic effort was made to assist migration. Over 5000 migrated to Hawaii (also acquired in 1898) to work in sugar plantations. By 1920 Puerto Ricans had full U.S. citizenship and had a presence in 45 states. New York City was the destination of 60%; children born anywhere on the mainland were dubbed "Nuyorican."[20]
Chicago[edit]
Fernandez (2005) documents the history of Mexican and Puerto Rican immigration and community formation in Chicago after World War II. Beginning with World War II, Mexican and Puerto Rican workers traveled to the Midwest through varying migrant streams to perform unskilled labor. They settled in separate areas of Chicago. These parallel migrations created historically unique communities where both groups encountered one another in the mid-twentieth century. By the 1950s and 1960s, both groups experienced repeated displacements and dislocations from the Near West Side, the Near North Side and the Lincoln Park neighborhood. At the macro level, Mexican and Puerto Rican workers' life chances were shaped by federal policies regarding immigration, labor, and citizenship. At the local level, they felt the impact of municipal government policies, which had specific racial dimensions. As these populations relocated from one neighborhood to the next, they made efforts to shape their own communities and their futures. During the period of the Civil Rights Movement, Mexicans and Puerto Ricans engaged in social struggles, both in coalition with one another but also as separate, distinct, national minorities. They created organizations and institutions such as Casa Aztlán, the Young Lords Organization, Mujeres Latinas en Acción, the Latin American Defense Organization, and El Centro de la Causa. These organizations drew upon differing strategies based on notions of nation, gender, and class, and at times produced inter-ethnic and inter-racial coalitions.[21]
Historiography[edit]
The study of Latino history raises issues regarding the definition and boundaries of "Latino." Are Latinos a "group" and if so, what are its defining boundaries and characteristics? Is speaking Spanish a requirement to be Latino? Are indigenous peoples from Latin America part of the group? Do Latinos consider themselves a group? Do they cluster along lines of geographical origin? What is the relationship between old established settlements and new arrivals? How does the presence of 12 million undocumented ("illegal") arrivals affect the 25 million "legal" residents of the U.S. How has nativism and the hostility of Anglos and blacks shaped the group identity and opportunity? What impact is the rapid diffusion across the country having on local communities, schools, labor markets. Will the Latinos start voting in large numbers and become a political force? What is the impact of high dropout rates? Will majority-Latino communities change the national culture? Does Latino immigration follow or alter traditional patterns of assimilation?
See also[edit]
- Raul Labrador - U.S. House of Representatives Conservative-Libertarian TEA Party Republican from Idaho
- Ted Cruz - Conservative Republican Senator from Texas
- Marco Rubio - Republican Senator from Florida
- Adolfo Carrion Jr.
- Alberto R. Gonzales
- Armando Hinojosa
- Ken Salazar
- California
- Los Angeles
- San Jose
- San Francisco Bay Area
- Unconstitutional Executive amnesty via Obama Executive Orders
- Universal health care for illegal aliens via ObamaCare
- Atheism and Latino Americans
External links[edit]
- Labor rights are Cvil rights
- Generations of diversity: Latinos in the United States
- Congressman Introduces Bill to End ‘Birthright Citizenship’
Further reading[edit]
- Aranda, José, Jr. When We Arrive: A New Literary History of Mexican America. U. of Arizona Press, 2003. 256 pp.
- Bean, Frank D., and Marta Tienda. The Hispanic Population of the United States (1987), statistical analysis of demography and social structure
- Bogardus, Emory S. The Mexican in the United States (1934), sociological
- De León, Arnoldo. Mexican Americans in Texas: A Brief History, 2nd ed. (1999)
- De Leon, Arnoldo, and Richard Griswold Del Castillo. North to Aztlan: A History of Mexican Americans in the United States (2006)
- Burt, Kenneth C. The Search for a Civic Voice: California Latino Politics, (2007). Excerpts and online search from Amazon.com
- Dolan, Jay P. and Gilberto M. Hinojosa; Mexican Americans and the Catholic Church, 1900-1965 (1994)
- García, María Cristina. Havana, USA: Cuban Exiles and Cuban Americans in South Florida, 1959–1994 (1996); excerpt and text search
- Gomez-Quiñones, Juan. Mexican American Labor, 1790-1990. (1994).
- Gomez-Quinones, Juan. Chicano Politics: Reality and Promise, 1940-1990 (1990)
- Gómez-Quiñones, Juan. Roots of Chicano Politics, 1600-1940 (1994)
- Gonzales-Berry, Erlinda, David R. Maciel, editors, The Contested Homeland: A Chicano History of New Mexico, 314 pages (2000), ISBN 0-8263-2199-2
- Grebler, Leo, Joan Moore, and Ralph Guzmán. The Mexican American People: The Nation's Second Largest Minority (1970), emphasis on census data and statistics
- Gutiérrez, David G. ed. The Columbia History of Latinos in the United States Since 1960 (2004) 512pp excerpt and text search
- Gutiérrez, David G. "Migration, Emergent Ethnicity, and the "Third Space": The Shifting Politics of Nationalism in Greater Mexico" Journal of American History 1999 86(2): 481–517. in JSTOR covers 1800 to the 1980s
- Gutiérrez, David G. Walls and Mirrors: Mexican Americans, Mexican Immigrants, and the Politics of Ethnicity in the Southwest, 1910-1986 1995. excerpt and text search
- Gutiérrez; Ramón A. When Jesus Came, the Corn Mothers Went Away: Marriage, Sexuality, and Power in New Mexico, 1500-1846 (1991)
- Handbook of Texas History Online
- Meier, Matt S., and Margo Gutierrez, ed. Encyclopedia of the Mexican American Civil Rights Movement (2000) excerpt and text search
- Meier, Matt S. Notable Latino Americans (1997), 127 very well written interpretive biographies
- Ruiz, Vicki L. “Nuestra América: Latino History as United States History,” Journal of American History, 93 (Dec. 2006), 655–72.
- Ruiz, Vicki L. From Out of the Shadows: Mexican Women in Twentieth-Century America (1998)
- Sãnchez Korrol, Virginia E. From Colonia to Community: The History of Puerto Ricans in New York City. (1994) complete text online free in California; excerpt and text search
- Valle, Victor M. and Torres, Rodolfo D. Latino Metropolis. 2000. 249 pp. on Los Angeles
- Weber, David J. The Mexican Frontier, 1821-1846: The American Southwest under Mexico (1982)
- Whalen, Carmen Teresa, and Victor Vásquez-Hernández, eds. The Puerto Rican Diaspora: Historical Perspectives (2005),
Primary sources[edit]
- Augenbraum, Harold, and Margarite Fernández Olmos, eds. The Latino Reader: An American Literary Tradition from 1542 to the Present (1997) 502 pages excerpts and text search
- Augenbraum, Harold, and Ilan Stavans, eds. Growing Up Latino: Memoirs and Stories (1993) 344 pages excerpts and text search
notes[edit]
- ↑ David G. Gutiérrez, ed. The Columbia History of Latinos in the United States Since 1960 (2004) pp 1-2 online excerpt
- ↑ Latino Dictionary.com
- ↑ See Census Bureau press release, July 16, 2007 at
- ↑ Mexican Immigrants in the United States, 2008
- ↑ Latinx -- The Latest Leftist Educational Maneuver at the American Thinker
- ↑ ‘Latinx’ Is Not A Real Word at the Daily Wire
- ↑ ‘Latinx’ Is a Stupid Word at National Review
- ↑ Survey: Only 2% of Hispanics Prefer the Politically Correct Term 'Latinx'
- ↑ Progressives, Hispanics are not 'Latinx.' Stop trying to Anglicize our Spanish language at USA Today
- ↑ Please don’t call me Latinx: Why it’s not my preferred term at the New York Daily News
- ↑ PC Term 'Latinx' Had an Outbreak at Vox at NewsBusters
- ↑ David G. Gutiérrez, "Migration, Emergent Ethnicity, and the "Third Space": The Shifting Politics of Nationalism in Greater Mexico" Journal of American History 1999 86(2): 481-517. ISSN: 0021-8723 in JSTOR
- ↑ Benjamin H. Johnson, Revolution in Texas: how a forgotten rebellion and its bloody suppression turned Mexicans into Americans. (2003).
- ↑ In Mexico itself, the emergence of a national identity for the average person was the work of the 20th century. After 1920 the national government promoted "true" mexicanismo by stirring up anti-American sentiment; promoting contemporary Mexican art, music, and literature; extolling and placing new emphasis on the value of the nation's indigenous peoples and the heritage of mestizaje. Gutiérrez (1999)
- ↑ 43% of the men were still unskilled workers or farm laborers in 1950; by 1960, the proportion had fallen to 33%.
- ↑ Bean and Tienda, The Hispanic Population of the United States (1987), 17-22, 280-337.
- ↑ Arlene Sanchez Walsh, Latino Pentecostal Identity: Evangelical Faith, Self, and Society (2003)
- ↑ See Census report May 17, 2007 at [1] with details at [2]
- ↑ Bullock and Hood (2006)
- ↑ Ruiz (2006)
- ↑ Lilia Fernández, "Latina/o Migration and Community Formation in Postwar Chicago: Mexicans, Puerto Ricans, Gender, and Politics, 1945-1975." PhD dissertation U. of California, San Diego 2005. 302 pp. DAI 2006 66(10): 3779-A. DA3191767 Fulltext: ProQuest Dissertations & Theses. See also Mérida M. Rúa, "Claims to `the City': Puerto Rican Latinidad amid Labors of Identity, Community, and Belonging in Chicago." PhD dissertation U. of Michigan 2004. 219 pp. DAI 2005 65(10): 3877-A. DA3150079 Fulltext: ProQuest Dissertations & Theses
Bibliography[edit]
Surveys and historiography[edit]
- Bean, Frank D., and Marta Tienda. The Hispanic Population of the United States (1987), statistical analysis of demography and social structure
- De Leon, Arnoldo, and Richard Griswold Del Castillo. North to Aztlan: A History of Mexican Americans in the United States (2006)
- Garcia, Richard A. "Religion as Language, Church as Culture: Changing Chicano Historiography," Reviews in American History 34.4 (2006) 521–528 in Project Muse.
- Gomez-Quiñones, Juan. Mexican American Labor, 1790-1990. (1994).
- Gutiérrez, David G. ed. The Columbia History of Latinos in the United States Since 1960 (2004) 512pp excerpt and text search
- Gutiérrez, David G. "Migration, Emergent Ethnicity, and the "Third Space": The Shifting Politics of Nationalism in Greater Mexico" Journal of American History 1999 86(2): 481–517. in JSTOR covers 1800 to the 1980s
- Rochín, Refugio I., and Denis N. Valdés, eds. Voices of a New Chicana/o History. (2000). 307 pp.
- Ruiz, Vicki L. “Nuestra América: Latino History as United States History,” Journal of American History, 93 (Dec. 2006), 655–72. in History Cooperative
- Ruiz, Vicki L. From Out of the Shadows: Mexican Women in Twentieth-Century America (1998)
- Samora, Julian, and Patricia Vandel Simon, A History of the Mexican-American People (1977) p 100
Pre 1965[edit]
- Bogardus, Emory S. The Mexican in the United States (1934), sociological
- Gamio, Manuel. The Life Story of the Mexican Immigrant (1931)
- Gamio, Manuel. Mexican Immigration to the United States (1939)
- García, Mario T. Mexican Americans: Leadership, Ideology and Identity, 1930–1960 (1989)
- García, Mario T. Desert Immigrants. The Mexicans of El Paso, 1880-1920 (1982) 348 pp; excerpt and text search
- Gomez-Quinones, Juan. Roots of Chicano Politics, 1600-1940 (1994)
- Grebler, Leo, Joan Moore, and Ralph Guzmán. The Mexican American People: The Nation's Second Largest Minority (1970), emphasis on census data and statistics
- MacDonald, Victoria-Maria. Latino Education in the United States: A Narrated History from 1513-2000 (2004)
- Rivas-Rodríguez, Maggie ed. Mexican Americans and World War II (2005)
- Sanchez, George J. Becoming Mexican American: Ethnicity, Culture, and Identity in Chicano Los Angeles, 1900-1945 (1995) excerpt and text search
Culture and politics, post 1965[edit]
- Aranda, José, Jr. When We Arrive: A New Literary History of Mexican America. U. of Arizona Press, 2003. 256 pp.
- Arreola, Daniel D., ed. Hispanic Spaces, Latino Places: Community and Cultural Diversity in Contemporary America. 2004. 334 pp.
- Berg, Charles Ramírez. Latino Images in Film: Stereotypes, Subversion, and Resistance. 2002. 314 pp.
- Branton, Regina. "Latino Attitudes toward Various Areas of Public Policy: The Importance of Acculturation," Political Research Quarterly, Vol. 60, No. 2, 293-303 (2007) Abstract
- Burt, Kenneth C. The Search for a Civic Voice: California Latino Politics, Regina Books, 2007. Excerpts and online search from Amazon.com
- DeGenova, Nicholas and Ramos-Zayas, Ana Y. Latino Crossings: Mexicans, Puerto Ricans, and the Politics of Race and Citizenship. 2003. 257 pp.
- Dolan, Jay P. and Gilberto M. Hinojosa; Mexican Americans and the Catholic Church, 1900-1965 (1994)
- Fregoso, Rosa Linda. The Bronze Screen: Chicana and Chicano Film Culture. (1993) excerpt and text search
- Garcia, Ignacio M. Viva Kennedy: Mexican Americans in Search of Camelot, Texas A&M University Press, 2000. 227pp Excerpts and online search from Amazon.com.
- García, Mario T. Mexican Americans: Leadership, Ideology and Identity, 1930–1960 (1989)
- Gomez-Quinones, Juan. Chicano Politics: Reality and Promise, 1940-1990 (1990)
- Gutiérrez, David G. Walls and Mirrors: Mexican Americans, Mexican Immigrants, and the Politics of Ethnicity in the Southwest, 1910-1986 1995. excerpt and text search
- Hammerback, John C., Richard J. Jensen, and Jose Angel Gutierrez. A War of Words: Chicano Protest in the 1960s and 1970s 1985.
- Kenski, Kate and Tisinger, Russell. "Hispanic Voters in the 2000 and 2004 Presidential General Elections." Presidential Studies Quarterly 2006 36(2): 189–202. Issn: 0360-4918
- Martinez, Juan Francisco. Sea La Luz: The Making of Mexican Protestantism in the American Southwest, 1829-1900 (2006)
- Matovina, Timothy. Guadalupe and Her Faithful: Latino Catholics in San Antonio, from Colonial Origins to the Present. 2005. 232 pp. excerpt and text search
- Meier, Matt S., and Margo Gutierrez, ed. Encyclopedia of the Mexican American Civil Rights Movement (2000) excerpt and text search
- Nuno, S. A. "Latino Mobilization and Vote Choice in the 2000 Presidential Election" American Politics Research, (2007); 35(2): 273 - 293. Abstract
- Saldívar-Hull, Sonia. Feminism on the Border: Chicana Gender Politics and Literature 2000. excerpt and text search
- Wegner, Kyle David, “Children of Aztlán: Mexican American Popular Culture and the Post-Chicano Aesthetic” (PhD dissertation State University of New York, Buffalo, 2006). Order No. DA3213898.
Immigration since 1965[edit]
- Badillo, David A. Latinos and the New Immigrant Church. 2006. 275 pp. excerpt and text search
- Costanza-Chock, Sasha. "The Immigrant Rights Movement on the Net: Between “Web 2.0” and Comunicación Popular," American Quarterly, Volume 60, Number 3, September 2008, pp. 851-864 in Project Muse
- García, María Cristina. Seeking Refuge: Central American Migration to Mexico, The United States, and Canada. (2006) 290pp
- Gutiérrez, David G. Walls and Mirrors: Mexican Americans, Mexican Immigrants, and the Politics of Ethnicity in the Southwest, 1910-1986 1995. excerpt and text search
- Haines, David W., and Karen E. Rosenblum. Illegal Immigration in America: A Reference Handbook (Greenwood Press, 1999) online edition
- Passel, Jeffrey S. "Unauthorized Migrants: Numbers and Characteristics," Pew Hispanic Center Reports and fact Sheets. (June 14, 2005), online
- Sadowski-Smith, Claudia. "Unskilled Labor Migration and the Illegality Spiral: Chinese, European, and Mexican Indocumentados in the United States, 1882–2007," American Quarterly, Volume 60, Number 3, September 2008, pp. 779–804 in Project Muse
Regional and Local[edit]
California[edit]
- Hubert Howe Bancroft. The Works of Hubert Howe Bancroft,
- Bedolla, Lisa García. Fluid Borders: Latino Power, Identity, and Politics in Los Angeles. 2005. 279 pp.
- Burt, Kenneth C. The Search for a Civic Voice: California Latino Politics (2007) excerpt and text search
- Camarillo, Albert. Chicanos in a Changing Society: From Mexican Pueblos to American Barrios in Santa Barbara and Southern California, 1848–1930 (1979)
- Camarillo, Albert M., “Cities of Color: The New Racial Frontier in California’s Minority-Majority Cities,” Pacific Historical Review, 76 (Feb. 2007), 1–28; looks at cities of Compton, East Palo Alto, and Seaside
- Daniel, Cletus E. Bitter Harvest: A History of California Farmworkers, 1870-1941 1981.
- García, Matt. A World of Its Own: Race, Labor, and Citrus in the Making of Greater Los Angeles, 1900-1970 (2001)
- Gutierrez, Ramon A., and Patricia Zavella, eds. Mexicans in California: Transformations and Challenges essays by leading scholars (2009)
- Hayes-Bautista, David E. La Nueva California: Latinos in the Golden State. (2004). 263 pp. excerpt and text search
- Hughes, Charles. "The Decline of the Californios: The Case of San Diego, 1846-1856" The Journal of San Diego History Summer 1975, Volume 21, Number 3 online at [3]
- McWilliams, Carey. North from Mexico. (1949), farm workers in California
- Pitt, Leonard. The Decline of the Californios: A Social History of the Spanish-Speaking Californians, 1846-1890 (ISBN 0-520-01637-8)
- Sánchez; George J. Becoming Mexican American: Ethnicity, Culture, and Identity in Chicano Los Angeles, 1900-1945 (1993) excerpt and text search
- Valle, Victor M. and Torres, Rodolfo D. Latino Metropolis. 2000. 249 pp. on Los Angeles
Texas and Southwest[edit]
- Alonzo, Armando C. Tejano Legacy: Rancheros and Settlers in South Texas, 1734-1900 (1998)
- Hubert Howe Bancroft. The Works of Hubert Howe Bancroft,
- Blackwelder, Julia Kirk. Women of the Depression: Caste and Culture in San Antonio 1984. excerpt and text search
- Buitron Jr., Richard A. The Quest for Tejano Identity in San Antonio, Texas, 1913-2000 (2004) excerpt and text search
- Chávez, John R. The Lost Land: The Chicano Image of the Southwest (Albuquerque, 1984)
- Chávez-García, Miroslava. Negotiating Conquest: Gender and Power in California, 1770s to 1880s (2004).
- De León, Arnoldo. They Called Them Greasers: Anglo Attitudes toward Mexicans in Texas, 1821–1900 (Austin, 1983)
- De León, Arnoldo. Mexican Americans in Texas: A Brief History, 2nd ed. (1999)
- Deutsch, Sarah No Separate Refuge: Culture, Class, and Gender on the Anglo-Hispanic Frontier in the American Southwest, 1880-1940 1987
- Dysart, Jane. "Mexican Women in San Antonio, 1830-1860: The Assimilation Process" Western Historical Quarterly 7 (October 1976): 365-375. in JSTOR
- Echeverría, Darius V., “Aztlán Arizona: Abuses, Awareness, Animosity, and Activism amid Mexican-Americans, 1968–1978” PhD dissertation (Temple University, 2006). Order No. DA3211867.
- Fregoso; Rosa Linda. Mexicana Encounters: The Making of Social Identities on the Borderlands (2003)
- García, Richard A. Rise of the Mexican American Middle Class: San Antonio, 1929-1941 1991
- Getz; Lynne Marie. Schools of Their Own: The Education of Hispanos in New Mexico, 1850-1940 (1997)
- Gómez-Quiñones, Juan. Roots of Chicano Politics, 1600-1940 (1994)
- Gonzales-Berry, Erlinda, David R. Maciel, editors, The Contested Homeland: A Chicano History of New Mexico, 314 pages (2000), ISBN 0-8263-2199-2
- González; Nancie L. The Spanish-Americans of New Mexico: A Heritage of Pride (1969)
- Guglielmo, Thomas A. "Fighting for Caucasian Rights: Mexicans, Mexican Americans, and the Transnational Struggle for Civil Rights in World War II Texas," Journal of American History, 92 (March 2006) in History Cooperative
- Gutiérrez; Ramón A. When Jesus Came, the Corn Mothers Went Away: Marriage, Sexuality, and Power in New Mexico, 1500-1846 (1991)
- Handbook of Texas History Online
- Márquez, Benjamin. LULAC: The Evolution of a Mexican American Political Organization (1993)
- Matovina, Timothy M. Tejano Religion and Ethnicity, San Antonio, 1821-1860 (1995)
- Montejano, David. Anglos and Mexicans in the Making of Texas, 1836-1986 (1987)
- Muñoz, Laura K., “Desert Dreams: Mexican American Education in Arizona, 1870–1930” (PhD dissertation Arizona State University, 2006). Order No. DA3210182.
- Quintanilla, Linda J., “Chicana Activists of Austin and Houston, Texas: A Historical Analysis” (University of Houston, 2005). Order No. DA3195964.
- Sánchez; George I. Forgotten People: A Study of New Mexicans (1940; reprint 1996) on New Mexico
- Taylor, Paul S. Mexican Labor in the United States. 2 vols. 1930-1932, on Texas
- Stewart, Kenneth L., and Arnoldo De León. Not Room Enough: Mexicans, Anglos, and Socioeconomic Change in Texas, 1850-1900 (1993)
- de la Teja, Jesús F. San Antonio de Béxar: A Community on New Spain's Northern Frontier (1995).
- Tijerina, Andrés. Tejanos and Texas under the Mexican Flag, 1821-1836 (1994),
- Tijerina, Andrés. Tejano Empire: Life on the South Texas Ranchos (1998).
- Timmons, W. H. El Paso: A Borderlands History (1990).
- Trevino, Roberto R. The Church in the Barrio: Mexican American Ethno-Catholicism in Houston. (2006). 308pp.
- Weber, David J. The Mexican Frontier, 1821-1846: The American Southwest under Mexico (1982) in ACLS e-book
- Garcia, Richard A. "Changing Chicano Historiography," Reviews in American History 34.4 (2006) 521-528 in Project Muse
Other regions[edit]
- Bullock, Charles S., III and Hood, M. V., III. "A Mile-wide Gap: the Evolution of Hispanic Political Emergence in the Deep South." Social Science Quarterly 2006 87(special Issue): 1117-1135. Issn: 0038-4941 Fulltext: in Blackwell Synergy
- García, María Cristina. Havana, USA: Cuban Exiles and Cuban Americans in South Florida, 1959–1994 (1996); excerpt and text search
- Korrol, Virginia Sánchez. From Colonia to Community: The History of Puerto Ricans in New York City, 1917–1948 (1994)
- Millard, Ann V. and Chapa, Jorge. Apple Pie and Enchiladas: Latino Newcomers in the Rural Midwest. 2004. 276 pp. excerpt and text search
- Murphy, Arthur D., Colleen Blanchard, and Jennifer A. Hill, eds. Latino Workers in the Contemporary South. 2001. 224 pp.
- Padilla, Felix M. Puerto Rican Chicago. (1987). 277 pp.
- Sãnchez Korrol, Virginia E. From Colonia to Community: The History of Puerto Ricans in New York City. (1994) complete text online free in California; excerpt and text search
- Vargas, Zaragosa. Proletarians of the North: A History of Mexican Industrial Workers in Detroit and the Midwest, 1917-1933 (1993) complete text online free in California; excerpt and text search
- Weise, Julie M. "Mexican Nationalisms, Southern Racisms: Mexicans and Mexican Americans in the U.S. South, 1908–1939," American Quarterly, Volume 60, Number 3, September 2008, pp. 749–777 in Project Muse
- Whalen, Carmen Teresa, and Victor Vásquez-Hernández, eds. The Puerto Rican Diaspora: Historical Perspectives (2005),
 KSF
KSF