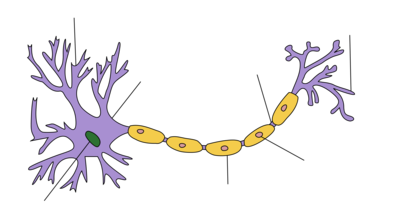
Neuron
 From Conservapedia - Reading time: 1 min
From Conservapedia - Reading time: 1 min
References[edit]
- Martin, JH (2003). Neuroanatomy text and atlas 3rd ed., New York: McGraw-Hill.
- Kandel, ER; Schwartz JH, Jessell TM (2000). Principles of Neural Science, 4th ed., New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-8385-7701-6.
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://www.conservapedia.com/Neuron26 views | Status: cached on March 06 2023 11:35:03↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF