4C-ID
 From EduTechWiki - Reading time: 5 min
From EduTechWiki - Reading time: 5 min
Definition[edit | edit source]
- 4C/ID is an instructional design model by van Merriënboer and others.
- "4C" means "four components", "ID" means "Instructional Design". It also can be found in Merrill's first principles of instruction.
- According to Martin Ryder, the The 4C-ID instructional model is characterized by four components: (1) Learning Tasks, (2) Supportive Information, (3) Procedural Information and (4) Part-Task Practice. The tasks are ordered by task difficulty and each task offers at the beginning a lot of scaffolding which is reduced as the learner progresses.
See also: Elaboration theory (a much earlier model from Reigeluth).
The design[edit | edit source]
4C/ID is what I call a "main-stream" Instructional Design Model that addresses the issue of how to teach complex skills, i.e. solid know-how that can be applied to real problem problems.
According to Merriënboer et al. (2002): “The 4C/ID-model [....] addresses at least three deficits in previous instructional design models. First, the 4C/ID-model focuses on the integration and coordinated performance of task-specific constituent skills rather than on knowledge types, context or presentation-delivery media. Second, the model makes a critical distinction between supportive information and required just-in-time (JIT) information (the latter specifies the performance required, not only the type of knowledge required). And third, traditional models use either part-task or whole-task practice; the 4C/IDmodel recommends a mixture where part-task practice supports very complex, "whole-task" learning.”
According to Merrill (2002:56), the model is clearly problem-based although not in the sense of typical problem-based learning models. “At the heart of this training strategy is whole-task practice, in which more and more complex versions of the whole complex cognitive skill are practiced. In ... the analysis phase ... the skill is decomposed in a hierarchy of constituent skills; ... classified as recurrent constituent skills, which require more-or-less consistent performance over problem situations, or nonrecurrent constituent skills, which require highly variable performance over situations" (p. 8). "While learners practice simple to complex versions of a whole task, instructional methods that promote just-intime information presentation are used to support the recurrent aspects of the whole task while, at the same time, instructional methods that promote elaboration are used to support the non-recurrent aspects of the task" (p. 10).”
The four components are described in detail in Merrienboer (2002) and from which this picture is taken:
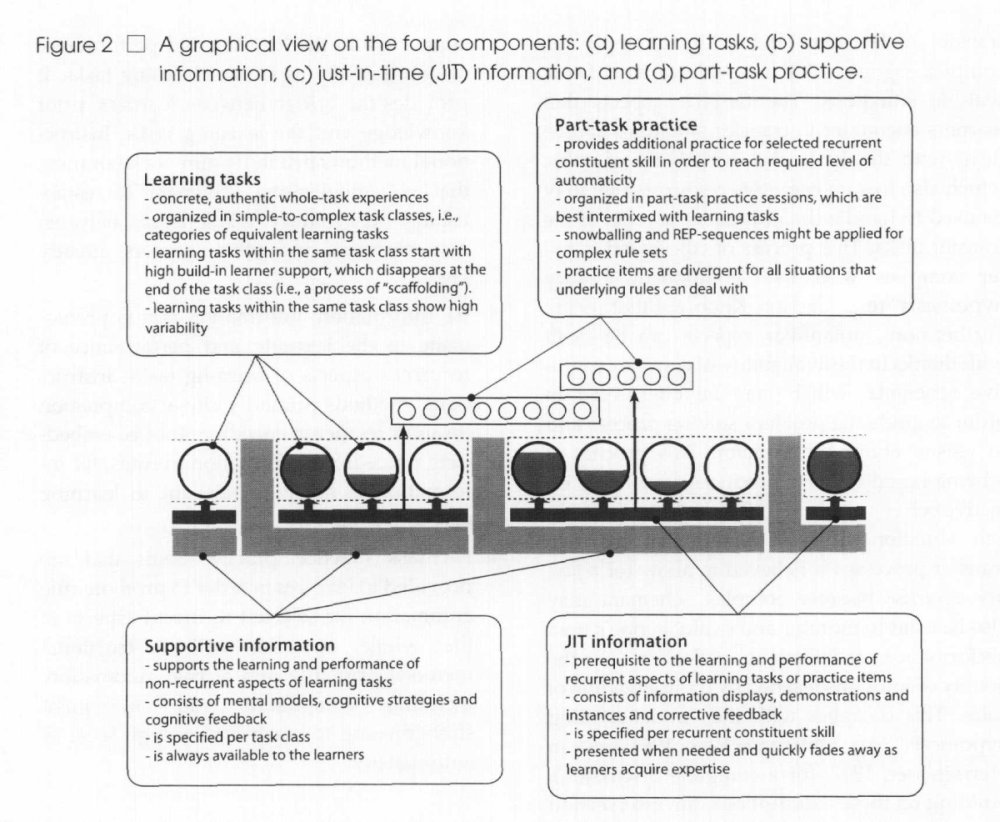
Some features of 4C/ID[edit | edit source]
This section are made from notes taken during a van Merriënboer keynote talk on March 14 2013.
4C/ID can be described as a method that will describe the backbone of a curriculum where each element is connected and does have a function with respect to the whole. It addresses two problems:
- Students can't apply "knowledge"
- Students and life-long learners are not self-directed learners
There is research-based evidence that transfer is improved when using a 4C/ID design.
Learning tasks[edit | edit source]
Create a "spiraled2 sequence of tasks, based on induction
- Provide variability in each task
- Provide task classes i.e. sequences of easy to difficult tasks. Each task should be meaningful right from the start. Make sure to offer several variants for each class, i.e. a series of task that address the same learning outcomes at same difficulty level.
- Provide guidance: Scaffolding should be provided in each task. However, for task set, define a Zone of proximal development using a sawtooth pattern: First task in a class uses a lot of support, last task in a class should have no support. If learners are successful, then move them to a higher level.
- Typical learning technologies for task support: Simulated/real task environments and development portfolios
Supportive information[edit | edit source]
Is information that helps learnings getting the tasks done. It shows how the domain is organized (e.g. anatomy in medicine) and shows how to approach a task. Design of supportive information is based on knowledge elaboration and is linked to all tasks in a given class. An other class may require more simple or more difficult information.
- Can be provided before (tell "theory") or during a task sequence (typically in project-oriented designs)
- "What should I study in order to be able to....." (self-directed learners)
- Typical learning technologies: Hypermedia and Internet in General
Procedural information[edit | edit source]
Refers to knowledge needed to solve parts of the task. Based on knowledge compilation and may require drill and practise (see next item)
- Routine aspects
- How-to information that is used "just-in-time"
Part-task practice[edit | edit source]
Based on strengthening
- Repetition and drill
- However, part-time practice should only be presented within a cognitive context, i.e. a whole task
- Sometimes more practice is needed for procedure learning
Use of simulation, real tasks and video[edit | edit source]
This section are made from notes taken during a van Merriënboer keynote talk on March 14 2013. 4C/ID also can be used as model for vocational training
Merriënboer presented three projects from which we point out a few highlights:
(1) STEP portfolio project with hairdressers.
Steps:
- Simulation in school
- Select and do a task in the work context
- Fill in a portfolio page that includes an evaluation grid, i.e. collect assessment information on each task
- Coaching meeting in regular intervals (e.g. once per week) with the teacher
Positive:
- Both students and teachers like
Negative:
- Teacher's complain about missing time (e.g. time for coaching meetings)
A mobile app project called "PERFECT" tries to implement a self-coaching approach.
(2) Care Village project, targeting nursing education:
- Web application
- Provides tasks to complete in various contexts
- A task describes a patient first, then defines 2 tasks one for the school and one for the workplace
- Again, all tasks can be scored in a portfolio
(3) CRAFT - Mechatronics project:
- Serious game
- In the virtual world, simulated machines can be explored
- In a virtual workplace, parts are made and then integrated into an attraction park
- In the real workplace, parts are made and the student can obtained credits for the game
Implementation[edit | edit source]
How to implement a 4C/ID design:
Work with a team:
- more than one teacher
- professionals (of the subject area)
- one or more students
- Media/technology specialists if needed
... i.e. have all stakeholders participate
Cost-effectiveness is an issue, ... being investigated now.
References[edit | edit source]
- Merrill, David, First Principles of Instruction, ETR&D, Vol. 50, No. 3, 2002, pp. 43-59 ISSN 1042-1629. Preprint version
- van Merriënboer, J.J.G (1997). Training complex cognitive skills: A four-component instructional design model for technical training. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Educational Technology Publications
- van Merriënboer, Jeroen.J.G, Richard E Clark, Marcel B M de Croock, (2002) Blueprints for complex learning: The 4C/ID-model, Educational Technology, Research and Development. 50 (2);39-64, DOI: 0.1007/BF02504993, Abstract/PDF (Access restricted).
- Frederick Kwaku Sarfo & Jan Elen, Powerful Learning Environments and the Development of Technical Expertise in Ghana: Investigating the Moderating Effect of Instructional Conceptions, IEEE Explore, ??? PDF
- van Merriënboer, J.J.G & Kirshner, P. (2007). Ten Steps to Complex Learning. Erlbaum.
 KSF
KSF