Methodology tutorial - conceptual frameworks
 From EduTechWiki - Reading time: 8 min
From EduTechWiki - Reading time: 8 min
This is part of the methodology tutorial (see its table of contents).
Introduction[edit | edit source]
- Learning goals
- Get inspiration from some examples
- Prerequisites
- Moving on
- Methodology tutorial - theory-driven research designs
- Methodology tutorial - theory-finding research designs
- Methodology tutorial - design-oriented research designs
- Level and target population
- This module is really optional. It complements the more systematic prerequisite.
- Quality
- Low, it's just a list of examples. Some stuff will have to be translated too.
It's good to work with some central conceptual artefacts. In this tutorial we present three types with a few examples.
- (1) Analytical frameworks
- Provide an overview of the phenomenon (elements and relations)
- Help to bridge the gap between theory and empirical research
- Direct analysis (e.g. what causalities to look at, what’s of interest, etc.)
- (2) Lists of dimensions
- Help to focus on all aspects of a concept
- (3) Analysis grids
- Help to organize data gathering and collection
- Will bridge the gap between general concepts at theory level (e.g. your research questions) and measurable indicators
Example frameworks[edit | edit source]
The inquiry circle in inquiry-based learning doctrine[edit | edit source]
Inquiry learning combines more radical open-ended socio-constructivist principles (discovery learning) with a model of guidance. As opposed to learning design, most inquiry-based models do advocate opportunistic (i.e. adaptive) planning by the teacher. However, there are many different ways to think about inquiry learning. A picture that shows the central concept can help. The example below was made by "Chip" Bruce et al.

This picture
- clearly identifies 5 elements of inquiry
- claims/shows that inquiry is circular
In other words, such a drawing both identifies important elements of a pedagogical scenario and it shows relations, the dynamics, etc.
Gonzalez 8-factor model for ICT usage in schools[edit | edit source]
Related to studies on teacher development, transformative pedagogy, etc.
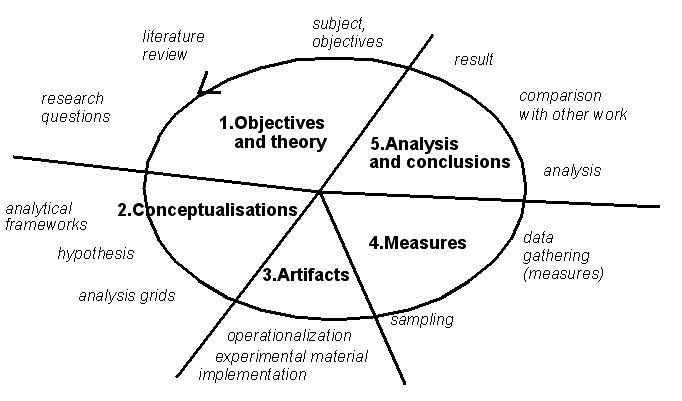
A linear model of research[edit | edit source]
Even this tutorial has a analytical organizing framework :)
Again, such a model does not exactly describe reality. A model (in the general sense of a conceptual framework) should rather be considered as a language that helps to look at a given set of phenomenons (and also to manipulate things). Research is much more unorderly than what we teach it to be ...
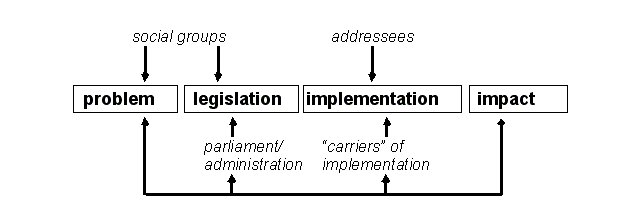
Implementation research model[edit | edit source]
Provides a certain "image" of the policy-making process:
- Actors intervene during the whole process (and not just in their "natural" stage"
- Problem perception, goals and other elements can be changed over time, i.e. sometimes the implementors may redefine the set goals !
Possible relevance for educational technologies: The fact that a government agency has been created to sponsor ICT-based pedagogical reform, does not entail that it will happen as they plan. Implementation "carriers" (e.g. schools) and addressees (e.g. teachers) may redefine goals and will have to establish operational practise.
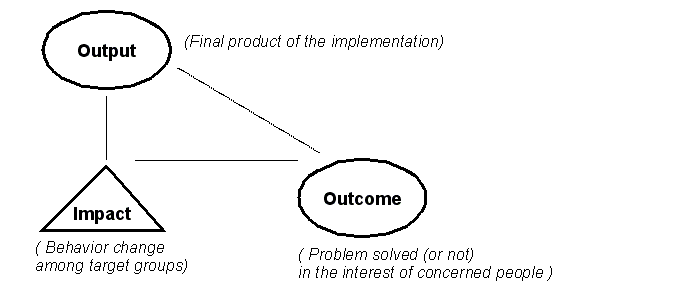
Policy outcomes[edit | edit source]
This drawing defines how to define "policy outcome":
- It could be useful to provide a perspective on the analysis of educational reform policies
- There are three major kinds of "results" you can study according to the author.
Source: Définition des prestations au sens de produits finaux de mise en oeuvre d’une politique publique [Knoepfel, P. (1996) TQM et fédéralisme, Cahier de l’IDHEAP, 159, p 10]
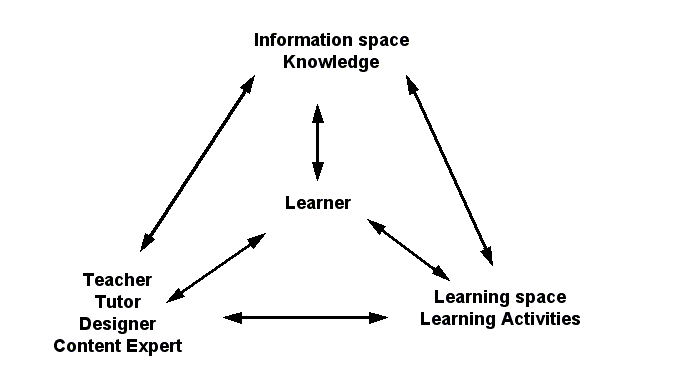
Functions of a learning environment: Where do we focus ?[edit | edit source]
- This model makes you think about functions that a learning environment should provide
and therefore about structure that will instantiate function
- It also allows to think about priorities in your design
- E.g. teacher role is central in activity-based designs
- E.g. Learning material is important in e-learning designs for mass-education
See learning environment and follow up the links for more information.
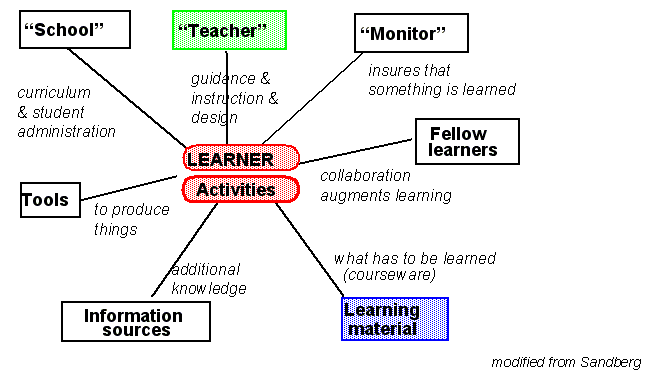
A simple picture defining key elements of an ICT design[edit | edit source]
This is not a great model, but it makes you think about the distinction between learning activities, informations (learning material) and people involved.
It also expresses a instructional design stance that can be found in the learning design community.
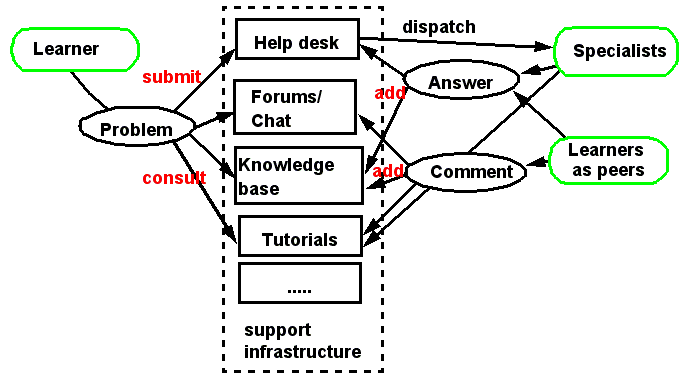
A "help desk model" for "on-the-spot" life-long learning[edit | edit source]
This model allows you to think at the same time about system components and actor’s roles. It also summarizes a kind of instructional design model
Technical infrastructure used: either C3MS portals, groupware, specialized help desk, knowledge management software.
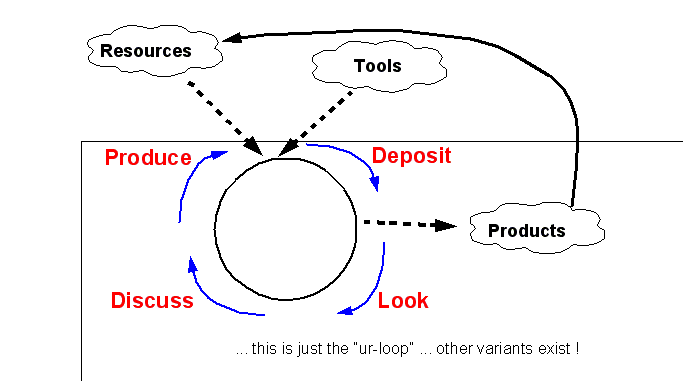
My favorite picture for introducing activity-based teaching[edit | edit source]
This figure defines scenarios as sequences of activity phases within which group members do tasks and play specific roles. That kind of orchestration implies organizing workflow loops.
Such a framework clearly shows that students have to engage in activities, that activities lead to products that can be discussed and reused. Read more in project-oriented learning and follow up the links or pick a random model from the category of project-oriented instructional designs
Definition of a C3MS (community) portal (Schneider)[edit | edit source]
|
Function |
C3MS modules (tools of the portal) |
|---|---|
|
Content management |
News engine (including a organization by topics and an annotation mechanism) - Content Management Systems (CMS)Collaborative hypertexts (Wikis) - Image albums (photos, drawings, etc.) - Glossary tool or similar - Individual weblogs (diaries) |
|
Knowledge exchange |
News syndication (headlines from other portals)File sharing(all CMS tools above) |
|
Exchange of arguments |
Forums and/or new News engine, Chats, ...... |
|
Project support |
Project management modules,Calendars, ...... |
|
Knowledge management |
FAQ manager - Links Manager (“Yahoo-like”)Search by keywords for all contents“top 10” box, rating systems for comments“What’s new” (forum messages, downloads, etc.), ..... |
|
Community management |
Presence, profile and identification of members, Shoutbox (mini-chat integrated into the portal page)Reputation system, Activity tracing for members, Event calendar, News engine, ...... |
This table provides associations between a list of functions and structure (software modules) that a teacher could use to support a project-based learning design.
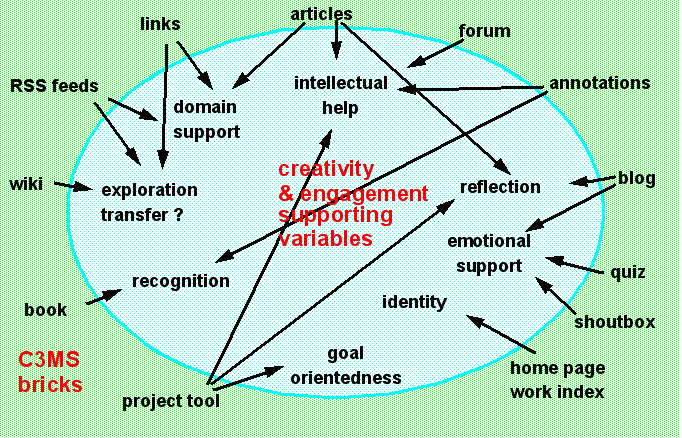
C3MS modules support for creativity and engagement variables[edit | edit source]
This figure makes the claim that using portalware or similar web 2.0 software like webtops are good to support creativity and engagement.
It links structure (software elements) to functions (creativity and engagement enhancing variables). Of course it also needs an appropriate instructional design...
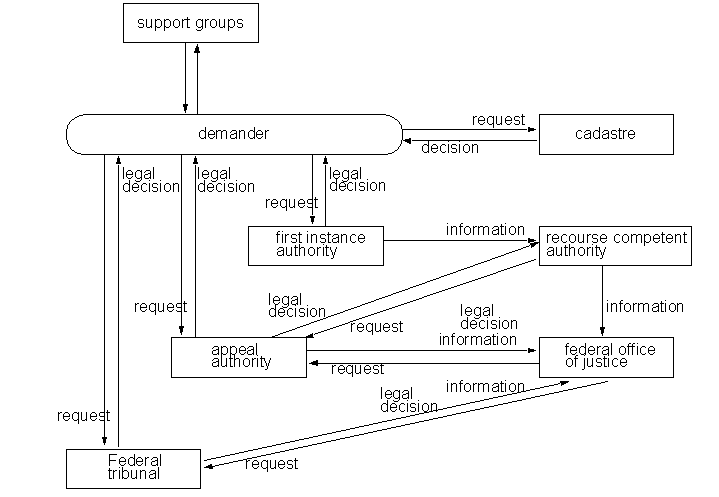
Visualization of formal procedures[edit | edit source]
This figure provides an overview of formal procedures defined in a law.
See also: UML, e.g. UML activity diagram for a design language used in Computer science.
Lists of dimensions and typologies[edit | edit source]
As you (hopefully) learned in then methodology tutorial - empirical research principles, it is important that you split high-level concepts into components.
Types of Learning (Kearsley’s http://tip.psychology.org/ )[edit | edit source]
- Attitudes : Disposition or tendency to respond positively or negatively ....
- Factual Information (memorization): Processing of factual information and remembering .....
- Concepts (discrimination): ... how to discriminate and categorize things. Concept mastery is not related to simple recall and must be constructed.
- Reasoning (inference, deduction): thinking activities that involve making or testing inferences
- Procedure learning: .... being able to solve a certain task by applying a procedure.
- Problem solving : identification of subgoals, use of methods to satisfy subgoals.
- Learning strategies : .... can hardly be taught and only be learned through appropriate experience and to some extent only !
Read more in learning type and learning level if you wish.
Major pedagogical approaches (strategies)[edit | edit source]
A table of pedagogical approaches may help you to decide what sort of teaching and learning you want to study or favor with an ICT-based environment
| Transfer | Tutor | Coach |
|---|---|---|
| Factual knowledge, know-that |
Procedural knowledge, know-how |
Social practise, knowing-in-action |
| Transfer of propositional knowledge | Presentation of predetermined problems | Action in (complex and social) situations |
| to know, to remember | to do, to practise | to cope, to master |
| Production of correct answers | Selection of correct methods and its use | Realization of adequate action strategies |
| Verbal knowledge, Memorization | Skill, Ability | Social Responsibility |
| to teach, to explain | to observe, to help,to demonstrate | to cooperate, to support |
| Teaching I | Teaching II | Teaching III |
Read more in in pedagogic strategy and instructional design model
Source: Baumgartner & Kalz, modifications by Schneider
Khan’s (2000) list of pedagogical methods and strategies[edit | edit source]
| Presentation | Exhibits |
| Demonstration | Drill and Practice |
| Tutorials | Games |
| Story Telling | Simulations |
| Role-playing | Discussion |
| Interaction | Modeling |
| Facilitation | Collaboration |
| Debate | Field Trips |
| Apprenticeship | Case Studies |
| Generative Development | Motivation |
Makes you worry a bit: Which pedagogical strategies work better for what types of learning ? Read more in pedagogic method.
Intrinsically motivating elements of gaming ...[edit | edit source]
The following table almost represents a theory:
- What could we learn from gaming ?
- Why do kids spend many hours playing games without getting bored or tired ?
| Element | |
|---|---|
| fantasy | triggers imagination and implies freedom (make believe + voluntary activity) |
| challenge &curiosity | games aim at a level of difficulty that triggers curiosity
|
| feedback | is immediate and clear (i.e. useful) |
| self-esteem | is achieved through adapted tasks provides encouragement to learn & augment scores |
| control | is implement through levels to play, user selection of goals, strategies & tactics |
Source: Frété 2002, Master thesis TECFA
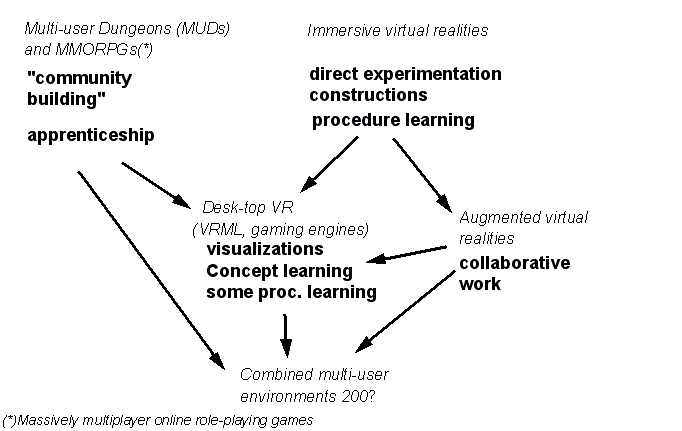
Typology and typical functions of virtual environments[edit | edit source]
This figure makes explicit what someone means by "virtual environment"
Is is safe to use the word "virtual environment" when you talk about an e-learning platform ? Daniel K. Schneider doesn't think so, since and LMS is not a virtual world, rather a CMC and content-delivery tool.
Computer supported collaborative learning[edit | edit source]
This picture makes the claim that collaborative learning can be very powerful because its properties engage students in various meta-cognitive activities.
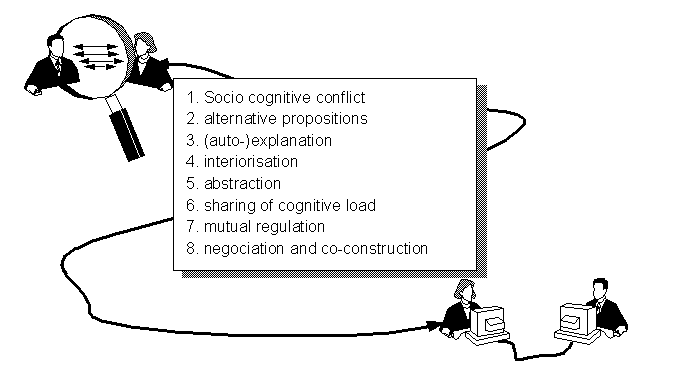
Source: Pierre Dillenbourg. Notice: Collaborative learning needs scenario-building (story-boarding), read CSCL script for more.
Example analysis grids[edit | edit source]
More grids (scales) are shown in quantitative design and analysis modules
Ergonomics criteria de Bastien[edit | edit source]
This is a check list for studying the ergonomics of a software or other artifact.
1. Guidage 1.1 Incitation 1.2 Groupement/Distinction entre items 1.2.1 Groupement/Distinction par la localisation 1.2.2 Groupement/Distinction par le format 1.3 Feed-back immédiat 1.4 Lisibilité 2. Charge de travail 2.1 Brièveté 2.1.1 Concision 2.1.2 Actions minimales 2.2 Densité informationnelle 3. Contrôle explicite 3.1 Actions explicites 3.2 Contrôle utilisateur |
4. Adaptabilité 4.1 Flexibilité 4.2 Prise en compte de l'expérience de l'utilisateur 5.Gestion des erreurs 5.1 Protection contre les erreurs 5.2 Qualité des messages d'erreur 5.3 Correction des erreurs 6. Homogénéité/Cohérence 7. Signifiance des codes et dénominations 8. Compatibilité |
Source: http://www.lergonome.org/pages/detail_articles.php?indice=22
Profil des compétences d’un manager (dimensions)[edit | edit source]
Emery, Y. (1997) Le centre d’évaluation pour managers publics, Cahier de l’IDHEAP 166, p9.
A. compétences personnelles:
- introspection et apprentissage permanent
- résistance aux tensions, énergie et ténacité
B. compétences intellectuelles:
- pensée systémique, capacité d’analyse et de synthèse
C. compétences relationnelles:
- leadership et de gestion de groupe
- capacité d’écoute et de communication
D. compétences managériales:
- attention à l’environnement et proactivité
- entrepreneurship et esprit de décision
- planification et controlling
Sur 4 pages l’auteur indique ensuite les sous-dimensions et ensuite comment les mesurer par des dispositifs expérimentaux variés....
COLLES Grid - socio-constructivist features of on-line teaching[edit | edit source]
(Taylor and Maor ) - Teacher education over the Internet
1. Relevance
- How relevant is on-line learning to students' professional practices?
2. Reflection
- Does on-line learning stimulate students' critical reflective thinking?
3. Interactivity
- To what extent do students engage on-line in rich educative dialogue?
4. Tutor Support
- How well do tutors enable students to participate in on-line learning?
5. Peer Support
- Is sensitive and encouraging support provided on-line by fellow students?
6. Interpretation
- Do students and tutors make good sense of each other's on-line communications?
Remarks:
- This grid clearly identifies 6 dimensions of socio-constructivism (there are many other grids)
- We will see in the data gathering and analysis modules how to make it operational
 KSF
KSF