As a service
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 15 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 15 min
"X as a service" (rendered as *aaS in acronyms) is a phrasal template for any business model in which a product use is offered as a subscription-based service rather than as an artifact owned and maintained by the customer. Originating from the software as a service concept that appeared in the 2010s with the advent of cloud computing,[1][2] the template has expanded to numerous offerings in the field of information technology and beyond it. The term XaaS can mean "anything as a service".[lower-alpha 1]
The following is an alphabetical list of business models named in this way, including certain forms of cybercrime (criminal business models).
B
Backend as a service (BaaS)
Banking as a service (BaaS)

Blockchain as a service (BaaS)
C
Content as a service (CaaS)
D
Data as a service (DaaS)
Database as a service (DBaaS)
With a database as a service model (DBaaS), users pay fees to a cloud provider for services and computing resources, reducing the amount of money and effort needed to develop and manage databases.[19] Users are given tools to create and manage database instances, and control users. Some cloud providers also offer tools to manage database structures and data.[20] Many cloud providers offer both relational (Amazon RDS, SQL Server) and NoSQL (MongoDB, Amazon DynamoDB) databases.[20] This is a type of software as a service (SaaS).
Data management as a service (DMaaS)
Data management can also be done through the "as a service" business model, according to the book Data Management as a Service for Dummies.[21]
Desktop as a service (DaaS)
E
Energy storage as a service (ESaaS)
Exploit as a service (EaaS)
Exploit as a service (EaaS) is a scheme of cybercriminals whereby zero-day vulnerabilities are leased to hackers.[22] EaaS is typically offered as a cloud service.[23] By the end of 2021, EaaS became more of a trend among ransomware groups.[24]
In the past, zero-day vulnerabilities were often sold on the dark web, but this was usually at very high prices, millions of US dollars per zero-day.[25] A leasing model makes such vulnerabilities more affordable for many hackers.[26] Even if such zero-day vulnerabilities will later be sold at high prices, they can be leased for some time.[27]Other "EaaS" business models
Under the acronym EaaS, the following business models have been discussed in journals and conferences:
- Edge as a service[28]
- Encryption as a service[29]
- Energy as a service[30]
- Evaluation as a service[31]
F
Function as a service (FaaS)
G
Games as a service (GaaS)
I
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
Integration platform as a service (IPaaS)
IT as a service (ITaaS)
K
Knowledge as a service (KaaS)
L
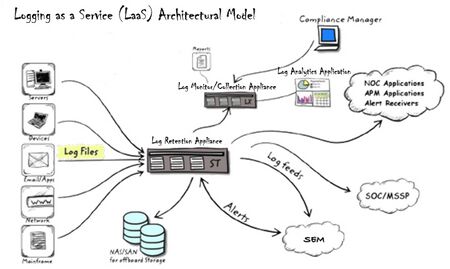
Logging as a service (LaaS)
Lighting as a service (LaaS)
M
Mobility as a service (MaaS)
Monitoring as a service (MaaS)
N
Network as a service (NaaS)
P
Payments as a service (PaaS)
Philanthropy as a service (PHaaS)
Platform as a service (PaaS)
R
Ransomware as a service (RaaS)
thumb
Ransomware as a service (RaaS) is a cybercrime business model, allowing ransomware developers to write and sell harmful code or malware to other hackers, often known as affiliates, for their own initiation of ransomware attacks through the use of their software.[45] Affiliates typically do not need to have any technical skills of their own but can solely rely on the technical skills of their operators. They provide attackers with easier entry for those who may not have skills to develop their own tools, but rather be able to utilize and manage ready-made tools to perform attacks. Most of the time they involve some type of arrangement between the affiliate and the operator, making successful ransomware and extortion attacks profitable for both parties.[46]Recovery as a service (RaaS)
Recovery as a service (RaaS),[47] sometimes referred to as disaster recovery as a service (DRaaS), is a category of cloud computing used for protecting an application or data from a natural or human disaster or service disruption at one location by enabling a full recovery in the cloud. RaaS differs from cloud-based backup services by protecting data and providing standby computing capacity on demand to facilitate more rapid application recovery. RaaS capacity is delivered in a cloud-computing model so recovery resources are only paid for when they are used, making it more efficient than a traditional disaster recovery warm site or hot site where the recovery resources must be running at all times.
The term "recovery as a service" (RaaS) is considered to be part of the nomenclature of cloud computing, along with infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and software as a service (SaaS).[48]Robot as a service (RaaS)
S
Search as a service (SaaS)
Security as a service (SECaaS)
Software as a service (SaaS)
See also
- Cloud computing § Service models
- "Windows as a service", Microsoft's attempt to apply the SaaS model to their operating system
Notes
References
- ↑ "What is XaaS (Anything as a Service)?". 12 August 2022. https://www.techtarget.com/searchcloudcomputing/definition/XaaS-anything-as-a-service.
- ↑ Robin Hastings, Making the Most of the Cloud: How to Choose and Implement the Best Services (2013), p. 3.
- ↑ Duan, Yucong; Fu, Guohua; Zhou, Nianjun (2015). "Everything as a Service(XaaS) on the Cloud: Origins, Current and Future Trends". IEEE 8th International Conference on Cloud Computing. IEEE Computer Society. pp. 621–628. doi:10.1109/CLOUD.2015.88. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/308817450.
- ↑ Monroe, Martin. "The Gospel of MBaaS (Part 1 of 2)". InfoQ. http://www.infoq.com/news/2013/05/MBaaS-Anypresence.
- ↑ Monroe, Martin. "The Gospel of MBaaS (Part 2)". InfoQ. http://www.infoq.com/news/2013/05/MBaas-Anypresence-Mendis.
- ↑ Lane, Kin (3 June 2012). "Rise of Mobile Backend as a Service (MBaaS) API Stacks". API Evangelist. http://apievangelist.com/2012/06/03/rise-of-mobile-backend-as-a-service-mbaas-api-stacks/.
- ↑ Carney, Michael. "AnyPresence partners with Heroku to beef up its enterprise mBaaS offering". PandoDaily. http://pandodaily.com/2013/06/24/anypresence-partners-with-heroku-to-beef-up-its-enterprise-mbaas-offering/.
- ↑ Williams, Alex (11 October 2012). "Kii Cloud Opens Doors For Mobile Developer Platform With 25 Million End Users". TechCrunch. https://techcrunch.com/2012/10/11/kii-cloud-opens-doors-for-mobile-developer-platform-with-25-million-end-users/.
- ↑ Tan, Aaron (30 September 2012). "FatFractal ups the ante in backend-as-a-service market". Techgoondu.com. http://www.techgoondu.com/2012/09/30/fatfractal-ups-the-ante-in-backend-as-a-service/.
- ↑ Rowinski, Dan (9 November 2011). "Mobile Backend As A Service Parse Raises $5.5 Million in Series A Funding". ReadWrite. http://readwrite.com/2011/11/09/mobile-backend-as-a-service-pa.
- ↑ Mishra, Pankaj (7 January 2014). "MobStac Raises $2 Million In Series B To Help Brands Leverage Mobile Commerce". TechCrunch. https://techcrunch.com/2014/01/07/mobstac-raises-2-million-in-series-b-to-help-brands-leverage-mobile-commerce/.
- ↑ Scholten, Ulrich. "Banking-as-a-Service - what you need to know". VentureSkies. http://www.ventureskies.com/blog/banking-as-a-service-categorizing-the-services. Retrieved 25 December 2016.
- ↑ Baalamurugan, K. M.; Kumar, S. Rakesh; Kumar, Abhishek; Kumar, Vishal; Padmanaban, Sanjeevikumar (2021-08-12) (in en). Blockchain Security in Cloud Computing. Springer Nature. ISBN 978-3-030-70501-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=V1w9EAAAQBAJ&q=Blockchain+as+a+Service.
- ↑ Grant, Mitchell; Kenton, Will. "Understanding Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)" (in en). https://www.investopedia.com/terms/s/software-as-a-service-saas.asp.
- ↑ Frankenfield, Jake. "Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS)" (in en). https://www.investopedia.com/terms/b/blockchainasaservice-baas.asp.
- ↑ Machan, Dyan (August 19, 2009). "DaaS:The New Information Goldmine". Wall Street Journal. https://www.wsj.com/articles/SB125071202052143965. "Unfortunately, the business world has given this baby a jargony name: data as a service, or its diminutive, DaaS."
- ↑ Olson, John A. (January 2010). "Data as a Service: Are We in the Clouds?". Journal of Map & Geography Libraries 6 (1): 76–78. doi:10.1080/15420350903432739.
- ↑ Dyche, Jill. "Data-as-a-service, explained and defined". SearchDataManagement.com. http://searchdatamanagement.techtarget.com/answer/Data-as-a-service-explained-and-defined.
- ↑ Chao, Lee (2014). Cloud database development and management. Boca Raton: Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1-4665-6506-7. OCLC 857081580.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 McHaney, Roger (2021). Cloud technologies: an overview of cloud computing technologies for managers. Hoboken, NJ. ISBN 978-1-119-76951-4. OCLC 1196822611.
- ↑ Linkin, Peter (2022). Data Management as a Service for Dummies. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.. ISBN 978-1-119-87093-7. https://www.cohesity.com/resource-assets/ebook/next-gen-data-management-for-dummies-ebook-en.pdf.
- ↑ "Exploit-as-a-service: Cybercriminals exploring potential of leasing out zero-day vulnerabilities". 16 November 2021. https://portswigger.net/daily-swig/exploit-as-a-service-cybercriminals-exploring-potential-of-leasing-out-zero-day-vulnerabilities.
- ↑ "New type of cloud: Exploits as a Service (EaaS)". 2021-01-19. https://www.trendmicro.com/en_us/research/11/d/new-type-of-cloud-emerges-exploits-as-a-service-eaas.html.
- ↑ "Zero-day Flaws and Exploit-as-a-Service Trending Among Ransomware Groups | Cyware Alerts - Hacker News". 2021-12-01. https://cyware.com/news/zero-day-flaws-and-exploit-as-a-service-trending-among-ransomware-groups-27991876.
- ↑ "Zero-day Flaws and Exploit-as-a-Service Trending Among Ransomware Groups | Cyware Alerts - Hacker News". 2021-12-01. https://cyware.com/news/zero-day-flaws-and-exploit-as-a-service-trending-among-ransomware-groups-27991876.
- ↑ "What is hacking as a service (HaaS)? - Definition from WhatIs.com". https://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/hacking-as-a-service-HaaS.
- ↑ "Exploit-as-a-service: Cybercriminals exploring potential of leasing out zero-day vulnerabilities". 16 November 2021. https://portswigger.net/daily-swig/exploit-as-a-service-cybercriminals-exploring-potential-of-leasing-out-zero-day-vulnerabilities.
- ↑ Varghese, Blesson; Wang, Nan; Li, Jianyu; Nikolopoulos, Dimitrios S. (October 27, 2017). "Edge-as-a-Service: Towards Distributed Cloud Architectures". EdgeComp Symposium 2017. Proceedings of the International Conference on Parallel Computing.
- ↑ Rahmani, Hossein; Sundararajan, Elankovan; Ali, Zulkarnain Md.; Zin, Abdullah Mohd. "Encryption as a Service (EaaS) as a Solution for Cryptography in Cloud". 4th International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Informatics (ICEEI 2013. https://reader.elsevier.com/reader/sd/pii/S2212017313004684?token=E284DCD827CEA5B49DC4A7BE62F249AC0E5652981D0BDFB1B10106B0DBE0BAE9C69188BBD17878D04EDB0DBFAD196AC5&originRegion=us-east-1&originCreation=20220724235958.
- ↑ Mawani, Vinod; Kalshetty, Kalleshwar; Kadam, Aniket; Chavan, Sagar. "Energy-as-a-Service (EaaS): Interfacing Android Application with Cloud to Save Smartphone Energy". Spvryan's International Journal of Engineering Sciences & Technology 2 (5). http://spvryan.org/archive/issue6volume2/25.pdf. Retrieved 25 July 2022.
- ↑ Hopfgartner, Frank; Hanbury, Allan; Müller, Henning; Eggel, Ivan (December 2018). "Evaluation-as-a-Service for the Computational Sciences: Overview and Outlook". Journal of Data and Information Quality 10 (4): 1–32. doi:10.1145/3239570. http://arodes.hes-so.ch/record/1697.
- ↑ "ISO/IEC 22123-2:2023 (E) - Information technology — Cloud computing — Part 2: Concepts". International Standard: 25.
- ↑ "What is IaaS?" (in en). https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/cloud-computing/what-is-iaas.
- ↑ "What Is IaaS? Infrastructure as a Service". https://www.oracle.com/cloud/what-is-iaas/.
- ↑ "An IT-as-a-Service Handbook: Ten Key Steps on the Journey to ITaaS". June 2012. http://www.emc.com/collateral/software/white-papers/h10801-stepstoitaas-wp.pdf.
- ↑ "Archived copy". http://www.peterhinssen.com/downloads/printmedia/179/08_it_as_a_service.pdf.
- ↑ Xu, S.; Zhang, W. (2005). "Knowledge as a service and knowledge breaching". 2005 IEEE International Conference on Services Computing (SCC'05) Vol-1. 1. IEEE. pp. 87–94. doi:10.1109/SCC.2005.60. ISBN 0-7695-2408-7.
- ↑ Barreto, R.G.; Aversari, L.O.C.; Gomes, C.N.A.P.; Lino, N.C.Q. (2018). "Clinical Decision Support Based on OWL Queries in a Knowledge-as-a-Service Architecture". International Joint Conference on Rules and Reasoning. Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Springer) 11092: 226–238. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-99906-7_15. ISBN 978-3-319-99905-0. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/327179382.
- ↑ Zettsu, K.; Thalheim, B.; Kidawara, Y.; Karttunen, E.; Jaakkola, H. (2011). "Future Directions of Knowledge Systems Environments for Web 3.0.". Information Modelling and Knowledge Bases XXII (IOS Press): 413–446. ISBN 9781607506898. https://www.academia.edu/download/48967588/Future_Directions_of_Knowledge_Systems_E20160919-26630-44u777.pdf.[|permanent dead link|dead link}}]
- ↑ Smith, Göran. "Making Mobility-as-a-Service: Towards Governance Principles and Pathways". https://research.chalmers.se/publication/516812.
- ↑ Mladenović, Miloš N. (2021). "Mobility as a Service". International Encyclopedia of Transportation. pp. 12–18. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-102671-7.10607-4. ISBN 978-0-08-102672-4.
- ↑ Hudson, Caroline (January 26, 2022). "CEO at local fintech firm talks 'generosity trend,' what's next for 2022". www.bizjournals.com. https://www.bizjournals.com/charlotte/inno/stories/news/2022/01/26/amicus-financial-technology-philanthropy-startup.html.
- ↑ Brandon Butler (February 11, 2013). "PaaS Primer: What is platform as a service and why does it matter?"". http://www.networkworld.com/article/2163430/cloud-computing/paas-primer--what-is-platform-as-a-service-and-why-does-it-matter-.html.
- ↑ William Y. Chang; Hosame Abu-Amara; Jessica Feng Sanford (15 November 2010). Transforming Enterprise Cloud Services. London: Springer, 2010. p. 55–56. ISBN 9789048198467. https://books.google.com/books?id=yyiPyIXgbxMC&pg=PA55.
- ↑ "What Is Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS)? | IBM" (in en). 2024-09-05. https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/ransomware-as-a-service.
- ↑ "What is Ransomware as a service (RaaS) | Security Insider" (in en-US). https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/security/security-insider/threat-landscape/ransomware-as-a-service.
- ↑ "Recovery as a Service – The Hype and the Reality". July 24, 2011. Archived from the original on 2012-06-18. https://web.archive.org/web/20120618120600/http://www.slideshare.net/gregorycc1/gartner-recovery-as-a-service-the-hype-and-the-reality.
- ↑ "ITU Focus Group on Cloud Computing - Part 1". International Telecommunication Union (ITU) Telecommunication Standardization Sector. http://www.itu.int/en/ITU-T/focusgroups/cloud/Documents/FG-coud-technical-report.zip. Retrieved 16 December 2012.
- ↑ Yinong Chen, Zhihui Du, and Marcos Garcia-Acosta, M., "Robot as a Service in Cloud Computing", In Proceedings of the Fifth IEEE International Symposium on Service Oriented System Engineering (SOSE), Nanjing, June, 2010, pp. 151–158.
- ↑ Yinong Chen, H. Hu, "Internet of Intelligent Things and Robot as a Service", Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, Volume 34, May 2013, Pages 159–171.
- ↑ Olavsrud, Thor (April 26, 2017). "Security-as-a-service model gains traction". http://www.cio.com/article/3192649/security/security-as-a-service-model-gains-traction.html.
- ↑ "Security as a Service". https://www.techopedia.com/definition/26746/security-as-a-service-secaas-saas.
- ↑ Furfaro, A.; Garro, A.; Tundis, A. (2014-10-01). "Towards Security as a Service (SecaaS): On the modeling of Security Services for Cloud Computing". 2014 International Carnahan Conference on Security Technology (ICCST). pp. 1–6. doi:10.1109/CCST.2014.6986995. ISBN 978-1-4799-3530-7.
- ↑ "Penetration Testing as a Service". http://www.penteston.com/.
- ↑ "Definition of Security as a Service". http://searchsecurity.techtarget.com/definition/Security-as-a-Service.
- ↑ Panker, Jon; Lewis, Mark; Fahey, Evan; Vasquez, Melvin Jafet (August 2007). "How do you pronounce IT?". TechTarget. http://searchservervirtualization.techtarget.com/definition/How-do-you-pronounce-IT.
- ↑ Turner, Brian. "What is SaaS? Everything you need to know about Software as a Service" (in en). TechRadar. https://www.techradar.com/news/what-is-saas.
- ↑ "Definition of Software as a Service (SaaS) - Gartner Information Technology Glossary" (in en). Gartner. https://www.gartner.com/en/information-technology/glossary/software-as-a-service-saas.
- ↑ "What is Software as a Service (SaaS): A Beginner's Guide - Salesforce" (in en-in). https://www.salesforce.com/in/saas/.
External links
 |
 KSF
KSF