3908 Nyx
Topic: Astronomy
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 4 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 4 min
Short description: Amor and Mars-crosser asteroid
 | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Hans-Emil Schuster |
| Discovery date | 6 August 1980 |
| Designations | |
| (3908) Nyx | |
| Pronunciation | /ˈnɪks/"Nyx". Dictionary.com Unabridged. Random House. https://www.dictionary.com/browse/Nyx. |
| Named after | Nyx |
| 1980 PA; 1988 XB1 | |
| Minor planet category | Amor; Mars-crosser |
| Adjectives | Nyctian |
| Orbital characteristics[1] | |
| Epoch 27 July 2005 (JD 2453578.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 13021 days (35.65 yr) |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 2.81198 astronomical unit|AU (420.666 Gm) |
| |{{{apsis}}}|helion}} | 1.04239 AU (155.939 Gm) |
| 1.92719 AU (288.304 Gm) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.45911 |
| Orbital period | 2.68 yr (977.20 d) |
| Mean anomaly | 99.7699° |
| Mean motion | 0° 22m 6.236s / day |
| Inclination | 2.17667° |
| Longitude of ascending node | 261.688° |
| 125.978° | |
| Earth MOID | 0.0563399 AU (8.42833 Gm) |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mean radius | 0.5 ± 0.075 km |
| Rotation period | 4.42601 h (0.184417 d) |
| Geometric albedo | 0.23 |
| V | |
| Absolute magnitude (H) | 17.3 |
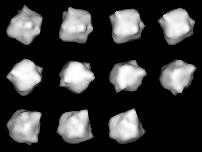
3908 Nyx is an Amor and Mars-crosser asteroid. It was discovered by Hans-Emil Schuster on August 6, 1980, and is named after Nyx, the Greek goddess of the night, after which Pluto's moon Nix is also named. It is 1–2 km in diameter and is a V-type asteroid, meaning that it may be a fragment of the asteroid 4 Vesta.
Observations
In 2000, radar observations conducted at the Arecibo and Goldstone observatories produced a model of Nyx's shape; the asteroid can best be described as spherical but with many protruding lumps.
Name
To avoid confusion with 3908 Nyx, Pluto's moon Nix was changed from the initial proposal of the classical spelling Nyx, to Nix.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ "3908 Nyx (1980 PA)". JPL Small-Body Database. NASA/Jet Propulsion Laboratory. https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=3908;cad=1.
- ↑ "Planet and Satellite Names and Discoverers". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS Astrogeology. July 21, 2006. http://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/append7.html.
External links
- 3908 Nyx at NeoDyS-2, Near Earth Objects—Dynamic Site
- Ephemeris · Obs prediction · Orbital info · MOID · Proper elements · Obs info · Close · Physical info · NEOCC
- 3908 Nyx at ESA–space situational awareness
- 3908 Nyx at the JPL Small-Body Database
 |
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Astronomy:3908_Nyx20 views | Status: cached on January 25 2026 14:03:32↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF