Hellas Planitia
Topic: Astronomy
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 10 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 10 min
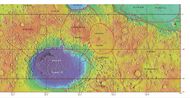
 Viking orbiter image mosaic of Hellas Planitia | |
| Planet | Mars |
|---|---|
| Region | Hellas quadrangle, south of Iapygia |
| Coordinates | [ ⚑ ] : 42°24′S 70°30′E / 42.4°S 70.5°E |
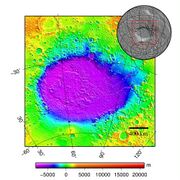
| Diameter | 2,300 km (1,400 mi) |
| Depth | 7,152 m (23,465 ft) |
Hellas Planitia /ˈhɛləs pləˈnɪʃiə/ is a plain located within the huge, roughly circular impact basin Hellas[lower-alpha 1] located in the southern hemisphere of the planet Mars.[3] Hellas is the third- or fourth-largest known impact crater in the Solar System. The basin floor is about 7,152 m (23,465 ft) deep, 3,000 m (9,800 ft) deeper than the Moon's South Pole-Aitken basin, and extends about 2,300 km (1,400 mi) east to west.[4][5] It is centered at [ ⚑ ] 42°24′S 70°30′E / 42.4°S 70.5°E.[3] Hellas Planitia spans the boundary between the Hellas quadrangle and the Noachis quadrangle.
Description
With a diameter of about 2,300 km (1,400 mi),[6] it is the largest unambiguous impact structure on the planet; the obscured Utopia Planitia is slightly larger (the Borealis Basin, if it proves to be an impact crater, is considerably larger). Hellas Planitia is thought to have been formed during the Late Heavy Bombardment period of the Solar System, approximately 4.1 to 3.8 billion years ago, when a protoplanet or large asteroid hit the surface.[7]
The altitude difference between the rim and the bottom is over 9,000 m (30,000 ft). The crater's depth of 7,152 m (23,465 ft)[1] below the topographic datum of Mars explains the atmospheric pressure at the bottom: 12.4 mbar (1240 Pa or 0.18 psi) during winter, when the air is coldest and reaches its highest density.[lower-alpha 2] This is 103% higher than the pressure at the topographical datum (610 Pa, or 6.1 mbar, or 0.09 psi) and above the triple point of water, suggesting that the liquid phase could be present under certain conditions of temperature, pressure, and dissolved salt content.[9] It has been theorized that a combination of glacial action and explosive boiling may be responsible for gully features in the crater.
Some of the low elevation outflow channels extend into Hellas from the volcanic Hadriacus Mons complex to the northeast, two of which Mars Orbiter Camera images show contain gullies: Dao Vallis and Reull Vallis. These gullies are also low enough for liquid water to be transient around Martian noon, if the temperature were to rise above 0 Celsius.[10]
Hellas Planitia is antipodal to Alba Patera.[11][12][13] It and the somewhat smaller Isidis Planitia together are roughly antipodal to the Tharsis Bulge, with its enormous shield volcanoes, while Argyre Planitia is roughly antipodal to Elysium, the other major uplifted region of shield volcanoes on Mars. Whether the shield volcanoes were caused by antipodal impacts like that which produced Hellas, or if it is mere coincidence, is unknown.
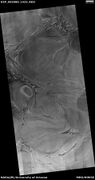
Twisted terrain in Hellas Planitia (actually located in Noachis quadrangle).
Discovery and naming
Due to its size and its light coloring, which contrasts with the rest of the planet, Hellas Planitia was one of the first Martian features discovered from Earth by telescope. Before Giovanni Schiaparelli gave it the name Hellas (which in Greek means Greece), it was known as Lockyer Land, having been named by Richard Anthony Proctor in 1867 in honor of Sir Joseph Norman Lockyer, an English astronomer who, using a 16 cm (6.3 in) refractor, produced "the first really truthful representation of the planet" (in the estimation of E. M. Antoniadi).[14]
Possible glaciers
Radar images by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) spacecraft's SHARAD radar sounder suggest that features called lobate debris aprons in three craters in the eastern region of Hellas Planitia are actually glaciers of water ice lying buried beneath layers of dirt and rock.[15] The buried ice in these craters as measured by SHARAD is about 250 m (820 ft) thick on the upper crater and about 300 m (980 ft) and 450 m (1,480 ft) on the middle and lower levels respectively. Scientists believe that snow and ice accumulated on higher topography, flowed downhill, and is now protected from sublimation by a layer of rock debris and dust. Furrows and ridges on the surface were caused by deforming ice.
Also, the shapes of many features in Hellas Planitia and other parts of Mars are strongly suggestive of glaciers, as the surface looks as if movement has taken place.
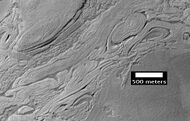
Honeycomb terrain
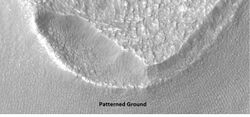
These relatively flat-lying "cells" appear to have concentric layers or bands, similar to a honeycomb. This honeycomb terrain was first discovered in the northwestern part of Hellas.[16] The geologic process responsible for creating these features remains unresolved.[17] Some calculations indicate that this formation may have been caused by ice moving up through the ground in this region. The ice layer would have been between 100 m and 1 km thick.[18][19][16] When one substance moves up through another denser substance, it is called a diapir. So, it seems that large masses of ice have pushed up layers of rock into domes that were subsequently eroded. After erosion removed the top of the layered domes, circular features remained.
Honeycomb terrain, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program
Layers
Layers in depression in crater, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program A special type of sand ripple called Transverse aeolian ridges, TAR's are visible and labeled.
Interactive Mars map
Error: Image is invalid or non-existent.
In popular culture
- Hellas Basin was a primary location in the 2017 video game Destiny 2. The location is part of the second game's Warmind downloadable content.
- It is also featured as a main location in the 2016 Bethesda video game reboot Doom.
- In Planet-Size X-Men #1, the X-Men terraform Mars, turning the basin into Lake Hellas and building the Lake Hellas Diplomatic Ring, where galactic ambassadors can meet within the Sol system.
See also
- Argyre Planitia
- Atmosphere of Mars e.g. pressure at floor of Hellas Planitia
- Dune
- Gale crater
- Geography of Mars
- Glaciers on Mars
- Groundwater on Mars
- List of plains on Mars
- Water on Mars
Notes
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Martian weather observation". Stanford University. http://www-star.stanford.edu/projects/mgs/sum/s0403210230.html. MGS radio science measured 11.50 mbar at 34.4° S 59.6° E −7152 meters
- ↑ "Hellas". United States Geological Survey. http://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/Feature/2429.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Hellas Planitia". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS Astrogeology Science Center. http://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/Feature/2432.
- ↑ The part below zero datum, see Geography of Mars#Zero elevation
- ↑ "Section 19-12". NASA. http://rst.gsfc.nasa.gov/Sect19/Sect19_12.html.
- ↑ Schultz, Richard A.; Frey, Herbert V. (1990). "A new survey of multi-ring impact basins on Mars". Journal of Geophysical Research 95: 14175. doi:10.1029/JB095iB09p14175. Bibcode: 1990JGR....9514175S. http://www.agu.org/pubs/crossref/1990/JB095iB09p14175.shtml.
- ↑ Acuña, M. H. (1999). "Global Distribution of Crustal Magnetization Discovered by the Mars Global Surveyor MAG/ER Experiment". Science 284 (5415): 790–793. doi:10.1126/science.284.5415.790. PMID 10221908. Bibcode: 1999Sci...284..790A. https://zenodo.org/record/1231157.
- ↑ Haberle, Robert M.; McKay, Christopher P.; Schaeffer, James; Cabrol, Nathalie A.; Grin, Edmon A.; Zent, Aaron P.; Quinn, Richard (October 25, 2001). "On the possibility of liquid water on present-day Mars". Journal of Geophysical Research 106 (EL0): 23,317–23,326. doi:10.1029/2000JE001360. Bibcode: 2001JGR...10623317H.
- ↑ "Making a splash on Mars" (Press release). NASA. 29 June 2000.
- ↑ Heldmann, Jennifer L. (2005). "Formation of Martian gullies by the action of liquid water flowing under current Martian environmental conditions". Journal of Geophysical Research 110: E05004. doi:10.1029/2004JE002261. – page 2, para 3: Martian Gullies Mars
- ↑ Peterson, J. E. (March 1978). "Antipodal Effects of Major Basin-Forming Impacts on Mars". Lunar and Planetary Science IX: 885–886. Bibcode: 1978LPI.....9..885P.
- ↑ Williams, D.A.; Greeley, R. (1991). "The Formation of Antipodal-Impact Terrains on Mars". Lunar and Planetary Science XXII: 1505–1506. http://www.lpi.usra.edu/meetings/lpsc1991/pdf/1748.pdf. Retrieved 2012-07-04.
- ↑ Williams, D.A.; Greeley, R. (August 1994). "Assessment of Antipodal-Impact Terrains on Mars". Icarus 110 (2): 196–202. doi:10.1006/icar.1994.1116. Bibcode: 1994Icar..110..196W.
- ↑ Sheehan, William (1996). The Planet Mars: A history of observation and discovery. Tucson, AZ: University of Arizona Press. Chapter 4. ISBN 9780816516414. http://www.uapress.arizona.edu/onlinebks/mars/chap04.htm. Retrieved 2021-02-19.
- ↑ "PIA11433: Three craters". NASA. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/?IDNumber=pia11433.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Bernhardt, H. (2016). "The honeycomb terrain on the Hellas basin floor, Mars: A case for salt or ice diapirism: Hellas honeycombs as salt / ice diapirs". J. Geophys. Res. 121 (4): 714–738. doi:10.1002/2016je005007. Bibcode: 2016JGRE..121..714B.
- ↑ "HiRISE | to Great Depths (ESP_049330_1425)". http://www.uahirise.org/ESP_049330_1425.
- ↑ Weiss, D.; Head, J. (2017). "Hydrology of the Hellas basin and the early Mars climate: Was the honeycomb terrain formed by salt or ice diapirism?". Lunar and Planetary Science XLVIII: 1060.
- ↑ Weiss, D.; Head, J. (2017). "Salt or ice diapirism origin for the honeycomb terrain in Hellas basin, Mars?: Implications for the early martian climate". Icarus 284: 249–263. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2016.11.016. Bibcode: 2017Icar..284..249W.
Further reading
- Antoniadi, E.M. (July 1897). "The hourglass sea on Mars". Knowledge: 169–172.
- Sedimentary Geology of Mars. SEPM. 2012.
- Lockyer, J.N. (1863). "Observations on the planet Mars". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 23: 246. doi:10.1093/mnras/23.8.246. Bibcode: 1863MNRAS..23..246L.
External links
- Ravenscroft, Peter (2000-08-16). "The Hellas of catastroph". http://www.spacedaily.com/news/mars-water-science-00i8.html.
- "Mars scrollable map". http://www.google.com/mars/#lat=-42.7&lon=70. – centered on Hellas
 |
 KSF
KSF