IMAGE
Topic: Astronomy
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 12 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 12 min
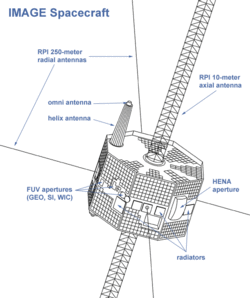 Diagram of IMAGE spacecraft | |||||||||||||||
| Names | Imager for Magnetopause-to-Aurora Global Exploration Explorer 78 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mission type | Magnetospheric physics | ||||||||||||||
| Operator | NASA / Goddard Applied Physics Laboratory | ||||||||||||||
| COSPAR ID | 2000-017A | ||||||||||||||
| SATCAT no. | 26113 | ||||||||||||||
| Website | pluto image | ||||||||||||||
| Mission duration | Planned: 2 years[1] Final: 5 years, 8 months, 22 days | ||||||||||||||
| Spacecraft properties | |||||||||||||||
| Manufacturer | Lockheed Martin Missiles & Space Southwest Research Institute | ||||||||||||||
| Launch mass | 494 kg (1,089 lb)[1] | ||||||||||||||
| Payload mass | 210 kg (463 lb)[2]: 17 | ||||||||||||||
| Dimensions | Bus: 2.25 × 1.52 m (7.4 × 5.0 ft)[1] Deployed: 504 × 22 m (1,652 × 71 ft)[1] | ||||||||||||||
| Power | 286 watts[1] (GaAs solar arrays, Super NiCd batteries) | ||||||||||||||
| Start of mission | |||||||||||||||
| Launch date | 25 March 2000, 20:34:43.929 UTC[3] | ||||||||||||||
| Rocket | Delta II 7326-9.5 #277[4] | ||||||||||||||
| Launch site | Vandenberg Air Force Base SLC-2W | ||||||||||||||
| Contractor | Boeing Launch Services | ||||||||||||||
| End of mission | |||||||||||||||
| Disposal | Contact lost | ||||||||||||||
| Last contact | 18 December 2005, 07:39 UTC[5] | ||||||||||||||
| Recovered by | Scott Tilley[6] | ||||||||||||||
| Recovery date | 20 January 2018[7] | ||||||||||||||
| Orbital parameters | |||||||||||||||
| Reference system | Geocentric | ||||||||||||||
| Regime | Polar | ||||||||||||||
| Semi-major axis | 29,880 km (18,567 mi) | ||||||||||||||
| Eccentricity | 0.75308 | ||||||||||||||
| Perigee altitude | 1,000 km (621 mi) | ||||||||||||||
| Apogee altitude | 46,004 km (28,586 mi) | ||||||||||||||
| Inclination | 90.01° | ||||||||||||||
| Period | 856 minutes | ||||||||||||||
| RAAN | 192.74° | ||||||||||||||
| Argument of perigee | 319.86° | ||||||||||||||
| Epoch | 25 March 2000, 16:30:34 UTC[8][9] | ||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
Explorers program | |||||||||||||||
IMAGE (Imager for Magnetopause-to-Aurora Global Exploration) is a NASA Medium Explorers mission that studied the global response of the Earth's magnetosphere to changes in the solar wind. It was believed lost but as of August 2018 might be recoverable. It was launched 25 March 2000 by a Delta II rocket from Vandenberg Air Force Base on a two-year mission. Almost six years later, it unexpectedly ceased operations in December 2005 during its extended mission and was declared lost.[10] The spacecraft was part of NASA's Sun-Earth Connections Program, and during its run had over 400 research articles published in peer-reviewed journals using its data.[11] It had special cameras that provided various breakthroughs in understanding the dynamics of plasma around the Earth. The Principal Investigator was Jim Burch of the Southwest Research Institute.
In January 2018, an amateur satellite tracker found it to be transmitting some signals back to Earth.[7] NASA made attempts to communicate with the spacecraft and determine its payload status, but has had to track down and adapt old hardware and software to the current systems.[12] On 25 February, contact with IMAGE was again lost, but if reestablished, NASA may decide to fund a restarted mission.[13]
Overview
IMAGE was the first spacecraft dedicated to imaging the Earth's magnetosphere.[1] IMAGE was a spacecraft developed by the Medium-Class Explorers (MIDEX) program, and it was the first spacecraft dedicated to observing the magnetosphere of the Earth, producing comprehensive global images of plasma in the inner magnetosphere. The IMAGE craft was placed in a 1,000×46,000 km orbit around the Earth, with an inclination of 90° (passing over the poles) and a 14.2 hour period.
By acquiring images every 2 minutes in wavelengths invisible to the human eye, it allowed detailed study of the interaction of the solar wind with the magnetosphere and the magnetosphere's response during a magnetic storm. From its distant orbit, the spacecraft produced a wealth of images of the previously invisible region of space in the inner magnetosphere, exceeded all its scientific goals. A senior review in 2005, just previous to its loss, described the mission as "extremely productive",[14] having confirmed several theoretical predictions (e.g., plasmasphere plumes, pre-midnight ring-current injection, and continuous antiparallel reconnection), discovered numerous new and unanticipated phenomena (e.g., plasmasphere shoulders, subauroral proton arcs, and a secondary interstellar neutral atom stream), and answered a set of outstanding questions regarding the source region of kilometric continuum radiation, the role of solar wind pressure pulses in ionospheric outflow, and the relationship between proton and electron auroras during substorms.[14][15] When the spacecraft went silent in December 2005, it had already been approved a mission extension until 2010.[14]
Costs for IMAGE are estimated at US$132 million, including the spacecraft, instruments, launch vehicle, and ground operations.[1]
Payload
Its science payload consists of three suites of instruments:[1]
- Energetic neutral atom imagers (LENA, MENA, HENA) — These instruments use hydrogen, helium, and oxygen atoms in the exosphere to form images and determine the properties of their low-, medium- and high-energy parent ions. HENA, the High Energy Neutral Atom imager is a modified version of the MIMI/INCA (Magnetospheric Imaging Instrument/Ion and Neutral Camera) sensor flown on the Cassini–Huygens mission.
- Ultraviolet imagers (FUV and EUV) — The Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) imager detects light from helium atoms in Earth's plasmasphere. The Far Ultraviolet (FUV) imager employs three detectors to image the auroras in different wavelengths and measure the distribution of different ions.
- Radio Plasma Imager (RPI) — This instrument uses pulses of radio waves to image the entire volume of the Earth's magnetic field. With its 502 meters-long antenna, it sends out a burst of radio waves, which reflect off of clouds of charged particles between the plasmasphere's outer boundary all the way out to the boundary where the Earth's magnetic field is impacted by the solar wind. RPI also measures naturally occurring plasma waves at the spacecraft's location.
The Central Instrument Data Processor (CIDP) as well as the Command & Data Handling Subsystem (main on-board computer) were built around the mission-proven IBM RAD6000 avionics processors.[1]
Loss
On 18 December 2005, the satellite failed to make an expected contact at 16:20 UTC. An earlier contact had ended successfully at 07:40 the same day with no sign of trouble.[16]: 14 Over the following days and weeks, commands were sent "blind" to reset the transmitter, change antennas, and otherwise attempt to re-establish contact with the spacecraft, but no signal (not even an unmodulated carrier wave) was received. Recovery efforts included using different DSN antennas, using non-NASA ground stations in case there was some systematic DSN error, transmitting no commands for several days to trigger a 72-hour watchdog timer, increasing transmit power in case the antenna was badly misaligned, and optical and radar observations of the satellite to check for debris, change in spin rate or change in orbit indicative of a collision or other damage.[16]: 16–17
The spacecraft was also commanded to slightly increase its spin rate and asymmetrically turn on its heaters. If observed, these would indicate that it could receive commands but not transmit. Neither change was seen and analysis later indicated that the temperature change would have been undetectable.[5]: 9–10 An attempt to observe the craft's temperature to determine if it was completely dead or consuming the power expected in safe mode was inconclusive.[5]: 10–11
A careful failure analysis revealed that, among plausible causes for an abrupt bidirectional loss of communication, the Solid State Power Converter (SSPC) for the transponder had, among its features, an "instant trip" shutdown in response to a high-current (100 A) short circuit.[17] Critically, such a shutdown was not reported in the power supply's telemetry output and this lack was not documented. [18] Because it was undocumented the spacecraft's hardware and software had no provision for attempting to reset the SSPC if it reported good status.[17][5]: 13 This would result in the observed symptoms: no radio communication with an apparently undamaged spacecraft.[5]: 1,12–13,22,29–31
Although such a short circuit would be almost impossible without fatal damage to the spacecraft, the shutdown could be falsely triggered by a radiation-induced single event upset.[17][5]: 1,30–31 It could be simply fixed by power-cycling the supply, but the spacecraft design left no way to send such a command, nor was one built in.
The same problem with the same model of power supply had affected the EO-1 and WMAP satellites (launched after IMAGE),[5]: 1,13 but they were able to recover.
In January 2006, NASA declared the mission over, declaring that "Preliminary analysis indicated the craft's power supply subsystems failed, rendering it lifeless."[11] Despite this, they continued to try and establish contact. In early 2006, NASA convened a board of experts to figure out what went wrong. After several months they created a report in which they theorized that IMAGE had tripped a power breaker and might fix itself.[19]
It was hoped that an eclipse when the spacecraft passed through the Earth's shadow in October 2007 would result in a sufficiently deep supply voltage sag that it would trigger a total bus reset, which would cause a power cycle of the suspect supply.[5]: 14–18 However, attempts to contact the craft after this eclipse were not successful.[7]
Recovery efforts
On 20 January 2018, IMAGE was found by Canadian radio amateur and satellite tracker Scott Tilley to be broadcasting, and he reported it to NASA. He had been scanning the S-band (microwaves) in the hopes of finding the Zuma satellite.[7][20]
On 24 January 2018, Richard Burley of NASA reported that they were trying to establish communication with the satellite using the NASA Deep Space Network.[21] Two days later, Burley reported that engineers at Goddard Space Flight Center successfully acquired the signal,[22] and confirmed on 30 January 2018 that IMAGE is the source.[12] It is not known when the satellite started broadcasting, but re-examination of old data recorded by Tilley and fellow satellite tracker Cees Bassa showed transmissions from the same satellite in October 2016 and May 2017.[23] Bassa hypothesized that while the 2007 eclipse did not manage to reset the satellite, another one did the trick, probably sometime between 2014 and 2016.[19]
On 8 February 2018, NASA published a detailed account of the IMAGE satellite's recovery.[24] The satellite was transmitting data beyond simple telemetry, indicating that some of its six onboard instruments were still active.[25] NASA engineers are attempting to determine the satellite's status,[12] but since the software and hardware type used in the IMAGE Mission Operations Center have been discarded and no longer exist, they are in the process of adapting old software and databases to their modern systems and track down replacement hardware.[12][26][27]
On 25 February 2018, NASA again lost contact with the satellite, but not in the same manner it did in 2005. Richard Burley, former IMAGE mission director, stated that he believes there is an issue with IMAGE's spin axis in relation to its medium-gain antenna placement. If NASA can regain control of the spacecraft, and the status of data and ground systems can be assessed, it will decide if it can fund a mission restart.[13]
On 4 March 2018, the Applied Physics Laboratory at Johns Hopkins University reported detecting the signal from the satellite, but it was too faint to lock onto.[28]
On 9 May 2018, Scott Tilley again detected a strong signal from IMAGE. Hours later NASA and APL engineers had locked onto the signal and were receiving telemetry. Commands were transmitted to IMAGE, but for unknown reasons the spacecraft only acknowledged receipt of a fraction of those commands.[28]
On 28 August 2018 NASA announced that the IMAGE team had stopped receiving any signals from the satellite, as previously happened in spring,[28] and would continue to try sending commands.[29]
Gallery
- Photos of IMAGE
-
False-colour image of ultraviolet aurora australis
-
Picture of the ultraviolet glow from relatively cold plasma surrounding Earth
-
An aurora as seen by the Far-Ultraviolet (FUV) imager
-
False-colour image of ultraviolet auroral lights from particles excited by collisions with protons, so called proton aurorae
-
IMAGE in preparation
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 "Press Kit for IMAGE Mission". NASA. March 2000. https://www.nasa.gov/home/hqnews/presskit/2000/image.pdf. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ↑ Burch, J. L., ed (2000). The IMAGE Mission. Springer Science+Business Media. doi:10.1007/978-94-011-4233-5. ISBN 978-94-010-5837-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=hT_wCAAAQBAJ.
- ↑ Airapetian, V.; Sedlak, J.; Hashmall, J. (2001). "On-Orbit Performance of Autonomous Star Trackers". Flight Mechanics Symposium. 19-21 June 2001. Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland.. NASA/CP-2001-209986. https://ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa.gov/20010084999.pdf.
- ↑ "The Delta 2 rocket". Spaceflight Now. 25 March 2000. https://spaceflightnow.com/delta/d277/000325delta.html. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 "IMAGE Failure Review Board Final Report: Executive Summary". NASA. 19 September 2006. https://image.gsfc.nasa.gov/publication/document/IMAGE_FRB_Final_Report.pdf.
- ↑ Chan, Athena (28 January 2018). "Lost NASA Satellite Found After A Decade By Amateur Astronomer". Tech Times. http://www.techtimes.com/articles/219836/20180128/lost-nasa-satellite-found-after-a-decade-by-amateur-astronomer.htm. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 Tilley, Scott (21 January 2018). "NASA’s Long Dead ‘IMAGE’ Satellite is Alive!". Riddles in the Sky. https://skyriddles.wordpress.com/2018/01/21/nasas-long-dead-image-satellite-is-alive/.
- ↑ "IMAGE - Spacecraft Orbit". NASA Space Science Data Coordinated Archive. https://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftOrbit.do?id=2000-017A. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ↑ "IMAGE Final Orbit Data". Southwest Research Institute. http://pluto.space.swri.edu/IMAGE/final_orbit.html. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ↑ "IMAGE - Spacecraft Details". NASA Space Science Data Coordinated Archive. https://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/masterCatalog.do?sc=2000-017A.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Hupp, Erica; Neal, Nancy; Steigerwald, Bill (20 January 2006). "NASA Magnetic Field Mission Ends". NASA. https://www.nasa.gov/home/hqnews/2006/jan/HQ_06030_IMAGE_quits.html.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 Garner, Rob; Hatfield, Miles (2 February 2018). "Latest Data From IMAGE Indicates Spacecraft’s Power Functional". NASA. https://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2018/nasa-image-confirmed. Retrieved 4 February 2018.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Fleishman, Glenn (April 2018). "NASA’s On-Again, Off-Again Satellite". Air & Space. https://www.airspacemag.com/space/24_am2018-soundings-180968357. Retrieved 22 March 2018.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 Burch, James L.; Moore, Thomas E.; Green, James L.; Fuselier, Stephen A.; Frey, Harald U.; Goldstein, Jerry (2005). "Imager for Magnetopause-to-Aurora Global Exploration (IMAGE)". Senior Review 2005. 5 October 2005. San Antonio, Texas.. https://image.gsfc.nasa.gov/publication/document/sr_rev_2005/2005_image_senior_review.pdf.
- ↑ "IMAGE Mission Highlights". Southwest Research Institute. http://pluto.space.swri.edu/IMAGE/highlights.html. Retrieved 4 February 2018.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Prior, Mike (21 April 2006). "IMAGE Failure Review Board Final Presentation". NASA. https://image.gsfc.nasa.gov/publication/document/IMAGE_FRB_Presentation_4-21-06.pdf.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 Hardy, Terry L. (16 April 2012). Software and System Safety: Accidents, Incidents, and Lessons Learned. AuthorHouse. p. 57. ISBN 978-1-4685-7470-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=o_yvbP5JMa0C&pg=PA57.
- ↑ The non-reporting was by design, as in non-spacecraft applications it would be dangerous to automatically restore power in such an event, while in a spacecraft failure to receive means loss of mission so there is nothing more to lose by trying.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 Selk, Avi (31 January 2018). "NASA lost contact with a satellite 12 years ago. An amateur just found its signal.". The Washington Post. https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/speaking-of-science/wp/2018/01/31/nasa-lost-contact-with-a-satellite-12-years-ago-an-amateur-just-found-its-signal/. Retrieved 1 February 2018.
- ↑ Voosen, Paul (26 January 2018). "Amateur astronomer discovers a revived NASA satellite". Science (American Association for the Advancement of Science). http://www.sciencemag.org/news/2018/01/amateur-astronomer-discovers-revived-nasa-satellite. Retrieved 28 January 2018.
- ↑ Burley, Richard J. (24 January 2018). "Re: NASA IMAGE - Returns from the Dead". SeeSat-L (Mailing list) – via Scott Tilley.
- ↑ Burley, Richard J. (26 January 2018). "Fwd: 20180126 Break-Break-Break IMAGE Status". SeeSat-L (Mailing list) – via Scott Tilley.
- ↑ Bassa, Cees (30 January 2018). "When did IMAGE return from the dead?". Riddles in the Sky. https://skyriddles.wordpress.com/2018/01/30/when-did-image-return-from-the-dead/.
- ↑ Blumberg, Sara (8 February 2018). "A Detailed Timeline of The IMAGE Mission Recovery" (in en). NASA. https://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2018/a-detailed-timeline-of-the-image-mission-recovery.
- ↑ McKay, Tom (27 January 2018). "Over a Decade Later, NASA's Long-Dead IMAGE Satellite May Have Come Back to Life". Gizmodo. https://gizmodo.com/over-a-decade-later-nasas-long-dead-image-satellite-ma-1822479068.
- ↑ Cofield, Calla (31 January 2018). "Signal Detected by Amateur Astronomer Came from Long-Lost Satellite, NASA Confirms". Space.com. https://www.space.com/39534-amateur-astronomer-finds-lost-nasa-satellite.html. Retrieved 4 February 2018.
- ↑ Szondy, David (30 January 2018). "NASA to attempt recovery of lost IMAGE satellite". New Atlas. https://newatlas.com/nasa-image-satellite-recovery/53174/.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 28.2 Hatfield, Miles. "Latest Updates from NASA on IMAGE Recovery". NASA. https://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2018/nasa-image-confirmed. Retrieved 12 October 2018.
- ↑ Thompson, Avery (30 August 2018). "NASA Already Lost the Satellite It Just Found in January". Popular Mechanics. https://www.popularmechanics.com/space/satellites/a22877021/nasa-already-lost-the-satellite-it-just-found-in-january/. Retrieved 31 August 2018.
External links
- IMAGE website by NASA / Goddard
- IMAGE website by the Southwest Research Institute
 KSF
KSF





