NEEMO
Topic: Astronomy
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 11 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 11 min
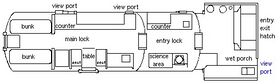
NASA Extreme Environment Mission Operations, or NEEMO,[1] is a NASA analog mission that sends groups of astronauts, engineers and scientists to live in the Aquarius underwater laboratory, the world's only undersea research station, for up to three weeks at a time in preparation for future space exploration.[2]
Aquarius is an underwater habitat 3.5 miles (5.6 km) off Key Largo, Florida, in the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary. It is deployed on the ocean floor next to deep coral reefs 62 feet (19 m) below the surface.
NASA has used it since 2001 for a series of space exploration simulation missions, usually lasting 7 to 14 days, with space research mainly conducted by international astronauts. The mission had cost about 500 million U.S. dollars. The crew members are called aquanauts (as they live underwater at depth pressure for a period equal to or greater than 24 continuous hours without returning to the surface), and they perform EVAs in the underwater environment.[2] A technique known as saturation diving allows the aquanauts to live and work underwater for days or weeks at a time. After twenty four hours underwater at any depth, the human body becomes saturated with dissolved gas. With saturation diving, divers can accurately predict exactly how much time they need to decompress before returning to the surface. This information limits the risk of decompression sickness. By living in the Aquarius habitat and working at the same depth on the ocean floor, NEEMO crews are able to remain underwater for the duration of their mission.
For NASA, the Aquarius habitat and its surroundings provide a convincing analog for space exploration.[2] Much like space, the undersea world is a hostile, alien place for humans to live. NEEMO crew members experience some of the same challenges there that they would on a distant asteroid, planet (i.e. Mars) or Moon. During NEEMO missions, the aquanauts are able to simulate living on a spacecraft and test spacewalk techniques for future space missions. Working in space and underwater environments requires extensive planning and sophisticated equipment. The underwater condition has the additional benefit of allowing NASA to "weight" the aquanauts to simulate different gravity environments.[3]
Until 2012, Aquarius was owned by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and operated by the National Undersea Research Center (NURC) at the University of North Carolina–Wilmington as a marine biology study base.
Since 2013, Aquarius is owned by Florida International University (FIU).[4] As part of the FIU Marine Education and Research Initiative, the Medina Aquarius Program is dedicated to the study and preservation of marine ecosystems worldwide and is enhancing the scope and impact of FIU on research, educational outreach, technology development, and professional training. At the heart of the program is the Aquarius Reef Base.[5]
Missions
NEEMO 1: October 21–27, 2001

NASA Aquanaut Crew:
NURC Support Crew:
NEEMO 2: May 13–20, 2002
NASA Aquanaut Crew:
NURC Support Crew:
NEEMO 3: July 15–21, 2002
NASA Aquanaut Crew:
NURC Support Crew:
NEEMO 4: September 23–27, 2002
NASA Aquanaut Crew:
NURC Support Crew:

NEEMO 5: June 16–29, 2003
NASA Aquanaut Crew:
NURC Support Crew:
NEEMO 6: July 12–21, 2004
NASA Aquanaut Crew:
- John Herrington
 , Commander[15][16]
, Commander[15][16] - Nicholas Patrick

- Douglas H. Wheelock

- Tara Ruttley

NURC Support Crew:
NEEMO 7: October 11–21, 2004
NASA Aquanaut Crew:
NURC Support Crew:
NEEMO 8: April 20–22, 2005
NASA Aquanaut Crew:
NURC Support Crew:
NEEMO 9: April 3–20, 2006

NASA Aquanaut Crew:
NURC Support Crew:
NEEMO 10: July 22–28, 2006
NASA Aquanaut Crew:
NURC Support Crew:
- Mark Hulsbeck
- Dominic Landucci
- Marc Reagan, Mission Director
NEEMO 11: September 16–22, 2006
NASA Aquanaut Crew:
- Sandra Magnus, Commander[26][27]
- Timothy Kopra
- Robert L. Behnken
- Timothy Creamer
NURC Support Crew:
- Larry Ward
- Roger Garcia
- Marc Reagan, Mission Director
NEEMO 12: May 7–18, 2007

NASA Aquanaut Crew:
- Heidemarie Stefanyshyn-Piper, Commander[28][29]
- José M. Hernández
- Josef Schmid, M.D.
- Timothy J. Broderick, M.D.
NURC Support Crew:
- Dominic Landucci
- James Talacek
- Marc Reagan, Mission Director
NEEMO 13: August 6–15, 2007
NASA Aquanaut Crew:
NURC Support Crew:
- James F. Buckley
- Dewey Smith
- Marc Reagan, Mission Director
NEEMO 14: May 10–23, 2010
NASA Aquanaut Crew:
Aquarius Reef Base support crew:
- James Talacek
- Nate Bender
- Bill Todd, Mission Director
NEEMO 15: October 20–26, 2011
NASA Aquanaut Crew:
- Shannon Walker, Commander[35][36]
- Takuya Onishi
- David Saint-Jacques
- Steve Squyres
Aquarius Reef Base support crew:
- James Talacek
- Nate Bender
DeepWorker 2000 submersible crew:
- Stanley G. Love[35]
- Richard R. Arnold
- Michael L. Gernhardt
NEEMO 16: June 11–22, 2012

NASA Aquanaut Crew:
- Dorothy Metcalf-Lindenburger, Commander[37][38][39]
- Kimiya Yui
- Timothy Peake
- Steve Squyres
Aquarius Reef Base support crew:
- James Talacek
- Justin Brown
DeepWorker 2000 submersible crew:
- Stanley G. Love[40][41][42][43]
- Steve Giddings
- Serena M. Auñón
- Bill Todd
- Michael L. Gernhardt
- Andrew Abercromby
- Steve Chappell
SEATEST II: September 9–13, 2013
Space Environment Analog for Testing EVA Systems and Training[44] ( NEEMO 17 ) Designation skipped[45]
NASA Aquanaut Crew:
- Joseph M. Acaba, Commander
- Kate Rubins
- Andreas Mogensen
- Soichi Noguchi
Aquarius Reef Base support crew:[46]
- Mark Hulsbeck
- Otto Rutten
NEEMO 18: July 21–29, 2014
NASA Aquanaut Crew:
- Akihiko Hoshide, Commander
- Jeanette J. Epps
- Mark T. Vande Hei
- Thomas Pesquet
Professional habitat technicians, Aquarius Reef Base support crew:
- James Talacek
- Hank Stark (FIU)
NEEMO 19: September 7–13, 2014

NASA Aquanaut Crew:
- Randolph Bresnik, commander[45]
- Andreas Mogensen, ESA
- Jeremy Hansen, CSA
- Hervé Stevenin, European Astronaut Centre EVA Training Unit[47]
Aquarius Reef Base support crew:
- Mark Hulsbeck
- Ryan LaPete
NEEMO 20: July 20 – August 2, 2015
NASA Aquanaut Crew:[48]

- Luca Parmitano, ESA, commander
- Serena M. Auñón, NASA
- David Coan, NASA EVA Management Office engineer[49]
- Norishige Kanai, JAXA
Professional habitat technicians, Aquarius Reef Base support crew:
- Mark Hulsbeck (FIU)
- Sean Moore (FIU)
NEEMO 20 mission objective was to simulate the time delays associated with sending and receiving commands between controllers on Earth and astronauts on Mars. Additional EVAs will simulate working on the surface of an asteroid, and the use of the DeepWorker submersible as an underwater stand-in for the Multi-Mission Space Exploration Vehicle.[50]
NEEMO 21: July 21 – August 5, 2016

The NEEMO 21 mission was scheduled to begin July 18, 2016 and conclude August 3, 2016; however, the mission start was shifted to July 21, 2016 as a result of unfavorable weather conditions.
NASA Aquanaut Crew:[51]
- Reid Wiseman, NASA, Commander 1
- Megan McArthur, NASA, Commander 2
- Marc O´Gríofa
- Matthias Maurer, ESA
- Noel Du Toit
- Dawn Kernagis
Professional habitat technicians, Aquarius Reef Base support crew:
- Hank Stark (FIU)
- Sean Moore (FIU)
NEEMO 22: June 18–27, 2017
NASA Aquanaut Crew:
- Kjell Lindgren, NASA, Commander
- Pedro Duque, ESA
- Trevor Graff, NASA/Jacobs
- Dominic D'Agostino, USF
Professional habitat technicians, Aquarius Reef Base support crew:
- Mark Hulsbeck (FIU)
- Sean Moore (FIU)
NEEMO 23: June 10–22, 2019
NASA all-female Aquanaut Crew:[52]
- Samantha Cristoforetti, ESA, Commander
- Jessica Watkins, NASA astronaut candidate
- Csilla Ari D’Agostino, a neurobiologist at the University of South Florida
- Shirley Pomponi, Marine biologist at Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institute of Florida Atlantic University
Professional habitat technicians, Aquarius Reef Base support crew:
- Mark Hulsbeck (FIU)
- Tom Horn (FIU)
See also
References
- ↑ Loff, Sarah (Jun 24, 2015). "NEEMO - NASA Extreme Environment MIssion Operations". http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/NEEMO/index.html.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 NASA (March 21, 2006). "NEEMO History". National Aeronautics and Space Administration. http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/NEEMO/history.html.
- ↑ Loff, Sarah (Jun 24, 2015). "About NEEMO (NASA Extreme Environment Mission Operations)". http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/NEEMO/about_neemo.html.
- ↑ Communications, Florida International University-Digital. "Medina Aquarius Program". https://environment.fiu.edu/coastlines-and-oceans/aquarius/.
- ↑ Communications, Florida International University-Digital. "About". https://environment.fiu.edu/coastlines-and-oceans/aquarius/about/.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 NASA (February 27, 2006). "Behind the Scenes: Training - NEEMO History". NASA. http://spaceflight.nasa.gov/shuttle/support/training/neemo/history.html.
- ↑ NASA (June 2011). "Astronaut Bio: Edward Michael "Mike" Fincke (06/2011)". NASA. http://www.jsc.nasa.gov/Bios/htmlbios/fincke.html.
- ↑ NASA (April 21, 2011). "Life Sciences Data Archive : Experiment". NASA. http://lsda.jsc.nasa.gov/scripts/mission/miss.cfm?mis_index=212.
- ↑ Walheim, Rex (September 24, 2002). "NEEMO 4 Journals". NASA. http://spaceflight.nasa.gov/shuttle/support/training/neemo/journals/4walheim2.html.
- ↑ NOAA (May 17, 2010). "NEEMO 4 Journals". NOAA. http://aquarius.uncw.edu/archive/2002/09_2002/journals.html.
- ↑ NASA (April 21, 2011). "Life Sciences Data Archive : Experiment". NASA. http://lsda.jsc.nasa.gov/scripts/mission/miss.cfm?mis_index=213.
- ↑ NASA (2003). "NEEMO 5". NASA. http://spaceflight.nasa.gov/shuttle/support/training/neemo/neemo5/.
- ↑ "Aquarius - First Space Station Science Officer Leads Crew of Four NASA Aquanauts On 14-Day NOAA Aquarius Undersea Mission". University of North Carolina Wilmington. May 17, 2010. http://aquarius.uncw.edu/archive/2003/06_2003/expd.htm.
- ↑ Whitson, Peggy (June 19, 2003). "NEEMO 5 Journals". NASA. http://spaceflight.nasa.gov/shuttle/support/training/neemo/journals/neemo5/5whitson4.html.
- ↑ NASA (August 3, 2004). "NEEMO 6". NASA. http://spaceflight.nasa.gov/shuttle/support/training/neemo/neemo6/.
- ↑ NASA (September 6, 2011). "Life Sciences Data Archive : Experiment". NASA. http://lsda.jsc.nasa.gov/scripts/mission/miss.cfm?mis_index=220&string=NEEMO%206&CURRENT_STRING2=NEEMO%206.
- ↑ NASA (October 13, 2004). "NEEMO 7". NASA. http://spaceflight.nasa.gov/shuttle/support/training/neemo/neemo7/.
- ↑ Canadian Space Agency (August 9, 2004). "CSA - Neemo 7 Mission". Canadian Space Agency. http://www.asc-csa.gc.ca/eng/missions/neemo7/backgrounder_0809.asp.
- ↑ NASA (April 21, 2011). "Life Sciences Data Archive : Experiment". NASA. http://lsda.jsc.nasa.gov/scripts/mission/miss.cfm?mis_index=243&string=NEEMO%207&CURRENT_STRING2=NEEMO%207.
- ↑ NOAA (May 18, 2010). "NEEMO 8". University of North Carolina Wilmington. http://aquarius.uncw.edu/archive/2005/04_2005/prof.htm.
- ↑ NASA (April 21, 2011). "Life Sciences Data Archive : Experiment". NASA. http://lsda.jsc.nasa.gov/scripts/mission/miss.cfm?mis_index=244.
- ↑ NASA (2006). "NASA's Undersea Crew is Heads Above Water". NASA. http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/NEEMO/NEEMO9/index.html.
- ↑ NASA (April 3, 2006). "NASA's NEEMO 9 Aquanaut Human Performance Study Begins". NASA. http://human-factors.arc.nasa.gov/awards_pubs/news_view.php?news_id=34.
- ↑ NASA (2006). "NASA Uses Undersea Lab to Prep for Future Space Exploration". NASA. http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/NEEMO/NEEMO10/index.html.
- ↑ NASA (July 22, 2006). "NASA - NEEMO 10 Mission Journal". NASA. http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/NEEMO/NEEMO10/mission_journal_1.html.
- ↑ NASA (May 11, 2010). "NEEMO 11". NASA. http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/NEEMO/NEEMO11/index.html.
- ↑ NASA (September 1, 2006). "NASA Continues Space Exploration Research With Undersea Lab". NASA. http://www.nasa.gov/home/hqnews/2006/sep/HQ_06309_NEEMO_11.html.
- ↑ NASA (May 17, 2007). "NEEMO 12". NASA. http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/NEEMO/NEEMO12/index.html.
- ↑ NEEMO 12 Topside Team (May 6, 2007). "NASA - NEEMO 12 Topside Journal". NASA. http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/NEEMO/NEEMO12/topside_journal_1.html.
- ↑ NASA (July 24, 2007). "NASA Announces Next Undersea Exploration Mission Dates and Crew". NASA. http://www.nasa.gov/home/hqnews/2007/jul/HQ_07164_NEEMO_13.html.
- ↑ Topside Team (August 8, 2007). "NEEMO 13 Topside Report - Training Week". NURC. http://www.nurc.net/blog/neemo-13/neemo-13-topside-report-training-week.
- ↑ NASA (July 9, 2010). "NASA - NEEMO 14". NASA. http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/NEEMO/NEEMO14/index.html.
- ↑ Alexander, Aaron (2010). "Archive for the 'NEEMO 14' Mission". NURC. http://www.nurc.net/blog/category/neemo-14.
- ↑ NASA (May 7, 2010). "NASA - NEEMO 14 Topside Report No. 1, May 7, 2010". NASA. http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/NEEMO/NEEMO14/topside_01.html.
- ↑ 35.0 35.1 NASA (September 19, 2011). "NASA - NASA Announces 15th Undersea Exploration Mission Date And Crew". NASA. http://www.nasa.gov/home/hqnews/2011/sep/HQ_11-309_NEEMO.html.
- ↑ NASA (October 27, 2011). "NASA - NEEMO 15 Topside Reports". NASA. http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/NEEMO/NEEMO15/topside-reports.html.
- ↑ NASA (April 16, 2012). "NASA - NASA Announces 16th Undersea Exploration Mission Dates and Crews". NASA. http://www.nasa.gov/home/hqnews/2012/apr/HQ_12-116_NEEMO.html.
- ↑ Peake, Tim (April 29, 2012). "NEEMO 16 - In search of an asteroid". European Space Agency. http://blogs.esa.int/astronauts/2012/04/29/neemo-16-in-search-of-an-asteroid/.
- ↑ The NEEMO Mission Management and Topside Support Team (June 12, 2012). "NEEMO 16 Mission Day 2 - Status Report". NASA. http://www.nasa.gov/pdf/659661main_Topside-Report-MD02-Final.pdf.
- ↑ Love, Stan (June 17, 2012). "Dr. Love's Underwater Blog: NEEMO 16". NASA. http://wiki.nasa.gov/cm/blog/analogsfieldtesting/posts/post_1339938072178.html.
- ↑ Squyres, Steve (June 17, 2012). "NEEMO 16: EVA Divers and Subs". NASA. http://wiki.nasa.gov/cm/blog/analogsfieldtesting/posts/post_1339979223707.html.
- ↑ Love, Stan (June 18, 2012). "Dr. Love's Underwater Blog: Mobility and Stability with DeepWorkers". NASA. http://wiki.nasa.gov/cm/blog/analogsfieldtesting/posts/post_1340021371063.html.
- ↑ Stevenin, Hervé (June 19, 2012). "The NEEMO 16 Aquanauts meet the Men in Black". Yahoo! Inc. https://www.flickr.com/photos/esastro_trainer/7414350644/.
- ↑ Garcia, Mark (Apr 13, 2015). "NASA, International Partners Plan Undersea Training Mission". http://www.nasa.gov/content/nasa-international-partners-plan-undersea-training-mission.
- ↑ 45.0 45.1 Bergin, Chris (June 11, 2014). "NEEMO returns with two new underwater missions". NASASpaceflight. http://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2014/06/neemo-returns-two-new-underwater-missions/.
- ↑ Computing, HySpeed (Sep 16, 2013). "Aquarius SEATEST II – Astronauts emerge from a successful underwater mission". https://hyspeedblog.wordpress.com/2013/09/16/aquarius-seatest-ii-astronauts-emerge-from-a-successful-underwater-mission/.
- ↑ "Hervé Stevenin". http://www.esa.int/About_Us/EAC/Herve_Stevenin.
- ↑ "NEEMO 20 Crew (L to R) CDR Luca Parmitano (ESA), Serena Aunon (NASA), David Coan (NASA), Norishige Kanai, (JAXA), inside Aquarius Mark Hulsbeck (FIU) and Sean Moore (FIU)". Jul 20, 2015. https://www.flickr.com/photos/40054892@N06/20061131081/.
- ↑ "NASA Prepares for Future Space Exploration with International Undersea Crew". June 24, 2015. https://www.nasa.gov/press-release/nasa-prepares-for-future-space-exploration-with-international-undersea-crew.
- ↑ "NEEMO 20 to build knowledge base on delayed deep space communications, Chris Bergin, nasaspaceflight". July 6, 2015. http://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2015/07/neemo-20-base-deep-space-communications/.
- ↑ Loff, Sarah (2016-07-22). "Aquanauts Splash Down, Beginning NEEMO 21 Research Mission". https://www.nasa.gov/image-feature/aquanauts-splash-down-beginning-neemo-21-research-mission.
- ↑ Emily Toomey (July 29, 2019). "NASA Scientists and Astronauts Practice for Space Missions on the Seafloor". Smithsonian magazine. https://www.smithsonianmag.com/science-nature/nasa-scientists-and-astronauts-practice-space-mission-seafloor-180972744/#3gRkwJRekZ6hSUDv.99.
External links
- Official website
- NEEMO missions
- Live webcams (subject to mission availability)
- Behind the Scenes: NEEMO
[ ⚑ ] 24°57′00″N 80°27′13″W / 24.95°N 80.45361°W
 |
 KSF
KSF
