Shenzhou 9
Topic: Astronomy
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 4 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 4 min
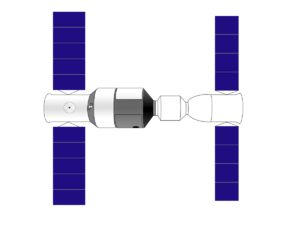 Diagram depicting Shenzhou 9 (right) docked with Tiangong-1 (left) | |
| COSPAR ID | 2012-032A |
|---|---|
| SATCAT no. | 38461 |
| Mission duration | 12 days, 15 hours and 25 minutes |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft type | Shenzhou |
| Crew | |
| Crew size | 3 |
| Members | Jing Haipeng Liu Wang Liu Yang |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 16 June 2012, 10:37:24 UTC |
| Rocket | Long March 2F |
| Launch site | Jiuquan LA-4/SLS-1 |
| End of mission | |
| Landing date | 29 June 2012, 02:01:16 UTC |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric |
| Regime | Low Earth |
| Docking with Tiangong-1 | |
| Docking date | 18 June 2012, 06:07 UTC |
| Undocking date | 24 June 2012, 03:08 UTC |
| Time docked | 3 days, 21 hours, 1 minute |
| Docking with Tiangong-1 | |
| Docking date | 24 June 2012, 04:38 UTC |
| Undocking date | 28 June 2012, 01:22 UTC |
| Time docked | 3 days, 20 hours, 44 minutes |
 (l-r) Jing Haipeng, Liu Wang, and Liu Yang | |
Shenzhou 9 (Chinese: 神舟九号) was the fourth crewed spacecraft flight of China 's Shenzhou program, launched at 18:37:24 CST (10:37:24 UTC), 16 June 2012. Shenzhou 9 was the second spacecraft and first crewed mission and expedition to dock with the Tiangong-1 space station, which took place on 18 June. The Shenzhou 9 spacecraft landed at 10:01:16 CST (02:01:16 UTC) on 29 June in the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. The mission's crew included the first Chinese female astronaut, Liu Yang. The next mission was Shenzhou 10, which launched on 11 June 2013.[1]
History
On 12 March 2012, it was announced that the initial crew selection roster for the mission included female astronauts.[2] The crew were unveiled to the press on 15 June. China's first female astronaut would be Liu Yang. Liu was selected ahead of her fellow female astronaut prospect Wang Yaping.[3] This mission also featured the first repeat astronaut, Jing Haipeng, the commander of the mission.[4] Shenzhou 9 was the 9th flight in China's Shenzhou program and the fourth crewed spaceflight. The mission's launch was 49 years to the day after that of the first woman in space, cosmonaut Valentina Tereshkova.[3]
Mission preparations
The Shenzhou 9 spacecraft arrived at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in the northwestern Gobi Desert on 9 April 2012 and its carrier rocket, the Long March 2F, arrived on 9 May.[5] On 9 June 2012, the Shenzhou 9 spacecraft and its carrier rocket were rolled out to launch pad.[6] On 12 June 2012 underwent system-wide joint exercises, and final health checks were completed the following day.
Expedition ceremony
On 16 June 2012, the expedition ceremony was held at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center. National People's Congress Standing Committee Chairman Wu Bangguo attended the ceremony. The astronauts, Liu Wang, Liu Yang, and Jing Haipeng, rode to the launch tower and turned in the entrance with the assistance of support staff.[7]
Mission
The Long March 2F rocket was launched on 16 June 2012 at 10:37 UTC.
Shenzhou 9 docked with China's first space lab Tiangong-1 at 06:07 UTC on 18 June, marking China's first crewed spacecraft rendezvous and docking.[8][9] This docking was remotely controlled from a ground station.[10] After about 3 hours, when the pressures inside the vessels were equalized, Jing Haipeng entered into Tiangong-1.[11] Six days later, Shenzhou 9 detached from the station and then redocked manually under the control of crew member Liu Wang, making it the first manual docking for the Chinese program.[10]
Shenzhou 9 landed by parachute in Siziwang Banner, Inner Mongolia on 29 June 2012.[12]
Crew
| Position | Crew member | |
|---|---|---|
| Commander | Jing Haipeng Second spaceflight First Chinese astronaut to fly more than once in space[3] | |
| Operator | Liu Wang First spaceflight | |
| Laboratory Assistant | Liu Yang First spaceflight First Chinese woman in space[3] | |
Backup crew
The backup crew for the flight was:[13]
| Position | Crew member | |
|---|---|---|
| Commander | Nie Haisheng | |
| Operator | Zhang Xiaoguang | |
| Laboratory Assistant | Wang Yaping | |
The backup crew later became the prime crew for Shenzhou 10.[14]
Mission timeline
- 9 April 2012
- Shenzhou 9 space capsule arrives at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center[5]
- 9 May 2012
- Long March 2F space launcher arrives at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center[6]
- 9 June 2012
- Launch stack rolled out to the launch pad[6]
- 15 June 2012
- Crew unveiled[3]
- 16 June 2012
- Launch, first woman in space for the Chinese program, first repeat traveller for the Chinese program, first crewed mission to a space station for the Chinese program[3]
- 18 June 2012
- First crewed rendezvous for the Chinese space program.
- Automated docking with Tiangong-1, first crewed docking by the Chinese program[8]
- 24 June 2012
- Shenzhou 9 undocks with Tiangong-1[10]
- Shenzhou 9 redocks with Tiangong-1, first manual docking by the Chinese space program,[10] second crewed docking by the program
- 29 June 2012
- Shenzhou 9 landed in Siziwang Banner, Inner Mongolia.[12]
See also
- Chinese space program
- Chinese women in space
- Tiangong program
- Long March 2F
- Yang Liwei
References
- ↑ "China Completes Tiangong-1 Space Module". 18 August 2010. http://www.2point6billion.com/news/2010/08/18/china-completes-tiangong-1-space-module-6770.html.
- ↑ "Shenzhou-9 may take female astronaut to space: official". People's Daily. Xinhua News Agency. 12 March 2012. http://english.peopledaily.com.cn/202936/7755164.html.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 3.8 Moskowitz, Clara (15 June 2012). "China Unveils Astronaut Crew, 1st Female Spaceflyer, for Saturday Launch". Space.com. http://www.space.com/16158-china-female-astronaut-crew-shenzhou-9.html.
- ↑ "China astronauts complete successful space docking". Reuters. 18 June 2012. https://www.reuters.com/article/us-china-space-idINBRE85E0NI20120618.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Shenzhou-9 spacecraft delivered to launch center". Xinhua News Agency. 9 April 2012. http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/china/2012-04/09/c_122951646.htm.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 "China to launch manned spacecraft this month". Business Line. Press Trust of India. 9 June 2012. http://www.thehindubusinessline.com/features/article3508490.ece.
- ↑ (in zh). China News Service. 2012-06-16. http://www.chinanews.com/gn/2012/06-16/3968395.shtml.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Barbosa, Rui C. (18 June 2012). "China's Shenzhou-9 successfully docks with Tiangong-1". http://www.nasaspaceflight.com/2012/06/chinas-shenzhou-9-successfully-docks-with-tiangong-1/.
- ↑ "China Will Conduct its First Manned Space Rendezvous and Docking Mission". China Manned Space Engineering Office. 10 June 2012. http://en.cmse.gov.cn/news/201206/t20120610_44532.html.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 "Chinese spacecraft Shenzhou 9 makes first manual docking with space module". The Guardian. Associated Press. 24 June 2012. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2012/jun/24/chinese-spacecraft-first-manual-docking.
- ↑ Xin, Dingding (19 June 2012). "China successfully completes space docking". China Daily. http://europe.chinadaily.com.cn/china/2012-06/19/content_15510702.htm.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 "China's Shenzhou-9 crew returns to Earth after history-making trip". NBC News. 29 June 2012. https://www.nbcnews.com/news/world/chinas-shenzhou-9-crew-returns-earth-after-history-making-trip-flna852872.
- ↑ Jones, Morris (3 April 2013). "Shenzhou's Shadow Crew". Space Daily. http://www.spacedaily.com/reports/Shenzhous_Shadow_Crew_999.html.
- ↑ "Astronauts of Shenzhou-10 mission meet press". Space Daily. Xinhua News Agency. 11 June 2013. http://www.spacedaily.com/reports/Astronauts_of_Shenzhou_10_mission_meet_press_999.html.
External links
- "China launches Shenzhou-9 Spacecraft". Xinhua News Agency. http://www.xinhuanet.com/english/special/shenzhou9/.
- "Shenzhou-9 Panoramic Report". People's Daily. http://english.people.com.cn/102775/205303/index.html.
- "Manned Space Mission Shenzhou-9's Docking Mission with Tiangong-1". CNTV. http://english.cntv.cn/special/shenzhou9/index.shtml.
- "Shenzhou 9 Mission Updates". http://www.spaceflight101.com/shenzhou-9-mission-updates.html.
- "Shenzhou 9 Mission Diary and Analyses". http://www.zarya.info/Diaries/China/Shenzhou/9/Shenzhou9Diary.php.
 |
 KSF
KSF