Sol (Day on Mars)
Topic: Astronomy
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
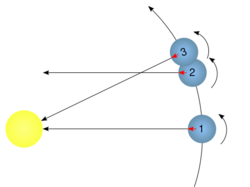
Sol (borrowed from the Latin word for sun) is a Mars solar day; that is, a Mars-day. A sol is the apparent interval between two successive returns of the Sun to same meridian (sundial time) as seen by an observer on Mars. The sol was originally adopted in 1976 during the Viking Lander missions and is a measure of time mainly used by NASA when, for example, scheduling the use of the Mars rover.[1]
Length
The duration of this day-and-night cycle (one day) is 24 hours, 39 minutes and 35.244 seconds.
The sidereal rotational period of Mars - its rotation compared to the fixed stars - is only 24 hours, 37 minutes and 22.66 seconds. The solar day lasts slightly longer because of its orbit around the sun which requires it to turn slightly further on its axis.
Future / Science Fiction
Considering a possible colonization of Mars, the question arises: how does one convert the Sol to standard Earth time? In the science fiction series Mars trilogy by Kim Stanley Robinson, the Mars settlers use traditional Earth watches that stop ticking at midnight for 39 minutes and 40 seconds before resuming their timekeeping. This creates something like a "witching hour" which compensates for the time difference between a Sol and an Earth day. This follows the method previously given by Philip K. Dick in his novel Martian Time-Slip.
An alternative idea was suggested in 1988 by David Powell (the Davidian Mars calendar). In this case the clocks simply run slower than the ones on Earth so that their hour hands complete two cycles per one Sol. For example, 1 Mars-second is 1.027 Earth-seconds, 1 Mars-minute is 61.62 Earth-seconds, and 1 Mars-hour is 61 minutes and 36.968 Earth-seconds.
See also
References
- ↑ Allison, Michael; Schmunk, Robert (June 30, 2015). "Technical Notes on Mars Solar Time as Adopted by the Mars24 Sunclock". National Aeronautics and Space Administration. https://www.giss.nasa.gov/tools/mars24/help/notes.html.
 KSF
KSF