Zwicky (crater)
Topic: Astronomy
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
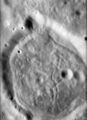
 Crater Zwicky (big eroded crater in the bottom and center of the image) as seen by a mapping camera attached to the Service Module of Apollo 17 | |
| Diameter | 126 km |
|---|---|
| Depth | 4.0 km (2.5 mi)[1][2] |
| Colongitude | 192° at sunrise |
Zwicky is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon. It lies to the west of the crater Aitken, and is attached to the western rim of Vertregt. Attached to the northern end of Zwicky is Heaviside. Zwicky is a considerably eroded formation with an irregular rim and interior. Portions of the southern rim still survive, but the remainder has been almost completely eradicated.
The satellite crater Zwicky N, located in the midst of the interior of Zwicky, has a relatively dark floor by comparison with the surrounding terrain. This smaller crater has a polygonal outline with relatively smooth inner walls. The interior floor is a lower albedo material that has a cracked surface. It is thought that this is caused by the cooling of molten material, or possibly tectonic movement. This is referred to informally as a "turtleback crater floor".
The crater is named after astronomer Fritz Zwicky (1898–1974), a professor at Caltech, Pasadena and pioneer in the study of supernovae and of galaxy clusters. The minor planet 1803 Zwicky is also named in his honour.[3]
Satellite craters
By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter on the side of the crater midpoint that is closest to Zwicky. Zwicky N crater had the proposed name of Ibn Hayyan,[1][2] but this was not approved by the IAU.
| Zwicky | Coordinates | Diameter, km |
|---|---|---|
| N | [ ⚑ ] 15°55′S 167°34′E / 15.92°S 167.57°E | 29.6 |
| R | [ ⚑ ] 18°08′S 163°35′E / 18.13°S 163.59°E | 29.0 |
| S | [ ⚑ ] 16°05′S 162°47′E / 16.09°S 162.79°E | 45.6 |
-
Zwicky N from Apollo 17 panoramic camera
-
Another view of Zwicky N from Apollo 17
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 LTO-103B2 Zwicky, Lunar Topographic Orthophotomap (LTO) Series, Publisher: Defense Mapping Agency, Scale: 1:250,000.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 LTO-85C3 Ibn Hayyan, Lunar Topographic Orthophotomap (LTO) Series, Publisher: Defense Mapping Agency, Scale: 1:250,000.
- ↑ Schmadel, Lutz D. (2007). "(1803) Zwicky". Dictionary of Minor Planet Names – (1803) Zwicky. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. p. 144. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-29925-7_1804. ISBN 978-3-540-00238-3.
- Andersson, L. E.; Whitaker, E. A. (1982). NASA Catalogue of Lunar Nomenclature. NASA RP-1097.
- Blue, Jennifer (July 25, 2007). "Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature". USGS. https://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/Feature/6770.
- Bussey, B.; Spudis, P. (2004). The Clementine Atlas of the Moon. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-81528-4.
- Cocks, Elijah E.; Cocks, Josiah C. (1995). Who's Who on the Moon: A Biographical Dictionary of Lunar Nomenclature. Tudor Publishers. ISBN 978-0-936389-27-1. https://archive.org/details/isbn_9780936389271.
- McDowell, Jonathan (July 15, 2007). "Lunar Nomenclature". Jonathan's Space Report. http://host.planet4589.org/astro/lunar/.
- Moore, Patrick (2001). On the Moon. Sterling Publishing Co.. ISBN 978-0-304-35469-6. https://archive.org/details/patrickmooreonmo00patr.
- Whitaker, Ewen A. (1999). Mapping and Naming the Moon. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-62248-6.
External links
- LTO-85C3, Ibn Hayyan, Lunar Topographic Orthophotomap (LTO) Series, Defense Mapping Agency, Scale: 1:250,000
 |
 KSF
KSF