BZIP intron basidiomycota
Topic: Biology
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 1 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 1 min
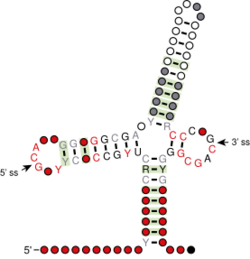
Consensus secondary structure and sequence conservation of bZIP intron in Basidiomycota
The bZIP intron basidiomycota is an unconventional bZIP intron found mainly in the Basidiomycota and some Mucoromycotina fungi. The consensus RNA structure is formed by three hairpins - two well conserved at the 5’ and 3’ ends and a variable one in between them.[1] The loop regions of 5’ and 3’ hairpins define the splice sites recognised by Ire1, which performs the unconventional splicing in response to ER stress. In Basidiomycota, splicing results in excised introns from 20 to 101 nt in length and it was first described in Cryptococcus neoformans.[2]
References
- ↑ "Conserved RNA structures in the non-canonical Hac1/Xbp1 intron". RNA Biol 8 (4): 552–556. 2011. doi:10.4161/rna.8.4.15396. PMID 21593604.
- ↑ Cheon, Seon Ah; Jung, Kwang-Woo; Chen, Ying-Lien; Heitman, Joseph; Bahn, Yong-Sun; Kang, Hyun Ah (2011). Doering, Tamara L.. ed. "Unique Evolution of the UPR Pathway with a Novel bZIP Transcription Factor, Hxl1, for Controlling Pathogenicity of Cryptococcus neoformans" (in en). PLOS Pathogens 7 (8): e1002177. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1002177. ISSN 1553-7374. PMID 21852949.
 |
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Biology:BZIP_intron_basidiomycota14 views | Status: cached on August 10 2024 08:24:57↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF