CEFIP
Topic: Biology
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 10 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 10 min
Cardiac-enriched FHL2-interacting protein (CEFIP) is a protein encoded by the gene C10orf71 on chromosome 10 open reading frame 71.[1][2] It is primarily understood that this gene is moderately expressed in muscle tissue and cardiac tissue.[3][4]
Gene
The cytogenic locus is found at 10q11.23.[1] C10orf71 encodes 28294 base pairs (bp) within chromosome 10 at 49299193-49327487 bp.[1] It is located on the plus strand and is flanked by several other genes.[1]

mRNA
The mRNA sequence of C10orf71 has 3 exons and 10 stop codons in the favorable splice form.[1][6] The two alternative splice forms had 47 and 75 stop codons interspersed throughout the sequence so they were not utilized to obtain further sequence information. The main splice form that was analyzed had the ten stop codons interspersed throughout the 5' and 3' UTR, which was why this splice form was utilized to further analyze. The mRNA of the Homo sapiens ortholog of C10orf71was 5286 bp in length.[1][6]
| Splice 1 | Stop Codons found starting at bp: 4, 150, 247, 310, 4645, 4774, 4783, 4855, 4986, and 5250
Exons found between bp: 431/432, 544/545, and 5285/5286 Kozak site found at bp 332-334 |
| Splice 2 | 47 Stop Codons found interspersed throughout the entire sequence |
| Splice 3 | 75 stop codons found interspersed throughout the entire sequence |
The three alternative splice forms found of C10orf71 mRNA sequence and the locations stop codons, exons and the Kozak site found in Splice 1. Splice 1 was utilized to analyze and obtain information about as all of the stop codons found in this splice form were found in the 5' and 3' UTR regions of the sequence. There were three exons found in Splice 1 with a Kozak consensus sequence in the overall sequence as well.[1][6]
Protein
The mature Homo sapiens homolog of the CEFIP protein encoded by C10orf71 is 1435 amino acids (aa) in length and weighs approximately 156.5 kDa.[6] This homolog has an isoelectric point of 5.94.[6] The range of pH values from Homo sapiens to the latest ortholog analyzed, Rhincodon types, ranged from 5.94-6.93, with it gradually increasing as it went later in the divergence of the ortholog.[6]
| Species | Length (aa) | Molecular Weight (kDa) | Isoelectric point |
| Homo sapiens | 1,435 | 156.5 | 5.94 |
| Gorilla gorilla | 1,435 | 156.2 | 5.91 |
| Mus muculus | 1,412 | 154.5 | 5.81 |
| Gallus gallus | 1,521 | 167.7 | 6.15 |
| Rhincodon typus | 1,253 | 138.8 | 6.93 |
Comparison of some of the orthologs analyzed when compared to Homo sapiens. The orthologs are arranged from species that are most closely related to the Homo sapiens ortholog to least closely related (top to bottom respectively).[6]
Composition of protein
CEFIP is predicted to be a non-transmembrane, soluble protein.[7] It is predicted to be a nuclear protein with 91.3% confidence with it being fairly confident to be a nuclear protein throughout the orthologs. There was one positive charge cluster found in CEFIP protein sequence, that is located from amino acids 1165–1193.[6] This cluster was moderately conserved throughout the orthologs analyzed. There was also a mixed charge cluster found in the Homo sapiens' sequence of this protein, located from amino acid 750–778, although this cluster was not highly conserved throughout the analyzed orthologs.[6] There was one repeat sequence found as well, TASKPPA, located at amino acids 163-169 and 116–1172. This protein is Proline and Serine rich as well.[6]
| Species | Nuclear | Cytoplasmic | Cytoskeletal |
| Homo sapiens | 91.3% | 4.3% | 4.3% |
| Gorilla gorilla | 91.3% | 4.3% | 4.3% |
| Mus musculus | 82.6% | 13.0% | — |
| Gallus gallus | 69.6% | 17.4% | 4.3% |
| Rhincodon typus | 69.6% | 21.7% | — |

Domains and motifs
One confirmed domain of unknown function (DUF) was found within the CEFIP protein sequence, DUF4585.[1] DUF4585 is located on the Homo sapiens protein sequence from amino acid 311–334. DUF4585 was highly conserved throughout the orthologs that were analyzed. There was also a small vacuolar targeting motif (VAC) found within the analyzed protein sequence spanning amino acids 543–546.
Protein structure
The mature CEFIP protein contains nuclear localization signals (NLS), pat4 (RKPK at aa 382, RPRK at aa 640, KRRK at aa 1190) and pat7 (PPWRKPK at aa 379 and PWRKPKT at aa 380) with an NLS score of 0.94. A secondary structure was constructed with a 6.1% confidence level.[7]
Post-translational modifications
There were seven GlcNAc O-glycosylation sites predicted within the protein sequence found at amino acids 116, 120, 139, 165, 468, 470, and 844.[7] There were also several phosphorylation sites found interspersed throughout the sequence. One propeptide cleavage site was predicted at amino acid 38.[7] There were three predicted sumoylation sites found at amino acids 599, 890, and 1176.
Expression
The C10orf71 mRNA was found to be highly expressed in cardiac, muscle, and liver tissue (biology).[1]
Regulation of expression
There were 6 possible promoters found in the sequence. Promoter GXP_6729162 is 1403 bp in length.[9] This promoter had several transcription factors of interest including those involved with myocytes.[9]
Function
There is little scientific information known about the function of CEFIP.
Interacting proteins
There was a total of 25 proteins generated that were predicted to interact with CEFIP (Homo sapiens ortholog).[10][11] Most of the interactions predicted were physical interactions with CEFIP.[10] These interactions were discovered through a variety of mechanisms including, but not limited to: affinity chromatography, microarray analysis, and tandem mass spectrometry among others.[10][11] Refer to table for details about the interacting proteins of CEFIP.[12]
| Interacting Protein | Name of Protein | Known Function | Location Expressed or Associated Diseases |
| C20orf78 | Chromosome 20 Open Reading Frame 78 | Unknown | Unconfirmed |
| BPIFA2[13] | BPI Fold Containing Family A Member 2 | Plays a role in antibacterial resistance in upper respiratory pathway | Expressed in salivary glands |
| PPIL6[14] | Peptidyl Prolyl Isomerase Like 6 | Accelerates folding of proteins | Unconfirmed |
| KIF17[15] | Kinesin Family Member 17 | Transports vesicles containing NMDA receptor 2B | Expressed in microtubules |
| KRT78[16] | Keratin 78 | Forms cytoplasmic network; encodes proteins with intermediate filament domains | Expressed in intermediate filaments |
| TBX4[17] | T-box4 Transcription Factor | Encode transcription factors involved in regulation of developmental processes; assists with regulation of mesoderm differentiation; could play a role in limb pattern formation | Associated with Small Patella Syndrome and Heritable Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension |
| DNAH8[18] | Dynein Axonemal Heavy Chain 8 | heavy chain of an axonemal dynein involved in sperm and respiratory cilia motility. | Associated with Colchicine Resistance and Mitochondrial Complex V Deficiency, Nuclear Type 1 |
| TSPAN17[19] | Tetraspanin 17 | Predicted to regulate ADAM10 maturation | Unconfirmed |
| C14orf80[20] | Chromosome 14 Open Reading Frame 80 | Unknown | Unconfirmed |
| SLC35F4[21] | Solute Carrier Family 35 Member F4 | Solute transporter | Unconfirmed |
| LHX4[22] | LIM Homeobox 4 | Predicted to play a role in maturing lungs, development of respiratory mechanisms, and development of the pituitary gland | Associated with Pituitary Hormone Deficiency, Combined 4 and Lhx4=Related Combined Pituitary Hormone |
| FAM53A[23] | Family With Sequence Similarity 53 Member A | Plays a role in neural development | Possibly expressed in ventricle tissue |
| GRIK5[24] | Glutamate Ionotropic Receptor Kainase Type Subunit 5 | Forms functional heteromeric kainite-preferring ionic channels | Associated with Schizophrenia |
| FADS2[25] | Fatty Acid Denaturase 2 | Regulates unsaturation of fatty acids through introduction of double bonds between define Cysteines of the fatty acid chains | Associated with Best Vitelliform Macular Dystrophy |
| GDF2[26] | Growth Differentiation Factor 2 | Regulates cartilage and bone development; differentiation of cholinergic receptors in CNS | Unconfirmed |
| C17orf77[27] | Chromosome 17 Open Reading Frame 77 | Unknown | Unconfirmed |
| CFAP45 (CCDC19)[28] | Cilia And Flagella Associated Protein 45 | Associated with pharynx cancer | Unconfirmed |
| DCST2[29] | DC-STAMP Domain Containing 2 | Unknown | Unconfirmed |
| CTXN1[30] | Cortexin 1 | Predicted to play a role in IC or EC signaling of the cortical neurons during the development of the forebrain. | Unconfirmed |
| C19orf68[31] | Chromosome 19 Open Reading Frame 68 | Unknown | Unconfirmed |
| DCAF7[32] | DDB1 And CUL4 Associated Factor 7 | It's been shown to function as a scaffold protein in kinase signaling. It's also been known to be involved with craniofacial development | Unconfirmed |
| DYRK1A[33] | Dual Specificity YAK1-Related Kinase | May play a role in brain development and cell proliferation; nuclear localized protein | Associated with Mental Retardation, Autosomal Dominant 7 and Microcephaly |
| DYRK1B[34] | Dual Specificity Tyrosine-(Y)-Phosphorylation Regulated Kinase 1B | Plays a role in the cell cycle; nuclear-localized protein | Associated with Abdominal Obesity-Metabolic Syndrome 3 and Abdominal Obesity-Metabolic Syndrome |
| FNTA[35] | Protein Farnesyltransferase/Geranylgeranyltransferase Type-1 Subunit Alpha | Helps regulate neuromuscular junction development | Unconfirmed |
| FNTB[36] | Protein Farnesyltransferase Subunit Beta | Catalyzes the transfer of a farnesyl moiety from farnesyl diphosphate to a cysteine | Unconfirmed |
Interacting proteins, their function if known, and any tissues they have been found or predicted to be expressed in and any diseases they have been associated with.[10][11][12]
Homologs
Paralogs
There are currently no known paralogs to the C10orf71 gene.
Orthologs
C10orf71 is known to have 68 orthologs in various species including primates (11 species), rodents (8 species), Laurasiatheria carnivores (14 species), Placental mammals (38 species), Sauropsida birds and reptiles (7 species), and fish (11 species).[37] The highly conserved sequences are primarily from primates with the identity percentage of these species being >90%, whereas species such as reptiles, birds, and fish had an identity percentage ≤30%.[6] Refer to table for additional information on dates of divergence, sequence length, and sequence identity and similarity for orthologs. C10orf71 is not present in prokaryotes, archaea, or fungi.[37]
| Abbreviation (for Phylogenetic Tree) | Species | Common Name | Protein Accession # | Estimated Date of Divergence (MYA) | Sequence Length (aa) | Sequence Identity to Human mRNA/protein (%) | Sequence Similarity to Human mRNA/protein (%) |
| HomS | Homo sapiens | human | NP_001128668.1 | 1435 | 100 | 100 | |
| GorG | Gorilla gorilla | western gorilla | XP_018889898.1 | 9.06 | 1435 | 98.3 | 98.7 |
| RhiR | Rhinopithecus roxellana | Golden snub-nosed monkey | XP_010381152.1 | 29.44 | 1435 | 93.4 | 95.3 |
| OtoG | Otolemur garnettii | small-eared galago | XP_003801705.1 | 74 | 1419 | 74.9 | 81.5 |
| TupC | Tupaia chinensis | Chinese tree shrew | XP_014439281.1 | 82 | 1186 | 61.5 | 67.8 |
| MusM | Mus musculus | house mouse | NP_001182026.1 | 90 | 1412 | 65.4 | 74.3 |
| OctD | Octodon degus | Common degu | XP_004647022.1 | 90 | 1407 | 63.3 | 73.1 |
| HetG | Heterocephalus glaber | Naked mole-rat | XP_004874589.1 | 90 | 1411 | 63.2 | 73.3 |
| CerS | Ceratotherium simum simum | Southern white rhinoceros | XP_004432504.1 | 96 | 1436 | 74 | 81 |
| OrcO | Orcinus orca | killer whale | XP_004286436 | 96 | 1433 | 72.6 | 79.4 |
| LoxA | Loxodonta Africana | African bush elephant | XP_003408977.1 | 105 | 1438 | 65.5 | 74.5 |
| SarH | Sarcophilus harrisii | Tasmanian devil | XP_003755230.2 | 159 | 1470 | 49.0 | 62.5 |
| GavG | Gavialis gangeticus | crocodile | XP_019358113.1 | 312 | 1538 | 32.8 | 46.7 |
| TinG | Tinamus guttatus | White-throated tinamou | XP_010216992.1 | 312 | 1529 | 32.4 | 46.3 |
| PelS | Pelodiscus sinensis | turtle | XP_006118195.1 | 312 | 1505 | 32.0 | 46.2 |
| GalG | Gallus gallus | chicken | XP_421655.3 | 312 | 1521 | 30.5 | 44.7 |
| MelU | Melopsittacus undulates | parrot | XP_005153970 | 312 | 1538 | 30.3 | 45.1 |
| OreN | Oreochromis niloticus | Nile tilapia | XP_019221822 | 435 | 661 | 12.0 | 18.7 |
| SclF | Scleropages formosus | Asian arowana | XP_018580403 | 435 | 3125 | 11.5 | 17.9 |
| DanR | Danio rerio | Zebrafish | XP_005157004.1 | 435 | 3591 | 9.2 | 16.0 |
| CluH | Clupea harengus | Atlantic herring | XP_012687674.1 | 435 | 3633 | 9.1 | 13.8 |
| RhiT | Rhincodon typus | whale shark | XP_020385611.1 | 473 | 1253 | 40.0 | 24.8 |
Ortholog table in descending order to latest ortholog diverged. This table compares the orthologs analyzed, their species names, common names, dates of divergence from Homo sapiens ortholog (MYA), length (aa), and percentage of similarity and identity.[1][6][37][38]
Phylogeny
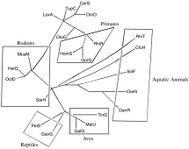
A phylogenetic tree was constructed for the orthologs that were analyzed in comparison to Homo sapiens. With the species of latest divergence being Rhincodon types, or the whale shark.[37][38]
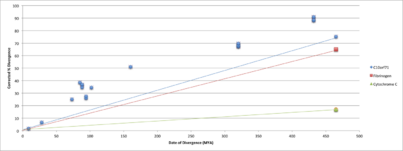
Evolutionary rate
C10orf71's rate of divergence was faster than that of fibrinogen or Cytochrome C.[37]
Clinical significance
There was a microarray experiment that also showed evidence that C10orf71's expression was lowered in skeletal muscle tissues that experienced sepsis.[39] There was clinical significance found in the expression level of C10orf71 in an experiment looking at those with Myotonic dystrophy.[39] One microarray analysis produced results that showed C10orf71's expression level decreased in those with prostate cancer as well.[39]
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 "Home - Gene - NCBI". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/118461.
- ↑ "HGNC database of human gene names | HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee" (in en). https://www.genenames.org/cgi-bin/gene_symbol_report?hgnc_id=HGNC:26973.
- ↑ "Home - UniGene - NCBI". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/UniGene/clust.cgi?UGID=1954269&TAXID=9606&SEARCH=homo%20sapiens%20c10orf71.
- ↑ Thierry-Mieg, Danielle; Thierry-Mieg, Jean (2012-10-16). "AceView a comprehensive annotation of human and worm genes with mRNAs or ESTsAceView.". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/IEB/Research/Acembly/.
- ↑ "National Center for Biotechnology Information" (in en). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- ↑ 6.00 6.01 6.02 6.03 6.04 6.05 6.06 6.07 6.08 6.09 6.10 6.11 Workbench, NCSA Biology. "SDSC Biology Workbench". http://seqtool.sdsc.edu.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 "ExPASy: SIB Bioinformatics Resource Portal - Home" (in en-US). https://www.expasy.org.
- ↑ "i-TASSER". https://zhanglab.ccmb.med.umich.edu/.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 "Genomatix: Genome Annotation and Browser: Query Input" (in en-US). https://www.genomatix.de/cgi-bin/eldorado/eldorado.pl?s=fb6b06f30e675413be702c154ef0fb1a.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 "GeneMANIA". http://genemania.org.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 Lab, Mike Tyers. "BioGRID | Database of Protein, Chemical, and Genetic Interactions" (in en). https://thebiogrid.org/125609/summary/homo-sapiens/c10orf71.html.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "GeneCards - Human Genes | Gene Database | Gene Search". https://www.genecards.org.
- ↑ Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "BPIFA2 Gene - GeneCards | BPIA2 Protein | BPIA2 Antibody". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=BPIFA2&keywords=BPIFA2.
- ↑ Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "PPIL6 Gene - GeneCards | PPIL6 Protein | PPIL6 Antibody". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=PPIL6&keywords=ppil6.
- ↑ Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "KIF17 Gene - GeneCards | KIF17 Protein | KIF17 Antibody". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=KIF17&keywords=kif17.
- ↑ Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "KRT78 Gene - GeneCards | K2C78 Protein | K2C78 Antibody". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=KRT78&keywords=krt78.
- ↑ Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "TBX4 Gene - GeneCards | TBX4 Protein | TBX4 Antibody". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=TBX4&keywords=tbx4.
- ↑ Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "DNAH8 Gene - GeneCards | DYH8 Protein | DYH8 Antibody". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=DNAH8&keywords=dnah8.
- ↑ Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "TSPAN17 Gene - GeneCards | TSN17 Protein | TSN17 Antibody". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=TSPAN17&keywords=tspan17.
- ↑ Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "C14orf80 Gene - GeneCards | CN080 Protein | CN080 Antibody". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=C14orf80&keywords=c14orf80.
- ↑ Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "SLC35F4 Gene - GeneCards | S35F4 Protein | S35F4 Antibody". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=SLC35F4&keywords=SLC35F4.
- ↑ Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "LHX4 Gene - GeneCards | LHX4 Protein | LHX4 Antibody". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=LHX4&keywords=lhx4.
- ↑ Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "FAM53A Gene - GeneCards | FA53A Protein | FA53A Antibody". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=FAM53A&keywords=FAM53A.
- ↑ Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "GRIK5 Gene - GeneCards | GRIK5 Protein | GRIK5 Antibody". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=GRIK5&keywords=grik5.
- ↑ Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "FADS2 Gene - GeneCards | FADS2 Protein | FADS2 Antibody". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=FADS2&keywords=fads2.
- ↑ Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "GDF2 Gene - GeneCards | GDF2 Protein | GDF2 Antibody". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=GDF2&keywords=gdf2.
- ↑ Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "C17orf77 Gene - GeneCards | CQ077 Protein | CQ077 Antibody". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=C17orf77&keywords=c17orf77.
- ↑ Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "CFAP45 Gene - GeneCards | CFA45 Protein | CFA45 Antibody". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=CFAP45&keywords=cfap45.
- ↑ Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "DCST2 Gene - GeneCards | DCST2 Protein | DCST2 Antibody". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=DCST2&keywords=dcst2.
- ↑ Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "CTXN1 Gene - GeneCards | CTXN1 Protein | CTXN1 Antibody". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=CTXN1&keywords=ctxn1.
- ↑ Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "C19orf68 Gene - GeneCards | CS068 Protein | CS068 Antibody". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=C19orf68&keywords=C19orf68.
- ↑ Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "DCAF7 Gene - GeneCards | DCAF7 Protein | DCAF7 Antibody". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=DCAF7&keywords=dcaf7.
- ↑ Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "DYRK1A Gene - GeneCards | DYR1A Protein | DYR1A Antibody". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=DYRK1A&keywords=dyrk1a.
- ↑ Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "DYRK1B Gene - GeneCards | DYR1B Protein | DYR1B Antibody". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=DYRK1B&keywords=dyrk1b.
- ↑ Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "FNTA Gene - GeneCards | FNTA Protein | FNTA Antibody". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=FNTA&keywords=fnta.
- ↑ Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "FNTB Gene - GeneCards | FNTB Protein | FNTB Antibody". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=FNTB&keywords=fntb.
- ↑ 37.0 37.1 37.2 37.3 37.4 "BLAST: Basic Local Alignment Search Tool". https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi.
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 "TimeTree :: The Timescale of Life". http://timetree.org.
- ↑ 39.0 39.1 39.2 "Home - GEO Profiles - NCBI". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geoprofiles/.
 |
 KSF
KSF