Cell death
Topic: Biology
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 11 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 11 min

Cell death is the event of a biological cell ceasing to carry out its functions. This may be the result of the natural process of old cells dying and being replaced by new ones, as in programmed cell death, or may result from factors such as diseases, localized injury, or the death of the organism of which the cells are part. Apoptosis or Type I cell-death, and autophagy or Type II cell-death are both forms of programmed cell death, while necrosis is a non-physiological process that occurs as a result of infection or injury.[1]
The term "cell necrobiology" has been used to describe the life processes associated with morphological, biochemical, and molecular changes which predispose, precede, and accompany cell death, as well as the consequences and tissue response to cell death.[2] The word is derived from the Greek νεκρό meaning "death", βìο meaning "life", and λόγος meaning "the study of". The term was initially coined to broadly define investigations of the changes that accompany cell death, detected and measured by multiparameter flow- and laser scanning- cytometry.[3] It has been used to describe the real-time changes during cell death, detected by flow cytometry.[4]
Types
Programmed cell death
Programmed cell death (PCD) is cell death mediated by an intracellular program.[5][6] PCD is carried out in a regulated process, which usually confers advantage during an organism's life-cycle. For example, the differentiation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the fingers apoptose; the result is that the digits separate. PCD serves fundamental functions during both plant and metazoa (multicellular animals) tissue development.
Apoptosis
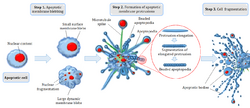
Apoptosis is the processor of programmed cell death (PCD) that may occur in multicellular organisms.[6] Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, and chromosomal DNA fragmentation. It is now thought that – in a developmental context – cells are induced to positively commit suicide whilst in a homeostatic context; the absence of certain survival factors may provide the impetus for suicide. There appears to be some variation in the morphology and indeed the biochemistry of these suicide pathways; some treading the path of "apoptosis", others following a more generalized pathway to deletion, but both usually being genetically and synthetically motivated. There is some evidence that certain symptoms of "apoptosis" such as endonuclease activation can be spuriously induced without engaging a genetic cascade, however, presumably true apoptosis and programmed cell death must be genetically mediated. It is also becoming clear that mitosis and apoptosis are toggled or linked in some way and that the balance achieved depends on signals received from appropriate growth or survival factors.[7]

Certain key proteins primarily employed in the repair of DNA damage can also induce apoptosis when DNA damage exceeds the cell’s repair capability.[8] These dual role proteins protect against proliferation of unstable damaged cells that might lead to cancer.
Autophagy
Autophagy is cytoplasmic, characterized by the formation of large vacuoles that eat away organelles in a specific sequence prior to the destruction of the nucleus.[9] Macroautophagy, often referred to as autophagy, is a catabolic process that results in the autophagosomic-lysosomal degradation of bulk cytoplasmic contents, abnormal protein aggregates, and excess or damaged organelles. Autophagy is generally activated by conditions of nutrient deprivation but has also been associated with physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection and cancer.
Other variations of PCD
Other pathways of programmed cell death have been discovered.[10] Called "non-apoptotic programmed cell-death" (or "caspase-independent programmed cell-death"), these alternative routes to death are as efficient as apoptosis and can function as either backup mechanisms or the main type of PCD.
Some such forms of programmed cell death are anoikis, almost identical to apoptosis except in its induction; cornification, a form of cell death exclusive to the eyes; excitotoxicity; ferroptosis, an iron-dependent form of cell death[11] and Wallerian degeneration.
Plant cells undergo particular processes of PCD similar to autophagic cell death. However, some common features of PCD are highly conserved in both plants and metazoa.
Activation-induced cell death (AICD) is a programmed cell death caused by the interaction of Fas receptor (Fas, CD95)and Fas ligand (FasL, CD95 ligand).[12] It occurs as a result of repeated stimulation of specific T-cell receptors (TCR) and it helps to maintain the periphery immune tolerance.[13] Therefore, an alteration of the process may lead to autoimmune diseases.[12] In the other words AICD is the negative regulator of activated T-lymphocytes.
Ischemic cell death, or oncosis, is a form of accidental, or passive cell death that is often considered a lethal injury. The process is characterized by mitochondrial swelling, cytoplasm vacuolization, and swelling of the nucleus and cytoplasm.[14]
Mitotic catastrophe is an oncosuppressive mechanism that can lead to cell death that is due to premature or inappropriate entry of cells into mitosis.[15] It is the most common mode of cell death in cancer cells exposed to ionizing radiation and many other anti-cancer treatments.[16]
Immunogenic cell death or immunogenic apoptosis is a form of cell death caused by some cytostatic agents such as anthracyclines, oxaliplatin and bortezomib, or radiotherapy and photodynamic therapy (PDT).[17]
Pyroptosis is a highly inflammatory form of programmed cell death that occurs most frequently upon infection with intracellular pathogens and is likely to form part of the antimicrobial response in myeloid cells.[3]
PANoptosis is an innate immune, lytic cell death pathway initiated by innate immune sensors and driven by caspases and RIP kinases through PANoptosome complexes. To date, several PANoptosome complexes have been characterized, including ZBP1-, AIM2-, RIPK1-, NLRC5-/NLRP12-, and NLRP3-PANoptosomes. PANoptosis is critical in innate immune responses for host defense, but it has also been implicated in inflammation and pathology in inflammatory diseases, infections, and cancers.[18][19][20][21][22][23][24][25][26][27]
Phagoptosis is cell death resulting from a live cell being phagocytosed (i.e. eaten) by another cell (usually a phagocyte), resulting in death and digestion of the engulfed cell. Phagoptosis can occur to cells that are pathogenic, cancerous, aged, damaged or excess to requirements.[28]
Necrotic cell death
Necrosis is cell death where a cell has been badly damaged through external forces such as trauma or infection and occurs in several different forms. It is the sum of what happens to cells after their deaths.[29] In necrosis, a cell undergoes swelling, followed by uncontrolled rupture of the cell membrane with cell contents being expelled. These cell contents often then go on to cause inflammation in nearby cells.[30] A form of programmed necrosis, called necroptosis, has been recognized as an alternative form of programmed cell death. It is hypothesized that necroptosis can serve as a cell-death backup to apoptosis when the apoptosis signaling is blocked by endogenous or exogenous factors such as viruses or mutations. Necroptotic pathways are associated with death receptors such as the tumor necrosis factor receptor 1.[30] Identification of cell death was previously classified based on morphology, but in recent years switched to molecular and genetic conditions.
See also
- Programmed cell death 1, a protein
- Tumor Necrosis Factor 1
- Cell Death eBook by Rockland Immunochemicals
- Cellular anastasis
References
- ↑ Histology and Cell Biology – An Introduction to Pathology. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders. 2012.
- ↑ "Cell death mechanisms in eukaryotes". Cell Biology and Toxicology 36 (2): 145–164. April 2020. doi:10.1007/s10565-019-09496-2. PMID 31820165.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Cytometry in cell necrobiology: analysis of apoptosis and accidental cell death (necrosis)". Cytometry 27 (1): 1–20. January 1997. doi:10.1002/(sici)1097-0320(19970101)27:1<1::aid-cyto2>3.0.co;2-l. PMID 9000580.
- ↑ "Real-time flow cytometry for the kinetic analysis of oncosis". Cytometry. Part A 79 (3): 181–191. March 2011. doi:10.1002/cyto.a.21022. PMID 21254392.
- ↑ "Bacterial programmed cell death and multicellular behavior in bacteria". PLOS Genetics 2 (10): e135. October 2006. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.0020135. PMID 17069462.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Means To An End. New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. 2011. ISBN 978-0-87969-887-4. http://celldeathbook.wordpress.com/.
- ↑ "Apoptosis or programmed cell death?". Cell Biology International 17 (4): 365–380. April 1993. doi:10.1006/cbir.1993.1075. PMID 8318948.
- ↑ "DNA repair/pro-apoptotic dual-role proteins in five major DNA repair pathways: fail-safe protection against carcinogenesis". Mutat Res 511 (2): 145–178. June 2002. doi:10.1016/s1383-5742(02)00009-1. PMID 12052432. Bibcode: 2002MRRMR.511..145B.
- ↑ "Do all programmed cell deaths occur via apoptosis?". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 90 (3): 980–984. February 1993. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.3.980. PMID 8430112. Bibcode: 1993PNAS...90..980S.;and, for a more recent view, see "Programmed cell death (PCD). Apoptosis, autophagic PCD, or others?". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 926 (1): 1–12. 2000. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb05594.x. PMID 11193023. Bibcode: 2000NYASA.926....1B.
- ↑ "Caspase-independent cell death". Nature Medicine 11 (7): 725–730. July 2005. doi:10.1038/nm1263. PMID 16015365.
- ↑ "Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death". Cell 149 (5): 1060–1072. May 2012. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042. PMID 22632970.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 "Activation-induced cell death in T cells and autoimmunity". Cellular & Molecular Immunology 1 (3): 186–192. June 2004. PMID 16219166.
- ↑ "Antigen-induced death of T-lymphocytes". Frontiers in Bioscience: A Journal and Virtual Library 2 (4): d61–d77. February 1997. doi:10.2741/a175. PMID 9159213.
- ↑ "Oncosis". Cell Communication Online Pathfinder Encyclopaedia (COPE). http://www.copewithcytokines.de/cope.cgi?key=Oncosis. Retrieved 10 August 2010.
- ↑ "Mitotic catastrophe: a mechanism for avoiding genomic instability". Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology 12 (6): 385–392. June 2011. doi:10.1038/nrm3115. PMID 21527953.
- ↑ "Mitotic Catastrophe in Apoptosis, Senescence, and Cancer". Revista Brasileira de Ciências Farmacêuticas. 44. Humana Press. 2007. pp. 73–91. doi:10.1007/978-1-59745-221-2. ISBN 978-1-58829-527-9. http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1516-93322008000100021.
- ↑ "Immunogenic cell death, DAMPs and anticancer therapeutics: an emerging amalgamation". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Cancer 1805 (1): 53–71. January 2010. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2009.08.003. PMID 19720113. https://lirias.kuleuven.be/bitstream/123456789/632508/2/BBA-RC%20Review%20-%20Final%20Revised%20MS.doc.
- ↑ "St. Jude finds NLRP12 as a new drug target for infection, inflammation and hemolytic diseases" (in en). https://www.stjude.org/media-resources/news-releases/2023-medicine-science-news/st-jude-finds-nlrp12-as-a-new-drug-target.html.
- ↑ "Caspase-6 Is a Key Regulator of Innate Immunity, Inflammasome Activation, and Host Defense". Cell 181 (3): 674–687.e13. 2020-04-30. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.040. ISSN 1097-4172. PMID 32298652.
- ↑ "Identification of the PANoptosome: A Molecular Platform Triggering Pyroptosis, Apoptosis, and Necroptosis (PANoptosis)". Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 10: 237. 2020. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2020.00237. ISSN 2235-2988. PMID 32547960.
- ↑ "AIM2 forms a complex with pyrin and ZBP1 to drive PANoptosis and host defence". Nature 597 (7876): 415–419. September 2021. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03875-8. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 34471287. Bibcode: 2021Natur.597..415L.
- ↑ "RIPK1 Distinctly Regulates Yersinia-Induced Inflammatory Cell Death, PANoptosis". ImmunoHorizons 4 (12): 789–796. 2020-12-11. doi:10.4049/immunohorizons.2000097. ISSN 2573-7732. PMID 33310881.
- ↑ "NLRP12-PANoptosome activates PANoptosis and pathology in response to heme and PAMPs". Cell 186 (13): 2783–2801.e20. 2023-06-22. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2023.05.005. ISSN 1097-4172. PMID 37267949.
- ↑ "NLRC5 senses NAD+ depletion, forming a PANoptosome and driving PANoptosis and inflammation". Cell 187 (15): 4061–4077.e17. June 2024. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2024.05.034. ISSN 0092-8674. PMID 38878777.
- ↑ "St. Jude scientists solve decades long mystery of NLRC5 sensor function in cell death and disease" (in en). https://www.stjude.org/media-resources/news-releases/2024-medicine-science-news/scientists-solve-decades-long-mystery-of-nlrc5-sensor-function-in-cell-death.html.
- ↑ "It's All in the PAN: Crosstalk, Plasticity, Redundancies, Switches, and Interconnectedness Encompassed by PANoptosis Underlying the Totality of Cell Death-Associated Biological Effects". Cells 11 (9): 1495. April 2022. doi:10.3390/cells11091495. PMID 35563804.
- ↑ "Therapeutic potential of PANoptosis: innate sensors, inflammasomes, and RIPKs in PANoptosomes". Trends in Molecular Medicine 30 (1): 74–88. January 2024. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2023.10.001. ISSN 1471-499X. PMID 37977994.
- ↑ "Cell death by phagocytosis". Nature Reviews. Immunology 24 (2): 91–102. February 2024. doi:10.1038/s41577-023-00921-6. PMID 37604896.
- ↑ "Apoptosis, Pyroptosis, and Necrosis: Mechanistic Description of Dead and Dying Eukaryotic Cells". Infection and Immunity 73 (4): 1907–1916. April 2005. doi:10.1128/IAI.73.4.1907-1916.2005. PMID 15784530.
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 "Cell death: a review of the major forms of apoptosis, necrosis and autophagy". Cell Biology International 43 (6): 582–592. June 2019. doi:10.1002/cbin.11137. PMID 30958602.
 |
 KSF
KSF