Chromosome 2
Topic: Biology
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 12 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 12 min
| Chromosome 2 | |
|---|---|
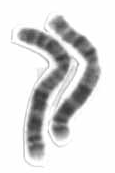 Human chromosome 2 pair after G banding. One is from mother, one is from father. | |
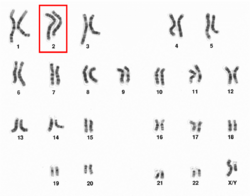 Chromosome 2 pair in human male karyogram. | |
| Features | |
| Length (bp) | 242,696,752 bp (CHM13) |
| No. of genes | 1,194 (CCDS)[1] |
| Type | Autosome |
| Centromere position | Submetacentric[2] (93.9 Mbp[3]) |
| Complete gene lists | |
| CCDS | Gene list |
| HGNC | Gene list |
| UniProt | Gene list |
| NCBI | Gene list |
| External map viewers | |
| Ensembl | Chromosome 2 |
| Entrez | Chromosome 2 |
| NCBI | Chromosome 2 |
| UCSC | Chromosome 2 |
| Full DNA sequences | |
| RefSeq | NC_000002 (FASTA) |
| GenBank | CM000664 (FASTA) |

Chromosome 2 is one of the twenty-three pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 2 is the second-largest human chromosome, spanning more than 242 million base pairs[4] and representing almost eight percent of the total DNA in human cells.
Chromosome 2 contains the HOXD homeobox gene cluster.[5]
Chromosomes
Humans have only twenty-three pairs of chromosomes, while all other extant members of Hominidae have twenty-four pairs.[6] It is believed that Neanderthals and Denisovans had twenty-three pairs.[6]
Human chromosome 2 is a result of an end-to-end fusion of two ancestral chromosomes.[7][8][9] The evidence for this includes:
- The correspondence of chromosome 2 to two ape chromosomes. The closest human relative, the chimpanzee, has nearly identical DNA sequences to human chromosome 2, but they are found in two separate chromosomes. The same is true of the more distant gorilla and orangutan.[10][11]
- The presence of a vestigial centromere. Normally a chromosome has just one centromere, but in chromosome 2 there are remnants of a second centromere in the q21.3–q22.1 region.[12]
- The presence of vestigial telomeres. These are normally found only at the ends of a chromosome, but in chromosome 2 there are additional telomere sequences in the q13 band, far from either end of the chromosome.[13]
| “ | We conclude that the locus cloned in cosmids c8.1 and c29B is the relic of an ancient telomere-telomere fusion and marks the point at which two ancestral ape chromosomes fused to give rise to human chromosome 2. | ” |
| — Jacob W. Ijdo[13] | ||
Genes
Number of genes
The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 2. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome vary. Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project (CCDS) takes an extremely conservative strategy. So CCDS's gene number prediction represents a lower bound on the total number of human protein-coding genes.[14]
| Estimated by | Protein-coding genes | Non-coding RNA genes | Pseudogenes | Source | Release date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CCDS | 1,194 | — | — | [1] | 2016-09-08 |
| HGNC | 1,196 | 450 | 931 | [15] | 2017-05-12 |
| Ensembl | 1,292 | 1,598 | 1,029 | [16] | 2017-03-29 |
| UniProt | 1,274 | — | — | [17] | 2018-02-28 |
| NCBI | 1,281 | 1,446 | 1,207 | [18][19][20] | 2017-05-19 |
List of genes
The following is a partial list of genes on human chromosome 2. For complete list, see the link in the infobox on the right.
p-arm
Partial list of the genes located on p-arm (short arm) of human chromosome 2:
- ACTR2: encoding protein Actin-related protein 2
- ADI1: encoding enzyme 1,2-dihydroxy-3-keto-5-methylthiopentene dioxygenase
- AFF3: encoding protein AF4/FMR2 family member 3
- AFTPH: encoding protein Aftiphilin
- ALMS1: Alstrom syndrome 1
- ABCG5 and ABCG8: ATP-binding cassette, subfamily A, members 5 and 8
- ASXL2: Additional sex combs like 2, transcriptional regulator
- ATOH8: encoding protein Atonal bHLH transcription factor 8
- ATRAID: encoding protein Apoptosis-related protein 3
- BCYRN1: BC200 lncRNA
- C2orf16: unknown protein C2orf16
- CAPG: capping acting protein
- CCDC104: Coiled-coil domain containing 104
- CCDC142: Coiled-coil domain containing 142
- CCDC142: Coiled-Coil Domain Containing 142
- CGREF1: encoding protein Cell growth regulator with EF-hand domain 1
- CLEC4F: encoding protein C-type lectin domain family 4 member F
- CTLA4: cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Antigen 4
- CYTOR: Cytoskeleton regulator RNA
- DHX57: DExH-box helicase 57
- DPYSL5: Dihydropyrimidinase like 5
- ERLEC1: Endoplasmic reticulum lectin 1
- EVA1A: encoding protein Eva-1 homolog A (C. elegans)
- EXOC6B: encoding protein Exocyst complex component 6b
- FAM49A: Family with sequence similarity 49 member A
- FAM98A: Family with sequence similarity 98 member A
- FAM136A: Family with sequence similarity 136 member A
- FBXO11: F-box protein 11
- FTH1P3: encoding protein Ferritin heavy chain 1 pseudogene 3
- GEN1 encoding protein GEN1, Holliday junction 5' flap endonuclease
- GCKR: Glucokinase regulator
- GFPT1: glutamine—fructose-6-phosphate transaminase 1
- GKN1: gastrokine 1
- GPATCH11: G-patch domain containing protein 11
- GTF2A1L: General transcription factor IIA subunit 1 like
- HADHA: hydroxyacyl-Coenzyme A dehydrogenase/3-ketoacyl-Coenzyme A thiolase/enoyl-Coenzyme A hydratase (trifunctional protein), alpha subunit
- HADHB: hydroxyacyl-Coenzyme A dehydrogenase/3-ketoacyl-Coenzyme A thiolase/enoyl-Coenzyme A hydratase (trifunctional protein), beta subunit
- HSPC159: Galectin-related protein
- ID2-AS1: encoding protein Id2 antisense rna 1 (head to head)
- LCLAT1: encoding protein Lysocardiolipin acyltransferase 1
- LEPQTL1: Leptin, serum levels of
- MBOAT2: encoding protein Membrane bound o-acyltransferase domain containing 2
- MEMO1: Mediator of cell motility 1
- MPHOSPH10: M-phase phosphoprotein 10
- MSH2: mutS homolog 2, colon cancer, nonpolyposis type 1 (E. coli)
- MSH6: mutS homolog 6 (E. coli)
- MTHFD2: Bifunctional methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase/cyclohydrolase, mitochondrial
- MTIF2: mitochondrial translational initiation factor 2
- NDUFAF7: Protein arginine methyltransferase NDUFAF7, mitochondrial
- NRBP1: Nuclear receptor-binding protein 1
- ODC1: Ornithine decarboxylase
- OTOF: otoferlin
- PAIP2B: Poly(a) binding protein interacting protein 2b
- PARK3 encoding protein Parkinson disease 3 (autosomal dominant, Lewy body)
- PCBP1-AS1: encoding protein PCBP1 antisense RNA 1
- PCYOX1: prenylcysteine oxidase 1
- PELI1: Ubiquitin ligase
- PLGLB2: Plasminogen-related protein B
- POLR1A: DNA-directed RNA polymerase I subunit RPA1
- PREPL: Prolyl endopeptidase-like
- PXDN: Peroxidasin homolog
- QPCT: Glutaminyl-peptide cyclotransferase
- RETSAT: All-trans-retinol 13,14-reductase
- RNF103: encoding protein Ring finger protein 103
- RNF103-CHMP3: encoding protein RNF103-CHMP3 readthrough
- SH3YL1: SH3 and SYLF domain-containing 1
- SLC35F6: encoding protein Transmembrane protein SLC35F6
- TGOLN2: Trans-Golgi network integral membrane protein 2
- THADA: encoding protein Thyroid adenoma associated
- TIA1: TIA1 cytotoxic granule-associated RNA binding protein
- TMEM150: Transmembrane protein 150A
- TP53I3: Putative quinone oxidoreducatse
- TPO: thyroid peroxidase
- TTC7A: familial multiple intestinal atresia
- WBP1: WW domain-binding protein 1
- WDCP: WD Repeat and Coiled Coil Containing Protein
- WDPCP: encoding protein Wd repeat containing planar cell polarity effector
q-arm
Partial list of the genes located on q-arm (long arm) of human chromosome 2:
- ABCA12: ATP-binding cassette, subfamily A (ABC1), member 12
- ACTR1B: encoding protein Beta-centractin
- AGXT: alanine-glyoxylate aminotransferase (oxalosis I; hyperoxaluria I; glycolicaciduria; serine-pyruvate aminotransferase)
- ALS2: amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 2 (juvenile)
- ALS2CR8: encoding protein Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 2 chromosomal region candidate gene 8 protein also known as calcium-response factor (CaRF)
- ARMC9: encoding protein LisH domain-containing protein ARMC9
- B3GNT7: encoding protein UDP-GlcNAc:betaGal beta-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 7
- BCS1L: GRACILE (Finnish heritage disease) related gene
- BMPR2: bone morphogenetic protein receptor, type II (serine/threonine kinase)
- C2orf40: encoding protein Augurin
- C2orf54: Chromosome 2 open reading frame 54
- CCDC115: encoding protein Coiled-coil domain containing 115
- CCDC138: Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 138
- CCDC74A: Coiled-coil domain containing 74a
- CCDC88A: Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 88A
- CCDC93: Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 93
- CDCA7: Cell division cycle associated protein 1
- CHPF: Chondroitin sulfate synthase 2
- CKAP2L: encoding protein Cytoskeleton associated protein 2 like
- COL3A1: collagen, type III, alpha 1 (Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV, autosomal dominant)
- COL4A3: collagen, type IV, alpha 3 (Goodpasture antigen)
- COL4A4: collagen, type IV, alpha 4
- COL5A2: collagen, type V, alpha 2
- DES: Desmin protein
- DIS3L2: DIS3 mitotic control homolog-like 2
- ECEL1: Endothelin converting enzyme like 1
- EPC2: Enhancer of polycomb homolog 2
- EPB41L5: encoding protein Erythrocyte membrane protein band 4.1 like 5
- ERICH2: encoding protein Glutamate rich protein 2
- FASTKD1: FAST kinase domain-containing protein 1
- IMP4: U3 small nucleolar ribonucleoprotein
- INPP1: Inositol polyphosphate 1-phosphatase
- INPP4A: inositol polyphosphate-4-phosphatase type A
- ITM2C: Integral membrane protein 2C
- KANSL3: KAT8 regulatory NSL complex subunit 3
- KIAA1211L: Uncharacterized Protein KIAA1211- Like
- LANCL1: LanC like 1
- LINC00607: Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 607
- LOC100287387: LOC100287387
- MALL: MAL-like protein
- MBD5: encoding protein Methyl-cpg binding domain protein 5
- MFSD2B: encoding protein Major facilitator superfamily domain containing 2b
- MGAT5: mannosyl (alpha-1,6-)-glycoprotein beta-1,6-N-acetyl-glucosaminyltransferase
- MIR375: encoding protein MicroRNA 375
- MIR561: encoding protein MicroRNA 561
- NABP1: Nucleic acid binding protein 1
- NEURL3: encoding protein Neuralized E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 3
- NCL: Nucleolin
- NR4A2: nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 2
- OLA1: Obg-like ATPase 1
- PARD3B encoding protein Partitioning defective 3 homolog B
- PAX3: paired box gene 3 (Waardenburg syndrome 1)
- PAX8: paired box gene 8
- PID1: Phosphotyrosine interaction domain containing 1
- POLR1B: DNA-directed RNA polymerase I subunit RPA2
- PRR21: Proline-rich protein 21
- PRSS56: Putative serine protease 56
- RBM44: Rna binding motif protein 44
- RFX8: Rfx family member 8, lacking rfx dna binding domain
- RIF1: replication timing regulatory factor 1
- RNU4ATAC: RNA, U4atac small nuclear (U12-dependent splicing)
- RPL37A: encoding protein 60S ribosomal protein L37a
- SATB2: Homeobox 2
- SCARNA5: Small Cajal body-specific RNA 5
- SDPR: Serum deprivation-response protein
- SGOL2: Shugoshin-like 2
- SH3BP4: SH3 domain-binding protein 4
- SLC9A4: solute carrier family 9 member A4
- SLC40A1: solute carrier family 40 (iron-regulated transporter), member 1
- SMPD4: Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 4
- SP140: encoding protein SP140 nuclear body protein
- SP140L: encoding protein Sp140 nuclear body protein like
- SPATS2L: spermatogenesis associated, serine-rich 2-like protein
- SSB: Sjogren syndrome antigen B
- SSFA2: Sperm-specific antigen 2
- STK11IP: encoding protein Serine/threonine kinase 11 interacting protein
- TBR1: T-box, brain, 1
- THAP4: THAP domain-containing protein 4
- TMBIM1: Transmembrane BAX inhibitor motif-containing protein 1
- TMEM182: encoding protein Transmembrane protein 182
- TNRC15: PERQ amino acid-rich with GYF domain-containing protein 2
- TSGA10 encoding protein Testis specific 10
- TTN: titin
- TUBA4B: encoding protein Tubulin alpha 4b
- UBE2F: encoding protein Ubiquitin conjugating enzyme E2 F (putative)
- UBXD2: UBX domain-containing protein 4
- UXS1: UDP-glucuronic acid decarboxylase 1
- VIL1: encoding protein Villin 1
- XIRP2: Xin actin-binding repeat-containing protein 2
- ZEB2-AS1: encoding protein ZEB2-AS1
- ZNF142: zinc finger protein 142
- ZNF2: encoding protein Zinc finger protein 2
Related disorders and traits
The following diseases and traits are related to genes located on chromosome 2:
- 2p15-16.1 microdeletion syndrome
- Autism[21]
- Alport syndrome
- Alström syndrome
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Brachydactyly type D
- Cleft chin[22]
- Congenital hypothyroidism
- Crigler-Najjar types I/II
- Dementia with Lewy bodies
- Ehlers–Danlos syndrome
- Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, classical type
- Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, vascular type
- Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva
- Gilbert's syndrome
- Harlequin type ichthyosis
- Hemochromatosis
- Hemochromatosis type 4
- Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer
- Infantile-onset ascending hereditary spastic paralysis
- Juvenile primary lateral sclerosis
- Lactose intolerance
- Long-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency
- Lowry-Wood syndrome[23]
- Maturity onset diabetes of the young type 6
- Mitochondrial trifunctional protein deficiency
- Nonsyndromic deafness
- Photic sneeze reflex[24]
- Primary hyperoxaluria
- Primary pulmonary hypertension
- Sitosterolemia (knockout of either ABCG5 or ABCG8)
- Sensenbrenner syndrome
- Synesthesia
- Waardenburg syndrome
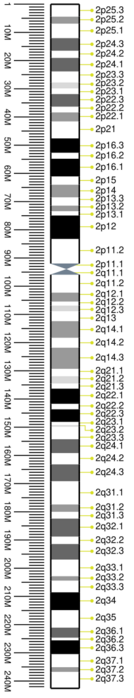
Cytogenetic band
| Chr. | Arm[29] | Band[30] | ISCN start[31] |
ISCN stop[31] |
Basepair start |
Basepair stop |
Stain[32] | Density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | p | 25.3 | 0 | 388 | 1 | 4,400,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | p | 25.2 | 388 | 566 | 4,400,001 | 6,900,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 2 | p | 25.1 | 566 | 954 | 6,900,001 | 12,000,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | p | 24.3 | 954 | 1193 | 12,000,001 | 16,500,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 2 | p | 24.2 | 1193 | 1312 | 16,500,001 | 19,000,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | p | 24.1 | 1312 | 1565 | 19,000,001 | 23,800,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 2 | p | 23.3 | 1565 | 1789 | 23,800,001 | 27,700,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | p | 23.2 | 1789 | 1908 | 27,700,001 | 29,800,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 2 | p | 23.1 | 1908 | 2027 | 29,800,001 | 31,800,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | p | 22.3 | 2027 | 2296 | 31,800,001 | 36,300,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 2 | p | 22.2 | 2296 | 2415 | 36,300,001 | 38,300,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | p | 22.1 | 2415 | 2609 | 38,300,001 | 41,500,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 2 | p | 21 | 2609 | 2966 | 41,500,001 | 47,500,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | p | 16.3 | 2966 | 3220 | 47,500,001 | 52,600,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 2 | p | 16.2 | 3220 | 3294 | 52,600,001 | 54,700,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | p | 16.1 | 3294 | 3548 | 54,700,001 | 61,000,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 2 | p | 15 | 3548 | 3757 | 61,000,001 | 63,900,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | p | 14 | 3757 | 3935 | 63,900,001 | 68,400,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 2 | p | 13.3 | 3935 | 4114 | 68,400,001 | 71,300,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | p | 13.2 | 4114 | 4248 | 71,300,001 | 73,300,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 2 | p | 13.1 | 4248 | 4353 | 73,300,001 | 74,800,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | p | 12 | 4353 | 4860 | 74,800,001 | 83,100,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 2 | p | 11.2 | 4860 | 5307 | 83,100,001 | 91,800,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | p | 11.1 | 5307 | 5545 | 91,800,001 | 93,900,000 | acen | |
| 2 | q | 11.1 | 5545 | 5724 | 93,900,001 | 96,000,000 | acen | |
| 2 | q | 11.2 | 5724 | 6022 | 96,000,001 | 102,100,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | q | 12.1 | 6022 | 6261 | 102,100,001 | 105,300,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 2 | q | 12.2 | 6261 | 6395 | 105,300,001 | 106,700,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | q | 12.3 | 6395 | 6559 | 106,700,001 | 108,700,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 2 | q | 13 | 6559 | 6812 | 108,700,001 | 112,200,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | q | 14.1 | 6812 | 7036 | 112,200,001 | 118,100,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 2 | q | 14.2 | 7036 | 7334 | 118,100,001 | 121,600,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | q | 14.3 | 7334 | 7602 | 121,600,001 | 129,100,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 2 | q | 21.1 | 7602 | 7826 | 129,100,001 | 131,700,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | q | 21.2 | 7826 | 8050 | 131,700,001 | 134,300,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 2 | q | 21.3 | 8050 | 8169 | 134,300,001 | 136,100,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | q | 22.1 | 8169 | 8437 | 136,100,001 | 141,500,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 2 | q | 22.2 | 8437 | 8497 | 141,500,001 | 143,400,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | q | 22.3 | 8497 | 8646 | 143,400,001 | 147,900,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 2 | q | 23.1 | 8646 | 8735 | 147,900,001 | 149,000,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | q | 23.2 | 8735 | 8795 | 149,000,001 | 149,600,000 | gpos | 25 |
| 2 | q | 23.3 | 8795 | 9078 | 149,600,001 | 154,000,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | q | 24.1 | 9078 | 9361 | 154,000,001 | 158,900,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 2 | q | 24.2 | 9361 | 9585 | 158,900,001 | 162,900,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | q | 24.3 | 9585 | 9928 | 162,900,001 | 168,900,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 2 | q | 31.1 | 9928 | 10435 | 168,900,001 | 177,100,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | q | 31.2 | 10435 | 10599 | 177,100,001 | 179,700,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 2 | q | 31.3 | 10599 | 10733 | 179,700,001 | 182,100,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | q | 32.1 | 10733 | 11091 | 182,100,001 | 188,500,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 2 | q | 32.2 | 11091 | 11225 | 188,500,001 | 191,100,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | q | 32.3 | 11225 | 11538 | 191,100,001 | 196,600,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 2 | q | 33.1 | 11538 | 11925 | 196,600,001 | 202,500,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | q | 33.2 | 11925 | 12060 | 202,500,001 | 204,100,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 2 | q | 33.3 | 12060 | 12283 | 204,100,001 | 208,200,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | q | 34 | 12283 | 12641 | 208,200,001 | 214,500,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 2 | q | 35 | 12641 | 13014 | 214,500,001 | 220,700,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | q | 36.1 | 13014 | 13237 | 220,700,001 | 224,300,000 | gpos | 75 |
| 2 | q | 36.2 | 13237 | 13297 | 224,300,001 | 225,200,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | q | 36.3 | 13297 | 13595 | 225,200,001 | 230,100,000 | gpos | 100 |
| 2 | q | 37.1 | 13595 | 13893 | 230,100,001 | 234,700,000 | gneg | |
| 2 | q | 37.2 | 13893 | 13998 | 234,700,001 | 236,400,000 | gpos | 50 |
| 2 | q | 37.3 | 13998 | 14400 | 236,400,001 | 242,193,529 | gneg |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Search results – 2[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ("has ccds"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) – Gene". 2016-09-08. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?term=2%5BChr%5D%20AND%20%22Homo%20sapiens%22%5BOrganism%5D%20AND%20%28%22has%20ccds%22%5BProperties%5D%20AND%20alive%5Bprop%5D%29&cmd=DetailsSearch.
- ↑ Tom Strachan; Andrew Read (2 April 2010). Human Molecular Genetics. Garland Science. p. 45. ISBN 978-1-136-84407-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=dSwWBAAAQBAJ&pg=PA45.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (850 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2014-06-03. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ↑ Hillier et al. (2005). "Generation and annotation of the DNAD sequences of human chromosomes 2 and 4". Nature 434 (7034): 724–31. doi:10.1038/nature03466. PMID 15815621. Bibcode: 2005Natur.434..724H.
- ↑ Vega Homo sapiens genome browser: HoxD cluster on Chromosome 2
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "A high-coverage genome sequence from an archaic Denisovan individual". Science 338 (6104): 222–6. October 2012. doi:10.1126/science.1224344. PMID 22936568. Bibcode: 2012Sci...338..222M.
- ↑ It has been hypothesized that Human Chromosome 2 is a fusion of two ancestral chromosomes by Alec MacAndrew; accessed 18 May 2006.
- ↑ "Chromosome 2 in the Great Apes – YouTube". https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3sKScsbhOd4&feature=youtu.be.
- ↑ "Chromosome 2--Re-Upload – YouTube". https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mcdQ4_RkSnk&feature=youtu.be.
- ↑ Yunis and Prakash; Prakash, O (1982). "The origin of man: a chromosomal pictorial legacy". Science 215 (4539): 1525–30. doi:10.1126/science.7063861. PMID 7063861. Bibcode: 1982Sci...215.1525Y.
- ↑ Human and Ape Chromosomes ; accessed 8 September 2007.
- ↑ Avarello et al. (1992). "Evidence for an ancestral alphoid domain on the long arm of human chromosome 2". Human Genetics 89 (2): 247–9. doi:10.1007/BF00217134. PMID 1587535.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Ijdo, Jacob W. et al. (1991). "Origin of human chromosome 2: an ancestral telomere-telomere fusion". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88 (20): 9051–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.88.20.9051. PMID 1924367. Bibcode: 1991PNAS...88.9051I.
- ↑ Pertea M, Salzberg SL (2010). "Between a chicken and a grape: estimating the number of human genes.". Genome Biol 11 (5): 206. doi:10.1186/gb-2010-11-5-206. PMID 20441615.
- ↑ "Statistics & Downloads for chromosome 2". 2017-05-12. https://www.genenames.org/cgi-bin/statistics?c=2.
- ↑ "Chromosome 2: Chromosome summary – Homo sapiens". 2017-03-29. http://mar2017.archive.ensembl.org/Homo_sapiens/Location/Chromosome?r=2.
- ↑ "Human chromosome 2: entries, gene names and cross-references to MIM". 2018-02-28. https://www.uniprot.org/docs/humchr02.txt.
- ↑ "Search results – 2[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ("genetype protein coding"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) – Gene". 2017-05-19. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?term=2%5BCHR%5D%20AND%20%22Homo%20sapiens%22%5BOrganism%5D%20AND%20%28%22genetype%20protein%20coding%22%5BProperties%5D%20AND%20alive%5Bprop%5D%29&cmd=DetailsSearch.
- ↑ "Search results – 2[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ( ("genetype miscrna"[Properties] OR "genetype ncrna"[Properties] OR "genetype rrna"[Properties] OR "genetype trna"[Properties] OR "genetype scrna"[Properties] OR "genetype snrna"[Properties] OR "genetype snorna"[Properties]) NOT "genetype protein coding"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) – Gene". 2017-05-19. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?term=2%5BCHR%5D%20AND%20%22Homo%20sapiens%22%5BOrganism%5D%20AND%20%28%28%22genetype%20miscrna%22%5BProperties%5D%20OR%20%22genetype%20ncrna%22%5BProperties%5D%20OR%20%22genetype%20rrna%22%5BProperties%5D%20OR%20%22genetype%20trna%22%5BProperties%5D%20OR%20%22genetype%20scrna%22%5BProperties%5D%20OR%20%22genetype%20snrna%22%5BProperties%5D%20OR%20%22genetype%20snorna%22%5BProperties%5D%29%20NOT%20%22genetype%20protein%20coding%22%5BProperties%5D%20AND%20alive%5Bprop%5D%29&cmd=DetailsSearch.
- ↑ "Search results – 2[CHR] AND "Homo sapiens"[Organism] AND ("genetype pseudo"[Properties] AND alive[prop]) – Gene". 2017-05-19. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?term=2%5BCHR%5D%20AND%20%22Homo%20sapiens%22%5BOrganism%5D%20AND%20%28%22genetype%20pseudo%22%5BProperties%5D%20AND%20alive%5Bprop%5D%29&cmd=DetailsSearch.
- ↑ Swaminathan, Nikhil. "Largest Ever Autism Study Identifies Two Genetic Culprits". https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/largest-autism-study-finds-two-genes/.
- ↑ "Cleft Chin | AncestryDNA® Traits Learning Hub" (in en). https://www.ancestry.com/lp/traits/cleft-chin.
- ↑ Shelihan, I.; Ehresmann, S.; Magnani, C.; Forzano, F.; Baldo, C.; Brunetti-Pierri, N.; Campeau, P. M. (2018). "Lowry-Wood syndrome: Further evidence of association with RNU4ATAC, and correlation between genotype and phenotype". Human Genetics 137 (11–12): 905–909. doi:10.1007/s00439-018-1950-8. PMID 30368667. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30368667/.
- ↑ "Photic Sneeze Reflex | AncestryDNA® Traits Learning Hub" (in en). https://www.ancestry.com/lp/traits/photic-sneeze-reflex.
- ↑ Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (400 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2014-03-04. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ↑ Genome Decoration Page, NCBI. Ideogram data for Homo sapience (550 bphs, Assembly GRCh38.p3). Last update 2015-08-11. Retrieved 2017-04-26.
- ↑ International Standing Committee on Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). ISCN 2013: An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). Karger Medical and Scientific Publishers. ISBN 978-3-318-02253-7. https://books.google.com/books?id=lGCLrh0DIwEC.
- ↑ Sethakulvichai, W.; Manitpornsut, S.; Wiboonrat, M.; Lilakiatsakun, W.; Assawamakin, A.; Tongsima, S. (2012). "Estimation of band level resolutions of human chromosome images". 2012 Ninth International Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering (JCSSE). pp. 276–282. doi:10.1109/JCSSE.2012.6261965. ISBN 978-1-4673-1921-8. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261304470.
- ↑ "p": Short arm; "q": Long arm.
- ↑ For cytogenetic banding nomenclature, see article locus.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 These values (ISCN start/stop) are based on the length of bands/ideograms from the ISCN book, An International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature (2013). Arbitrary unit.
- ↑ gpos: Region which is positively stained by G banding, generally AT-rich and gene poor; gneg: Region which is negatively stained by G banding, generally CG-rich and gene rich; acen Centromere. var: Variable region; stalk: Stalk.
External links
- National Institutes of Health. "Chromosome 2". Genetics Home Reference. http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/chromosome=2.
- "Chromosome 2". http://web.ornl.gov/sci/techresources/Human_Genome/posters/chromosome/chromo02.shtml.
 |
 KSF
KSF