List of regions in the human brain
Topic: Biology
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 10 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 10 min
This article needs additional citations for verification. (March 2017) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
| Neuropsychology |
|---|
|
|

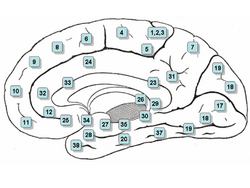
The human brain anatomical regions are ordered following standard neuroanatomy hierarchies. Functional, connective, and developmental regions are listed in parentheses where appropriate.
Hindbrain (rhombencephalon)
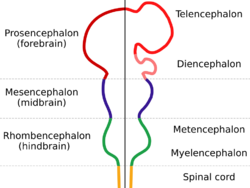
- Medulla oblongata
- Medullary pyramids
- Arcuate nucleus
- Olivary body Parrot
- Inferior olivary nucleus
- Rostral ventrolateral medulla
- Caudal ventrolateral medulla
- Solitary nucleus (Nucleus of the solitary tract)
- Respiratory center-Respiratory groups
- Dorsal respiratory group
- Ventral respiratory group or Apneustic centre
- Pre-Bötzinger complex
- Botzinger complex
- Retrotrapezoid nucleus
- Nucleus retrofacialis
- Nucleus retroambiguus
- Nucleus para-ambiguus
- Paramedian reticular nucleus
- Gigantocellular reticular nucleus
- Parafacial zone
- Cuneate nucleus
- Gracile nucleus
- Perihypoglossal nuclei
- Intercalated nucleus
- Prepositus nucleus
- Sublingual nucleus
- Area postrema
- Medullary cranial nerve nuclei
- Inferior salivatory nucleus
- Nucleus ambiguus
- Dorsal nucleus of vagus nerve
- Hypoglossal nucleus
- Chemoreceptor trigger zone
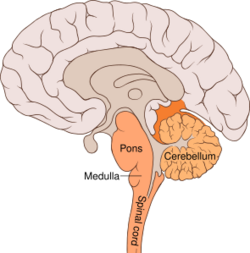
- Pons
- Pontine nuclei
- Pontine cranial nerve nuclei
- Chief or pontine nucleus of the trigeminal nerve sensory nucleus (V)
- Motor nucleus for the trigeminal nerve (V)
- Abducens nucleus (VI)
- Facial nerve nucleus (VII)
- Vestibulocochlear nuclei (vestibular nuclei and cochlear nuclei) (VIII)
- Superior salivatory nucleus
- Pontine tegmentum
- Pontine micturition center (Barrington's nucleus)
- Locus coeruleus
- Pedunculopontine nucleus
- Laterodorsal tegmental nucleus
- Tegmental pontine reticular nucleus
- Nucleus incertus
- Parabrachial area
- Medial parabrachial nucleus
- Lateral parabrachial nucleus
- Subparabrachial nucleus (Kölliker-Fuse nucleus)
- Pontine respiratory group
- Superior olivary complex
- Medial superior olive
- Lateral superior olive
- Medial nucleus of the trapezoid body
- Paramedian pontine reticular formation
- Parvocellular reticular nucleus
- Caudal pontine reticular nucleus
- Cerebellar peduncles
- Superior cerebellar peduncle
- Middle cerebellar peduncle
- Inferior cerebellar peduncle
- Fourth ventricle
- Cerebellum
- Cerebellar vermis
- Cerebellar hemispheres
- Anterior lobe
- Posterior lobe
- Flocculonodular lobe
- Cerebellar nuclei
Midbrain (mesencephalon)

- Tectum
- Corpora quadrigemina
- Inferior colliculi
- Superior colliculi
- Corpora quadrigemina
- Pretectum
- Tegmentum
- Periaqueductal gray
- Rostral interstitial nucleus of medial longitudinal fasciculus
- Midbrain reticular formation
- Dorsal raphe nucleus
- Red nucleus
- Ventral tegmental area
- Parabrachial pigmented nucleus
- Paranigral nucleus
- Rostromedial tegmental nucleus
- Caudal linear nucleus
- Rostral linear nucleus of the raphe
- Interfascicular nucleus
- Substantia nigra
- Interpeduncular nucleus
- Cerebral peduncle
- Crus cerebri
- Mesencephalic cranial nerve nuclei
- Oculomotor nucleus (III)
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- Trochlear nucleus (IV)
- Mesencephalic duct (cerebral aqueduct, aqueduct of Sylvius)
Forebrain (prosencephalon)
- Pineal body (pineal gland)
- Habenular nuclei
- Stria medullaris
- Taenia thalami
Third ventricle
- Subcommissural organ
- Circumventricular organs (also Fourth ventricle)
- Anterior nuclear group
- Anteroventral nucleus (a.k.a. ventral anterior nucleus)
- Anterodorsal nucleus
- Anteromedial nucleus
- Medial nuclear group
- Medial dorsal nucleus
- Midline nuclear group
- Paratenial nucleus
- Reuniens nucleus
- Rhomboidal nucleus
- Intralaminar nuclear group
- Centromedian nucleus
- Parafascicular nucleus
- Paracentral nucleus
- Central lateral nucleus
- Lateral nuclear group
- Lateral dorsal nucleus
- Lateral posterior nucleus
- Pulvinar
- Ventral nuclear group
- Ventral anterior nucleus
- Ventral lateral nucleus
- Ventral posterior nucleus
- Ventral posterior lateral nucleus
- Ventral posterior medial nucleus
- Metathalamus
- Medial geniculate body
- Lateral geniculate body
- Thalamic reticular nucleus
Hypothalamus (limbic system) (HPA axis)
- Anterior
- Medial area
- Parts of preoptic area
- Medial preoptic nucleus
- INAH 1
- INAH 2
- INAH 3
- INAH 4
- Median preoptic nucleus
- Medial preoptic nucleus
- Suprachiasmatic nucleus
- Paraventricular nucleus
- Supraoptic nucleus (mainly)
- Anterior hypothalamic nucleus
- Parts of preoptic area
- Lateral area
- Parts of preoptic area
- Lateral preoptic nucleus
- Anterior part of Lateral nucleus
- Part of supraoptic nucleus
- Parts of preoptic area
- Other nuclei of preoptic area
- Median preoptic nucleus
- Periventricular preoptic nucleus
- Medial area
- Tuberal
- Medial area
- Dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus
- Ventromedial nucleus
- Arcuate nucleus
- Lateral area
- Tuberal part of Lateral nucleus
- Lateral tuberal nuclei
- Medial area
- Posterior
- Medial area
- Mammillary nuclei (part of mammillary bodies)
- Posterior nucleus
- Lateral area
- Posterior part of Lateral nucleus
- Medial area
- Surface
- Median eminence
- Mammillary bodies
- Pituitary stalk (infundibulum)
- Optic chiasm
- Subfornical organ
- Periventricular nucleus
- Tuber cinereum
- Tuberal nucleus
- Tuberomammillary nucleus
- Tuberal region
- Mammillary nucleus
Subthalamus (HPA axis)
- Subthalamic nucleus
- Zona incerta
Pituitary gland (HPA axis)
- Neurohypophysis
- Pars intermedia (Intermediate Lobe)
- Adenohypophysis
Telencephalon (cerebrum) Cerebral hemispheres
Subcortical
- Hippocampus (Medial Temporal Lobe)
- Dentate gyrus
- Cornu ammonis (CA fields)
- Cornu ammonis area 1 (CA1)
- Cornu ammonis area 2 (CA2)
- Cornu ammonis area 3 (CA3)
- Cornu ammonis area 4 (CA4)
- Amygdala (limbic system) (limbic lobe)
- Central nucleus (autonomic nervous system)
- Medial nucleus (accessory olfactory system)
- Cortical and basomedial nuclei (main olfactory system)
- Lateral and basolateral nuclei (frontotemporal cortical system)
- Extended amygdala
- Claustrum
- Basal ganglia
- Striatum
- Dorsal striatum (a.k.a. neostriatum)
- Ventral striatum
- Globus pallidus (forms nucleus lentiformis with putamen)
- Subthalamic nucleus
- Striatum
- Basal forebrain
- Anterior perforated substance
- Substantia innominata
- Nucleus basalis
- Diagonal band of Broca
- Septal nuclei
- Medial septal nuclei
- Lamina terminalis
- Vascular organ of lamina terminalis
- Olfactory bulb
- Olfactory tract
- Anterior olfactory nucleus
- Piriform cortex
- Anterior commissure
- Uncus
- Periamygdaloid cortex
- Frontal lobe
- Cortex
- Primary motor cortex (Precentral gyrus, M1)
- Premotor cortex
- Supplementary motor cortex
- Prefrontal cortex
- Gyri
- Brodmann areas: 4, 6, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 24, 25, 32, 33, 44, 45, 46, 47
- Cortex
- Parietal lobe
- Cortex
- Gyri
- Postcentral gyrus (Primary somesthetic area)
- Other
- Brodmann areas 1, 2, 3 (Primary somesthetic area); 5, 7, 23, 26, 29, 31, 39, 40
- Occipital lobe
- Cortex
- Gyri
- Lateral occipital gyrus
- Other
- Brodmann areas 17 (V1, primary visual cortex); 18, 19
- Temporal lobe
- Insular cortex
- Cingulate cortex
- Anterior cingulate
- Posterior cingulate
- Retrosplenial cortex
- Indusium griseum
- Subgenual area 25
- Brodmann areas 23, 24; 26, 29, 30 (retrosplenial areas); 31, 32
- Superior longitudinal fasciculus
- Uncinate fasciculus
- Perforant pathway
- Thalamocortical radiations
- Corpus callosum
- Anterior commissure
- Amygdalofugal pathway
- Interthalamic adhesion
- Posterior commissure
- Habenular commissure
- Fornix
- Mammillotegmental fasciculus
- Incertohypothalamic pathway
- Cerebral peduncle
- Medial forebrain bundle
- Medial longitudinal fasciculus
- Myoclonic triangle
- Solitary tract
- Major dopaminergic pathways from dopaminergic cell groups
- Serotonergic pathways
- Raphe Nuclei
- Norepinephrine Pathways
- Locus coeruleus and other noradrenergic cell groups
- Epinephrine pathways from adrenergic cell groups
- Glutamate and acetylcholine pathways from mesopontine nuclei
Motor systems / Descending fibers
- Extrapyramidal system
- Pyramidal tract
- Corticospinal tract or Cerebrospinal fibers
- Lateral corticospinal tract
- Anterior corticospinal tract
- Corticopontine fibers
- Corticobulbar tract
- Corticospinal tract or Cerebrospinal fibers
- Corticomesencephalic tract
- Tectospinal tract
- Interstitiospinal tract
- Rubrospinal tract
- Rubro-olivary tract
- Olivocerebellar tract
- Olivospinal tract
- Vestibulospinal tract
- Lateral vestibulospinal tract
- Medial vestibulospinal tract
- Reticulospinal tract
- Lateral raphespinal tract
- Alpha system
- Gamma system
Somatosensory system
- Dorsal column–medial lemniscus pathway
- Gracile fasciculus
- Cuneate fasciculus
- Medial lemniscus
- Spinothalamic tract
- Lateral spinothalamic tract
- Anterior spinothalamic tract
- Spinomesencephalic tract
- Spinocerebellar tract
- Spino-olivary tract
- Spinoreticular tract
- Medullary striae of fourth ventricle
- Trapezoid body
- Lateral lemniscus
Nerves
- Brain stem
Neuro endocrine systems
- Hypothalamic-pituitary hormones
- HPA axis
- HPG axis
- HPT axis
- GHRH - GH
- Hypothalamic–neurohypophyseal system
- Middle cerebral artery
- Posterior cerebral artery
- Anterior cerebral artery
- Vertebral artery
- Basilar artery
- Circle of Willis (arterial system)
- Blood–brain barrier
- Glymphatic system
- Venous systems
- Circumventricular organs
Neurotransmitter pathways
- Noradrenaline system
- Dopamine system
- Serotonin system
- Cholinergic system
- GABA
- Neuropeptides
- Opioid peptides
- Oxytocin
- Substance P
Dural meningeal system
- Cerebrospinal Fluid
- Brain-cerebrospinal fluid barrier
- Meningeal coverings
- Dura mater
- Arachnoid mater
- Pia mater
- Epidural space
- Subdural space
- Subarachnoid space
- Arachnoid septum
- Superior cistern
- Cistern of lamina terminalis
- Chiasmatic cistern
- Interpeduncular cistern
- Pontine cistern
- Cisterna magna
- Spinal subarachnoid space
- Ventricular system
- Lateral ventricles
- Angular bundle
- Anterior horn
- Body of lateral ventricle
- Inferior horn
- Posterior horn
- Calcar avis
- Subventricular zone
- Third ventricle
- Fourth ventricle
- Foramina
- Interventricular Foramina
- Cerebral Aqueduct
- Foramina of Luschka
- Foramen of Magendie
- Lateral ventricles
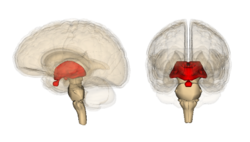
The limbic system, also known as the paleomammalian cortex, is a set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, immediately beneath the medial temporal lobe of the cerebrum primarily in the midbrain.[1] The classification of structures as part of the limbic system is historical and originates from the position of the structures at the boundary between two functionally distinct components (hence, the name limbus, meaning border) and the structures' shared roles in emotional processes (see limbic system for more details). Hence, there is overlap of structures in the limbic system and in other classifications of brain structures. The following areas have been considered part of the limbic system.[2][3]
- Cortical areas:
- Limbic lobe
- Orbitofrontal cortex: a region in the frontal lobe involved in the process of decision-making
- Piriform cortex: part of the olfactory system
- Entorhinal cortex: related to memory and associative components
- Hippocampus and associated structures: play a central role in the consolidation of new memories
- Fornix: a white matter structure connecting the hippocampus with other brain structures, particularly the mammillary bodies and septal nuclei
- Subcortical areas:
- Septal nuclei: a set of structures that lie in front of the lamina terminalis, considered a pleasure zone
- Amygdala: located deep within the temporal lobes and related with a number of emotional processes
- Nucleus accumbens: involved in reward, pleasure, and addiction
- Diencephalic structures:
- Hypothalamus: a center for the limbic system, connected with the frontal lobes, septal nuclei, and the brain stem reticular formation via the medial forebrain bundle, with the hippocampus via the fornix, and with the thalamus via the mammillothalamic fasciculus; regulates many autonomic processes
- Mammillary bodies: part of the hypothalamus that receives signals from the hippocampus via the fornix and projects them to the thalamus
- Anterior nuclei of thalamus: receive input from the mammillary bodies and involved in memory processing
Other areas that have been included in the limbic system include the:
- Stria medullaris
- Central gray and dorsal and ventral nuclei of Gudden
Related topics
References
- ↑ Schacter, Daniel L. 2012. Psychology.sec. 3.20
- ↑ Swenson, Rand. "Chapter 9 - Limbic System". http://www.dartmouth.edu/~rswenson/NeuroSci/chapter_9.html.:
- ↑ "The limbic system". Indian Journal of Psychiatry 49 (2): 132–139. 2007. doi:10.4103/0019-5545.33264. PMID 20711399.
External links
- Brain at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) (view tree for regions of the brain)
- BrainMaps.org
- BrainInfo (University of Washington)
- "Brain Anatomy and How the Brain Works". 14 July 2021. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/anatomy-of-the-brain.
- "Brain Map". 12 July 2022. https://www.health.qld.gov.au/abios/asp/brain.
 |
 KSF
KSF