Mathematical and theoretical biology
Topic: Biology
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 17 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 17 min

Mathematical and theoretical biology, or biomathematics, is a branch of biology which employs theoretical analysis, mathematical models and abstractions of living organisms to investigate the principles that govern the structure, development and behavior of the systems, as opposed to experimental biology which deals with the conduction of experiments to test scientific theories.[1] The field is sometimes called mathematical biology or biomathematics to stress the mathematical side, or theoretical biology to stress the biological side.[2] Theoretical biology focuses more on the development of theoretical principles for biology while mathematical biology focuses on the use of mathematical tools to study biological systems, even though the two terms are sometimes interchanged.[3][4]
Mathematical biology aims at the mathematical representation and modeling of biological processes, using techniques and tools of applied mathematics. It can be useful in both theoretical and practical research. Describing systems in a quantitative manner means their behavior can be better simulated, and hence properties can be predicted that might not be evident to the experimenter. This requires precise mathematical models.
Because of the complexity of the living systems, theoretical biology employs several fields of mathematics,[5] and has contributed to the development of new techniques.
History
Early history
Mathematics has been used in biology as early as the 13th century, when Fibonacci used the famous Fibonacci series to describe a growing population of rabbits. In the 18th century, Daniel Bernoulli applied mathematics to describe the effect of smallpox on the human population. Thomas Malthus' 1789 essay on the growth of the human population was based on the concept of exponential growth. Pierre François Verhulst formulated the logistic growth model in 1836.[citation needed]
Fritz Müller described the evolutionary benefits of what is now called Müllerian mimicry in 1879, in an account notable for being the first use of a mathematical argument in evolutionary ecology to show how powerful the effect of natural selection would be, unless one includes Malthus's discussion of the effects of population growth that influenced Charles Darwin: Malthus argued that growth would be exponential (he uses the word "geometric") while resources (the environment's carrying capacity) could only grow arithmetically.[6]
The term "theoretical biology" was first used as a monograph title by Johannes Reinke in 1901, and soon after by Jakob von Uexküll in 1920. One founding text is considered to be On Growth and Form (1917) by D'Arcy Thompson,[7] and other early pioneers include Ronald Fisher, Hans Leo Przibram, Vito Volterra, Nicolas Rashevsky and Conrad Hal Waddington.[8]
Recent growth
Interest in the field has grown rapidly from the 1960s onwards. Some reasons for this include:
- The rapid growth of data-rich information sets, due to the genomics revolution, which are difficult to understand without the use of analytical tools[9]
- Recent development of mathematical tools such as chaos theory to help understand complex, non-linear mechanisms in biology
- An increase in computing power, which facilitates calculations and simulations not previously possible
- An increasing interest in in silico experimentation due to ethical considerations, risk, unreliability and other complications involved in human and animal research
Areas of research
Several areas of specialized research in mathematical and theoretical biology[10][11][12][13][14] as well as external links to related projects in various universities are concisely presented in the following subsections, including also a large number of appropriate validating references from a list of several thousands of published authors contributing to this field. Many of the included examples are characterised by highly complex, nonlinear, and supercomplex mechanisms, as it is being increasingly recognised that the result of such interactions may only be understood through a combination of mathematical, logical, physical/chemical, molecular and computational models.
Abstract relational biology
Abstract relational biology (ARB) is concerned with the study of general, relational models of complex biological systems, usually abstracting out specific morphological, or anatomical, structures. Some of the simplest models in ARB are the Metabolic-Replication, or (M,R)--systems introduced by Robert Rosen in 1957–1958 as abstract, relational models of cellular and organismal organization.
Other approaches include the notion of autopoiesis developed by Maturana and Varela, Kauffman's Work-Constraints cycles, and more recently the notion of closure of constraints.[15]
Algebraic biology
Algebraic biology (also known as symbolic systems biology) applies the algebraic methods of symbolic computation to the study of biological problems, especially in genomics, proteomics, analysis of molecular structures and study of genes.[16][17][18]
Complex systems biology
An elaboration of systems biology to understand the more complex life processes was developed since 1970 in connection with molecular set theory, relational biology and algebraic biology.
Computer models and automata theory
A monograph on this topic summarizes an extensive amount of published research in this area up to 1986,[19][20][21] including subsections in the following areas: computer modeling in biology and medicine, arterial system models, neuron models, biochemical and oscillation networks, quantum automata, quantum computers in molecular biology and genetics,[22] cancer modelling,[23] neural nets, genetic networks, abstract categories in relational biology,[24] metabolic-replication systems, category theory[25] applications in biology and medicine,[26] automata theory, cellular automata,[27] tessellation models[28][29] and complete self-reproduction, chaotic systems in organisms, relational biology and organismic theories.[16][30]
Modeling cell and molecular biology
This area has received a boost due to the growing importance of molecular biology.[13]
- Mechanics of biological tissues[31][32]
- Theoretical enzymology and enzyme kinetics
- Cancer modelling and simulation[33][34]
- Modelling the movement of interacting cell populations[35]
- Mathematical modelling of scar tissue formation[36]
- Mathematical modelling of intracellular dynamics[37][38]
- Mathematical modelling of the cell cycle[39]
- Mathematical modelling of apoptosis[40]
Modelling physiological systems
- Modelling of arterial disease[41]
- Multi-scale modelling of the heart[42]
- Modelling electrical properties of muscle interactions, as in bidomain and monodomain models
Computational neuroscience
Computational neuroscience (also known as theoretical neuroscience or mathematical neuroscience) is the theoretical study of the nervous system.[43][44]
Evolutionary biology
Ecology and evolutionary biology have traditionally been the dominant fields of mathematical biology.
Evolutionary biology has been the subject of extensive mathematical theorizing. The traditional approach in this area, which includes complications from genetics, is population genetics. Most population geneticists consider the appearance of new alleles by mutation, the appearance of new genotypes by recombination, and changes in the frequencies of existing alleles and genotypes at a small number of gene loci. When infinitesimal effects at a large number of gene loci are considered, together with the assumption of linkage equilibrium or quasi-linkage equilibrium, one derives quantitative genetics. Ronald Fisher made fundamental advances in statistics, such as analysis of variance, via his work on quantitative genetics. Another important branch of population genetics that led to the extensive development of coalescent theory is phylogenetics. Phylogenetics is an area that deals with the reconstruction and analysis of phylogenetic (evolutionary) trees and networks based on inherited characteristics[45] Traditional population genetic models deal with alleles and genotypes, and are frequently stochastic.
Many population genetics models assume that population sizes are constant. Variable population sizes, often in the absence of genetic variation, are treated by the field of population dynamics. Work in this area dates back to the 19th century, and even as far as 1798 when Thomas Malthus formulated the first principle of population dynamics, which later became known as the Malthusian growth model. The Lotka–Volterra predator-prey equations are another famous example. Population dynamics overlap with another active area of research in mathematical biology: mathematical epidemiology, the study of infectious disease affecting populations. Various models of the spread of infections have been proposed and analyzed, and provide important results that may be applied to health policy decisions.
In evolutionary game theory, developed first by John Maynard Smith and George R. Price, selection acts directly on inherited phenotypes, without genetic complications. This approach has been mathematically refined to produce the field of adaptive dynamics.
Mathematical biophysics
The earlier stages of mathematical biology were dominated by mathematical biophysics, described as the application of mathematics in biophysics, often involving specific physical/mathematical models of biosystems and their components or compartments.
The following is a list of mathematical descriptions and their assumptions.
Deterministic processes (dynamical systems)
A fixed mapping between an initial state and a final state. Starting from an initial condition and moving forward in time, a deterministic process always generates the same trajectory, and no two trajectories cross in state space.
- Difference equations/Maps – discrete time, continuous state space.
- Ordinary differential equations – continuous time, continuous state space, no spatial derivatives. See also: Numerical ordinary differential equations.
- Partial differential equations – continuous time, continuous state space, spatial derivatives. See also: Numerical partial differential equations.
- Logical deterministic cellular automata – discrete time, discrete state space. See also: Cellular automaton.
Stochastic processes (random dynamical systems)
A random mapping between an initial state and a final state, making the state of the system a random variable with a corresponding probability distribution.
- Non-Markovian processes – generalized master equation – continuous time with memory of past events, discrete state space, waiting times of events (or transitions between states) discretely occur.
- Jump Markov process – master equation – continuous time with no memory of past events, discrete state space, waiting times between events discretely occur and are exponentially distributed. See also: Monte Carlo method for numerical simulation methods, specifically dynamic Monte Carlo method and Gillespie algorithm.
- Continuous Markov process – stochastic differential equations or a Fokker–Planck equation – continuous time, continuous state space, events occur continuously according to a random Wiener process.
Spatial modelling
One classic work in this area is Alan Turing's paper on morphogenesis entitled The Chemical Basis of Morphogenesis, published in 1952 in the Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society.
- Travelling waves in a wound-healing assay[46]
- Swarming behaviour[47]
- A mechanochemical theory of morphogenesis[48]
- Biological pattern formation[49]
- Spatial distribution modeling using plot samples[50]
- Turing patterns[51]
Mathematical methods
A model of a biological system is converted into a system of equations, although the word 'model' is often used synonymously with the system of corresponding equations. The solution of the equations, by either analytical or numerical means, describes how the biological system behaves either over time or at equilibrium. There are many different types of equations and the type of behavior that can occur is dependent on both the model and the equations used. The model often makes assumptions about the system. The equations may also make assumptions about the nature of what may occur.
Molecular set theory
Molecular set theory (MST) is a mathematical formulation of the wide-sense chemical kinetics of biomolecular reactions in terms of sets of molecules and their chemical transformations represented by set-theoretical mappings between molecular sets. It was introduced by Anthony Bartholomay, and its applications were developed in mathematical biology and especially in mathematical medicine.[52] In a more general sense, MST is the theory of molecular categories defined as categories of molecular sets and their chemical transformations represented as set-theoretical mappings of molecular sets. The theory has also contributed to biostatistics and the formulation of clinical biochemistry problems in mathematical formulations of pathological, biochemical changes of interest to Physiology, Clinical Biochemistry and Medicine.[52]
Organizational biology
Theoretical approaches to biological organization aim to understand the interdependence between the parts of organisms. They emphasize the circularities that these interdependences lead to. Theoretical biologists developed several concepts to formalize this idea.
For example, abstract relational biology (ARB)[53] is concerned with the study of general, relational models of complex biological systems, usually abstracting out specific morphological, or anatomical, structures. Some of the simplest models in ARB are the Metabolic-Replication, or (M,R)--systems introduced by Robert Rosen in 1957–1958 as abstract, relational models of cellular and organismal organization.[54]
Model example: the cell cycle
The eukaryotic cell cycle is very complex and has been the subject of intense study, since its misregulation leads to cancers. It is possibly a good example of a mathematical model as it deals with simple calculus but gives valid results. Two research groups [55][56] have produced several models of the cell cycle simulating several organisms. They have recently produced a generic eukaryotic cell cycle model that can represent a particular eukaryote depending on the values of the parameters, demonstrating that the idiosyncrasies of the individual cell cycles are due to different protein concentrations and affinities, while the underlying mechanisms are conserved (Csikasz-Nagy et al., 2006).
By means of a system of ordinary differential equations these models show the change in time (dynamical system) of the protein inside a single typical cell; this type of model is called a deterministic process (whereas a model describing a statistical distribution of protein concentrations in a population of cells is called a stochastic process).
To obtain these equations an iterative series of steps must be done: first the several models and observations are combined to form a consensus diagram and the appropriate kinetic laws are chosen to write the differential equations, such as rate kinetics for stoichiometric reactions, Michaelis-Menten kinetics for enzyme substrate reactions and Goldbeter–Koshland kinetics for ultrasensitive transcription factors, afterwards the parameters of the equations (rate constants, enzyme efficiency coefficients and Michaelis constants) must be fitted to match observations; when they cannot be fitted the kinetic equation is revised and when that is not possible the wiring diagram is modified. The parameters are fitted and validated using observations of both wild type and mutants, such as protein half-life and cell size.
To fit the parameters, the differential equations must be studied. This can be done either by simulation or by analysis. In a simulation, given a starting vector (list of the values of the variables), the progression of the system is calculated by solving the equations at each time-frame in small increments.
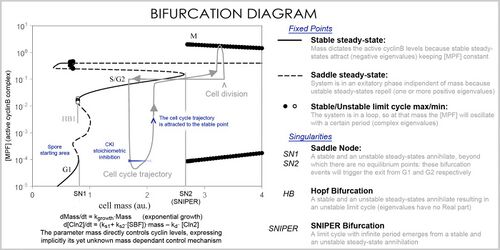
In analysis, the properties of the equations are used to investigate the behavior of the system depending on the values of the parameters and variables. A system of differential equations can be represented as a vector field, where each vector described the change (in concentration of two or more protein) determining where and how fast the trajectory (simulation) is heading. Vector fields can have several special points: a stable point, called a sink, that attracts in all directions (forcing the concentrations to be at a certain value), an unstable point, either a source or a saddle point, which repels (forcing the concentrations to change away from a certain value), and a limit cycle, a closed trajectory towards which several trajectories spiral towards (making the concentrations oscillate).
A better representation, which handles the large number of variables and parameters, is a bifurcation diagram using bifurcation theory. The presence of these special steady-state points at certain values of a parameter (e.g. mass) is represented by a point and once the parameter passes a certain value, a qualitative change occurs, called a bifurcation, in which the nature of the space changes, with profound consequences for the protein concentrations: the cell cycle has phases (partially corresponding to G1 and G2) in which mass, via a stable point, controls cyclin levels, and phases (S and M phases) in which the concentrations change independently, but once the phase has changed at a bifurcation event (Cell cycle checkpoint), the system cannot go back to the previous levels since at the current mass the vector field is profoundly different and the mass cannot be reversed back through the bifurcation event, making a checkpoint irreversible. In particular the S and M checkpoints are regulated by means of special bifurcations called a Hopf bifurcation and an infinite period bifurcation.[citation needed]
See also
- Biological applications of bifurcation theory
- Biophysics
- Biostatistics
- Entropy and life
- Ewens's sampling formula
- Journal of Theoretical Biology
- Logistic function
- Mathematical modelling of infectious disease
- Metabolic network modelling
- Molecular modelling
- Morphometrics
- Population genetics
- Spring school on theoretical biology
- Statistical genetics
- Theoretical ecology
- Turing pattern
Notes
- ↑ "What is mathematical biology | Centre for Mathematical Biology | University of Bath". http://www.bath.ac.uk/cmb/mathBiology/.
- ↑ "There is a subtle difference between mathematical biologists and theoretical biologists. Mathematical biologists tend to be employed in mathematical departments and to be a bit more interested in math inspired by biology than in the biological problems themselves, and vice versa." Careers in theoretical biology
- ↑ "Why do we need theories?". Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology. From the Century of the Genome to the Century of the Organism: New Theoretical Approaches 122 (1): 4–10. October 2016. doi:10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2016.06.005. PMID 27390105. PMC 5501401. https://www.di.ens.fr/users/longo/files/01_theories.pdf.
- ↑ "Modeling mammary organogenesis from biological first principles: Cells and their physical constraints". Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology. From the Century of the Genome to the Century of the Organism: New Theoretical Approaches 122 (1): 58–69. October 2016. doi:10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2016.08.004. PMID 27544910.
- ↑ "Mathematical biology modules based on modern molecular biology and modern discrete mathematics". CBE: Life Sciences Education (The American Society for Cell Biology) 9 (3): 227–40. Fall 2010. doi:10.1187/cbe.10-03-0019. PMID 20810955.
- ↑ "Mimicry: an interface between psychology and evolution". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 98 (16): 8928–30. July 2001. doi:10.1073/pnas.171326298. PMID 11481461. Bibcode: 2001PNAS...98.8928M.
- ↑ Ian Stewart (1998), Life's Other Secret: The New Mathematics of the Living World, New York: John Wiley, ISBN 978-0471158455
- ↑ Making Sense of Life: Explaining Biological Development with Models, Metaphors and Machines. Harvard University Press. 2002. ISBN 978-0674012509. https://books.google.com/books?id=NdtbR_N_vKYC.
- ↑ "Mathematical Biology is Good for Mathematics". Notices of the AMS 62 (10): 1172–1176. November 2015. doi:10.1090/noti1288.
- ↑ "Complex Non-linear Biodynamics in Categories, Higher Dimensional Algebra and Łukasiewicz–Moisil Topos: Transformations of Neuronal, Genetic and Neoplastic Networks". Axiomathes 16 (1–2): 65–122. 2006. doi:10.1007/s10516-005-3973-8.
- ↑ "Łukasiewicz-Topos Models of Neural Networks, Cell Genome and Interactome Nonlinear Dynamic Models". 2004. http://cogprints.org/3701/01/ANeuralGenNetworkLuknTopos_oknu4.pdf/.
- ↑ "Complex Systems Analysis of Arrested Neural Cell Differentiation during Development and Analogous Cell Cycling Models in Carcinogenesis.". Nature Precedings. April 2012. doi:10.1038/npre.2012.7101.1.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "Research in Mathematical Biology". Maths.gla.ac.uk. http://www.maths.gla.ac.uk/research/groups/biology/kal.htm.
- ↑ "Ten equations that changed biology: mathematics in problem-solving biology curricula.". Bioscene 23 (1): 11–36. May 1997. http://acube.org/volume_23/v23-1p11-36.pdf.
- ↑ "Biological organisation as closure of constraints". Journal of Theoretical Biology 372: 179–91. May 2015. doi:10.1016/j.jtbi.2015.02.029. PMID 25752259. Bibcode: 2015JThBi.372..179M. https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01192916/file/Montevil-Mossio_2015_Closure-of-constraints.pdf.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 "Computer Models and Automata Theory in Biology and Medicine". Mathematical Models in Medicine. 7. New York: Pergamon Press. 1987. pp. 1513–1577. http://cogprints.org/3687/.
- ↑ "Symbolic calculation in the life sciences: trends and prospects". Algebraic Biology 2005. Computer Algebra in Biology. Tokyo: Universal Academy Press. 2006. http://www.princeton.edu/~allengrp/ms/annobib/mb.pdf.
- ↑ Cancer Modelling and Simulation. Chapman Hall/CRC Press. 2003. ISBN 1-58488-361-8. http://library.bjcancer.org/ebook/109.pdf.
- ↑ "Computer Models and Automata Theory in Biology and Medicine". Mathematical Modeling : Mathematical Models in Medicine. 7. New York: Pergamon Press. 1986. pp. 1513–1577. https://cdsweb.cern.ch/record/746663/files/COMPUTER_MODEL_AND_AUTOMATA_THEORY_IN_BIOLOGY2p.pdf.
- ↑ "Computer Simulations and the Question of Computability of Biological Systems". 2004. https://tspace.library.utoronto.ca/bitstream/1807/2951/2/compauto.pdf.
- ↑ Computer Models and Automata Theory in Biology and Medicine. 1986.
- ↑ "Natural Transformations Models in Molecular Biology". SIAM and Society of Mathematical Biology, National Meeting (Bethesda, MD) N/A: 230–232. 1983. http://cogprints.org/3675/.
- ↑ "Quantum Interactomics and Cancer Mechanisms". Research Report Communicated to the Institute of Genomic Biology, University of Illinois at Urbana. 2004. https://tspace.library.utoronto.ca/retrieve/4969/QuantumInteractomicsInCancer_Sept13k4E_cuteprt.pdf.
- ↑ "Category Theory and Living Systems". Charles Ehresmann's Centennial Conference Proceedings. University of Amiens, France, October 7–9th, 2005. 2005. pp. 1–5. http://vbm-ehr.pagesperso-orange.fr/ChEh/articles/Kainen.pdf.
- ↑ "bibliography for category theory/algebraic topology applications in physics". PlanetPhysics. http://planetphysics.org/encyclopedia/BibliographyForCategoryTheoryAndAlgebraicTopologyApplicationsInTheoreticalPhysics.html.
- ↑ "bibliography for mathematical biophysics and mathematical medicine". PlanetPhysics. 2009-01-24. http://planetphysics.org/encyclopedia/BibliographyForMathematicalBiophysicsAndMathematicalMedicine.html.
- ↑ "Cellular Automata". Los Alamos Science Fall 1983.
- ↑ Modern Cellular Automata. Springer. 1985-02-28. ISBN 9780306417375. https://books.google.com/books?id=l0_0q_e-u_UC.
- ↑ "Dual Tessellation – from Wolfram MathWorld". Mathworld.wolfram.com. 2010-03-03. http://mathworld.wolfram.com/DualTessellation.html.
- ↑ "Computer models and automata theory in biology and medicine | KLI Theory Lab". Theorylab.org. 2009-05-26. http://theorylab.org/node/56690.
- ↑ "rwo_research_details". Maths.gla.ac.uk. 2004-07-02. http://www.maths.gla.ac.uk/~rwo/research_areas.htm.
- ↑ "Impact of tumor-parenchyma biomechanics on liver metastatic progression: a multi-model approach". Scientific Reports 11 (1): 1710. January 2021. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-78780-7. PMID 33462259. Bibcode: 2021NatSR..11.1710W.
- ↑ "A Computational Model of Oncogenesis using the Systemic Approach". Axiomathes 16 (1–2): 155–163. 2006. doi:10.1007/s10516-005-4943-x.
- ↑ "MCRTN – About tumour modelling project". Calvino.polito.it. http://calvino.polito.it/~mcrtn/.
- ↑ "Jonathan Sherratt's Research Interests". Ma.hw.ac.uk. http://www.ma.hw.ac.uk/~jas/researchinterests/index.html.
- ↑ "Jonathan Sherratt's Research: Scar Formation". Ma.hw.ac.uk. http://www.ma.hw.ac.uk/~jas/researchinterests/scartissueformation.html.
- ↑ "A macroscopic model of traffic jams in axons". Mathematical Biosciences 218 (2): 142–52. April 2009. doi:10.1016/j.mbs.2009.01.005. PMID 19563741.
- ↑ "Modeling and simulation of intracellular dynamics: choosing an appropriate framework". IEEE Transactions on NanoBioscience 3 (3): 200–7. September 2004. doi:10.1109/TNB.2004.833694. PMID 15473072.
- ↑ "Tyson Lab". http://mpf.biol.vt.edu/Research.html.
- ↑ "A mathematical model of caspase function in apoptosis". Nature Biotechnology 18 (2): 768–74. July 2000. doi:10.1038/77589. PMID 10888847.
- ↑ "Inference in a Partial Differential Equations Model of Pulmonary Arterial and Venous Blood Circulation using Statistical Emulation". 13th International Conference on Computational Intelligence Methods for Bioinformatics and Biostatistics, Stirling, UK, 1–3 Sep 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. 10477. 2017. pp. 184–198. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-67834-4_15. ISBN 9783319678337. http://eprints.gla.ac.uk/129013/7/129013.pdf.
- ↑ "Integrative Biology – Heart Modelling". Integrativebiology.ox.ac.uk. http://www.integrativebiology.ox.ac.uk/heartmodel.html.
- ↑ Fundamentals of Computational Neuroscience. United States: Oxford University Press Inc.. 2002. pp. 1. ISBN 978-0-19-851582-1. https://archive.org/details/fundamentalscomp00ttra.
- ↑ "What Is Computational Neuroscience?". Biology And Computation: A Physicist's Choice. 3. World Scientific. March 1994. pp. 25–34. ISBN 9789814504140. https://books.google.com/books?id=l7vsCgAAQBAJ&pg=PT42.
- ↑ SAC Phylogenetics. Oxford University Press. 2003. ISBN 978-0-19-850942-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=uR8i2qet.
- ↑ "Travelling waves in a wound". Maths.ox.ac.uk. http://www.maths.ox.ac.uk/~maini/public/gallery/twwha.htm.
- ↑ "Leah Edelstein-Keshet: Research Interests f". http://www.math.ubc.ca/people/faculty/keshet/research.html.
- ↑ "The mechanochemical theory of morphogenesis". Maths.ox.ac.uk. http://www.maths.ox.ac.uk/~maini/public/gallery/mctom.htm.
- ↑ "Biological pattern formation". Maths.ox.ac.uk. http://www.maths.ox.ac.uk/~maini/public/gallery/bpf.htm.
- ↑ "Spatial Distribution of the Montane Unicorn". Oikos 58 (3): 257–271. 1990. doi:10.2307/3545216.
- ↑ "Chapter 34: Turing's theory of morphogenesis". The Turing Guide. Oxford University Press. 2017. ISBN 978-0198747826.
- ↑ 52.0 52.1 "molecular set category". PlanetPhysics. http://planetphysics.org/encyclopedia/CategoryOfMolecularSets2.html.
- ↑ "Abstract Relational Biology (ARB)". http://planetphysics.org/encyclopedia/AbstractRelationalBiologyARB.html.
- ↑ (in en) Life Itself: A Comprehensive Inquiry Into the Nature, Origin, and Fabrication of Life. Columbia University Press. 2005-07-13. ISBN 9780231075657.
- ↑ "The JJ Tyson Lab". Virginia Tech. http://mpf.biol.vt.edu/Tyson%20Lab.html.
- ↑ "The Molecular Network Dynamics Research Group". Budapest University of Technology and Economics. http://cellcycle.mkt.bme.hu/.
References
- Mathematical Models in Biology. SIAM. 2004. ISBN 0-07-554950-6.
- Mathematical Theories of Populations: Demographics, Genetics and Epidemics (Reprinted ed.). Philadelphia: SIAM. 1993. ISBN 0-89871-017-0.
- Modelling Biological Populations in Space and Time. C.U.P.. 1991. ISBN 0-521-44855-7. https://archive.org/details/modellingbiologi0000rens.
- Introduction to Mathematical Biology. John Wiley. 1975. ISBN 0-471-74446-8.
- Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos: Applications to Physics, Biology, Chemistry, and Engineering. Perseus. 2001. ISBN 0-7382-0453-6. https://archive.org/details/nonlineardynamic00stro.
- "Biologist Salary | Payscale". Payscale.Com, 2021, Biologist Salary | PayScale. Accessed 3 May 2021.
- Theoretical biology
- The Evolution of Complexity by Means of Natural Selection. Princeton: Princeton University Press. 1988. ISBN 0-691-08493-9. https://archive.org/details/evolutionofcompl0000bonn.
- The Theoretical Biologist's Toolbox. Quantitative Methods for Ecology and Evolutionary Biology. Cambridge University Press. 2006. ISBN 0-521-53748-7.
Further reading
- "Getting Started in Mathematical Biology". Notices of the American Mathematical Society. September 1995. https://www.ams.org/notices/199509/hoppensteadt.pdf.
- "Uses and abuses of mathematics in biology". Science 303 (5659): 790–3. February 2004. doi:10.1126/science.1094442. PMID 14764866. Bibcode: 2004Sci...303..790M.
- "How the leopard gets its spots?". Scientific American 258 (3): 80–87. 1988. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0388-80. Bibcode: 1988SciAm.258c..80M. http://www.resnet.wm.edu/~jxshix/math490/murray.doc.
- "Why Is Mathematical Biology So Hard?". Notices of the American Mathematical Society. March 2004. http://www.resnet.wm.edu/~jxshix/math490/reed.pdf.
- Complex Systems and Their Use in Medicine: Concepts, Methods and Bio-Medical Applications. 2019. doi:10.13140/RG.2.2.29919.30887. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/330546521.
External links
 |
 KSF
KSF