Transsulfuration pathway
Topic: Biology
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 3 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 3 min
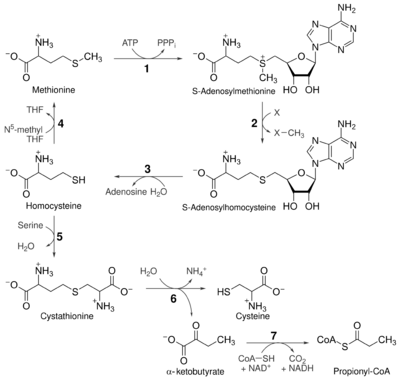
The transsulfuration pathway is a metabolic pathway involving the interconversion of cysteine and homocysteine through the intermediate cystathionine. Two transsulfurylation pathways are known: the forward and the reverse.[1]
The forward pathway is present in several bacteria, such as Escherichia coli[2] and Bacillus subtilis,[3] and involves the transfer of the thiol group from cysteine to homocysteine (methionine precursor with the S-methyl group), thanks to the γ-replacement of the acetyl or succinyl group of a homoserine with cysteine via its thiol group to form cystathionine (catalysed by cystathionine γ-synthase, which is encoded by metB in E. coli and metI in B. subtilis). Cystathionine is then cleaved by means of the β-elimination of the homocysteine portion of the molecule leaving behind an unstable imino acid, which is attacked by water to form pyruvate and ammonia (catalysed by the metC-encoded cystathionine β-lyase[4]). The production of homocysteine through transsulfuration allows the conversion of this intermediate to methionine, through a methylation reaction carried out by methionine synthase.
The reverse pathway is present in several organisms, including humans, and involves the transfer of the thiol group from homocysteine to cysteine via a similar mechanism. In Klebsiella pneumoniae the cystathionine β-synthase is encoded by mtcB, while the γ-lyase is encoded by mtcC.[5] Humans are auxotrophic for methionine, hence it is called an "essential amino acid" by nutritionists, but are not for cysteine due to the reverse trans-sulfurylation pathway. Mutations in this pathway lead to a disease known as homocystinuria, due to homocysteine accumulation.
Role of pyridoxal phosphate
All four transsulfuration enzymes require vitamin B6 in its active form (pyridoxal phosphate or PLP). Three of these enzymes (cystathionine γ-synthase excluded) are part of the Cys/Met metabolism PLP-dependent enzyme family (type I PLP enzymes). {{#section-h:Cys/Met metabolism PLP-dependent enzyme family|Family members}}
Direct sulfurization
The direct sulfurylation pathways for the synthesis of cysteine or homocysteine proceeds via the replacement of the acetyl/succinyl group with free sulfide (via the cysK or cysM -encoded cysteine synthase.[6] and the metZ or metY -encoded homocysteine synthase,[7]
References
- ↑ Weekley, C. M. and Harris, H. H. (2013). "Which form is that? The importance of selenium speciation and metabolism in the prevention and treatment of disease". Chem. Soc. Rev. 42 (23): 8870–8894. doi:10.1039/c3cs60272a. PMID 24030774.
- ↑ Aitken, S. M.; Lodha, P. H.; Morneau, D. J. K. (2011). "The enzymes of the transsulfuration pathways: Active-site characterizations". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Proteins and Proteomics 1814 (11): 1511–7. doi:10.1016/j.bbapap.2011.03.006. PMID 21435402.
- ↑ Auger, S.; Yuen, W. H.; Danchin, A.; Martin-Verstraete, I. (2002). "The metIC operon involved in methionine biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis is controlled by transcription antitermination". Microbiology 148 (Pt 2): 507–518. doi:10.1099/00221287-148-2-507. PMID 11832514.
- ↑ Clausen, T.; Huber, R.; Laber, B.; Pohlenz, H. D.; Messerschmidt, A. (1996). "Crystal Structure of the Pyridoxal-5′-phosphate Dependent Cystathionine β-lyase fromEscherichia coliat 1.83 Å". Journal of Molecular Biology 262 (2): 202–224. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1996.0508. PMID 8831789.
- ↑ Seiflein, T. A.; Lawrence, J. G. (2006). "Two Transsulfurylation Pathways in Klebsiella pneumoniae". Journal of Bacteriology 188 (16): 5762–5774. doi:10.1128/JB.00347-06. PMID 16885444.
- ↑ Rabeh, W. M.; Cook, P. F. (2004). "Structure and Mechanism of O-Acetylserine Sulfhydrylase". Journal of Biological Chemistry 279 (26): 26803–26806. doi:10.1074/jbc.R400001200. PMID 15073190.
- ↑ Hwang, B. J.; Yeom, H. J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, H. S. (2002). "Corynebacterium glutamicum utilizes both transsulfuration and direct sulfhydrylation pathways for methionine biosynthesis". Journal of Bacteriology 184 (5): 1277–1286. doi:10.1128/JB.184.5.1277-1286.2002. PMID 11844756.
<ref> tag with name "review" defined in <references> is not used in prior text.
 |
 KSF
KSF