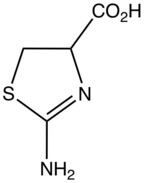
2-Aminothiazoline-4-carboxylic acid
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 1 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 1 min
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Amino-4,5-dihydro-1,3-thiazole-4-carboxylic acid | |
| Other names
ACTA
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H6N2O2S | |
| Molar mass | 146.16 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Melting point | 212 °C (414 °F; 485 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
2-Aminothiazoline-4-carboxylic acid (ACTA) is the organosulfur compound and a heterocycle with the formula HO2CCHCH2SCNH2N. This derivative of thiazoline is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of L-cysteine, an amino acid. ACTA exists in equilibrium with its tautomer 2-iminothiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid.
It is produced by the reaction of methyl chloroacrylate with thiourea.[1] It is also a biomarker for cyanide poisoning, as it results from the condensation of cysteine and cyanide.[2]
References
- ↑ Karlheinz Drauz; Ian Grayson; Axel Kleemann; Hans-Peter Krimmer; Wolfgang Leuchtenberger, Christoph Weckbecker (2006). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a02_057.pub2.
- ↑ Logue, Brian A.; Kirschten, Nicholas P.; Petrikovics, Ilona; Moser, Matthew A.; Rockwood, Gary A.; Baskin, Steven I. (2005). "Determination of the cyanide metabolite 2-aminothiazoline-4-carboxylic acid in urine and plasma by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry". Journal of Chromatography B 819 (2): 237–244. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2005.01.045. PMID 15833287. https://openprairie.sdstate.edu/chem_pubs/42.
 |
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:2-Aminothiazoline-4-carboxylic_acid1 | Status: cached on March 14 2026 15:54:20↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF