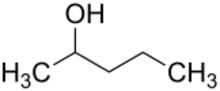
2-Pentanol
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 3 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 3 min
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Pentan-2-ol | |
| Other names
2-Pentanol
sec-amyl alcohol | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H12O | |
| Molar mass | 88.148 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.812 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −73 °C (−99 °F; 200 K) |
| Boiling point | 119.3 °C (246.7 °F; 392.4 K) |
| 45 g/L | |
| Solubility | soluble in ethanol, diethyl ether, carbon tetrachloride, chloroform |
| Vapor pressure | 0.804 kPa |
| -69.1·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Viscosity | 3.470 mPa·s |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C)
|
2.716 J·g−1·K−1 (liquid) |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
-365.2 kJ·mol−1 (liquid) -311.0 kJ·mol−1 (gas) |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 34 °C (93 °F; 307 K) |
| 343 °C (649 °F; 616 K) | |
| Explosive limits | 1.2–9% |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Amyl alcohol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
2-Pentanol (IUPAC name: pentan-2-ol; also called sec-amyl alcohol) is an organic chemical compound. It is used as a solvent and an intermediate in the manufacturing of other chemicals. 2-Pentanol is a component of many mixtures of amyl alcohols sold industrially. 2-Pentanol is chiral and thus can be obtained as either of two stereoisomers designated as (R)-(−)-2-pentanol and (S)-(+)-2-pentanol.
2-Pentanol has been detected in fresh bananas by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry, at an abundance of 14.26±2.63 ppm.[2]
Reactions
2-Pentanol can be manufactured by hydration of pentene.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Lide, David R. (1998), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.), Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, pp. 3-454, 5-42, 6-188, 8-102, 15-23, ISBN 0-8493-0594-2
- ↑ Jordán, María J.; Tandon, Kawaljit; Shaw, Philip E.; Goodner, Kevin L. (2001), "Aromatic Profile of Aqueous Banana Essence and Banana Fruit by Gas Chromatography−Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) and Gas Chromatography−Olfactometry (GC-O)", Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 49 (10): 4813–4817, doi:10.1021/jf010471k, PMID 11600027
- ↑ McKetta, John J.; Cunningham, William Aaron (1977), Encyclopedia of Chemical Processing and Design, 3, Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, pp. 280–281, ISBN 978-0-8247-2480-1, https://books.google.com/books?id=iwSU5G5VzO0C&pg=PA279, retrieved 2010-01-17
 |
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:2-Pentanol5 views | Status: cached on August 23 2024 10:21:32↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF