ACPD
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 4 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 4 min
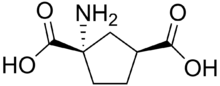
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-Aminocyclopentane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | ACPD |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | 1-amino-1,3-dicarboxycyclopentane |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H11NO4 | |
| Molar mass | 173.168 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| 20 g dm−3 | |
| Solubility in ethanol | 240 mg dm−3 |
| log P | -0.709 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.112 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 11.885 |
| Isoelectric point | 2.84 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H302, H312, H315, H319, H332, H335 | |
| P261, P280, P305+351+338 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
1-Amino-1,3-dicarboxycyclopentane (ACPD) is a chemical compound that binds to the metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR),[2] acting as a mGluR agonist. ACPD is a rigid analogue of the neurotransmitter glutamate and does not activate ionotropic glutamate receptors.[3] However, it has been reported to be an agonist of the glycine site of the NMDA receptor.[citation needed] ACPD can induce convulsions in neonatal rats.[4]
References
- ↑ "1-amino-1,3-dicarboxycyclopentane - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 25 March 2005. Identification and Related Records. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?cid=1310.
- ↑ "1S,3R-ACPD-sensitive (metabotropic) [3H]glutamate receptor binding in membranes". Neurosci. Lett. 145 (1): 100–4. September 1992. doi:10.1016/0304-3940(92)90213-Q. PMID 1461560.
- ↑ "(trans)-1-amino-cyclopentyl-1,3-dicarboxylate stimulates quisqualate phosphoinositide-coupled receptors but not ionotropic glutamate receptors in striatal neurons and Xenopus oocytes". Mol. Pharmacol. 38 (1): 1–6. July 1990. PMID 2164627. http://molpharm.aspetjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=2164627.
- ↑ "Seizures and brain injury in neonatal rats induced by 1S,3R-ACPD, a metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist". J. Neurosci. 13 (10): 4445–55. October 1993. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-10-04445.1993. PMID 8410197.
 |
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:ACPD5 views | Status: cached on August 21 2024 23:39:29↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF