Aluminium iodide
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 5 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 5 min
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Aluminium iodide | |
| Other names
Aluminium(III) iodide
Aluminum iodide | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
| UN number | UN 3260 |
| |
| Properties | |
| AlI3, AlI3·6H2O (hexahydrate) | |
| Molar mass | 407.695 g/mol (anhydrous) 515.786 g/mol (hexahydrate)[1] |
| Appearance | white (anhydrous) or yellow powder (hexahydrate)[1] |
| Density | 3.98 g/cm3 (anhydrous)[1] 2.63 g/cm3 (hexahydrate)[2] |
| Melting point | 188.28 °C (370.90 °F; 461.43 K) (anhydrous) 185 °C, decomposes (hexahydrate)[1][2] |
| Boiling point | 382 °C (720 °F; 655 K) anhydrous, sublimes[1] |
| very soluble, partial hydrolysis | |
| Solubility in alcohol, ether | soluble (hexahydrate) |
| Structure[3] | |
| Monoclinic, mP16 | |
| P21/c, No. 14 | |
a = 1.1958 nm, b = 0.6128 nm, c = 1.8307 nm α = 90°, β = 90°, γ = 90°
| |
Formula units (Z)
|
8 |
| Thermochemistry[1] | |
Heat capacity (C)
|
98.7 J/(mol·K) |
Std molar
entropy (S |
195.9 J/(mol·K) |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
-302.9 kJ/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Aluminium iodide is a chemical compound containing aluminium and iodine. Invariably, the name refers to a compound of the composition AlI3, formed by the reaction of aluminium and iodine[4] or the action of HI on Al metal. The hexahydrate is obtained from a reaction between metallic aluminum or aluminum hydroxide with hydrogen iodide or hydroiodic acid. Like the related chloride and bromide, AlI3 is a strong Lewis acid and will absorb water from the atmosphere. It is employed as a reagent for the scission of certain kinds of C-O and N-O bonds. It cleaves aryl ethers and deoxygenates epoxides.[5]
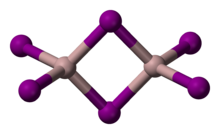
Structure
Solid AlI3 is dimeric, consisting of Al2I6, similar to that of AlBr3.[3] The structure of monomeric and dimeric forms have been characterized in the gas phase.[6] The monomer, AlI3, is trigonal planar with a bond length of 2.448(6) Å, and the bridged dimer, Al2I6, at 430 K is a similar to Al2Cl6 and Al2Br6 with Al–I bond lengths of 2.456(6) Å (terminal) and 2.670(8) Å (bridging). The dimer is described as floppy with an equilibrium geometry of D2h.
Aluminium(I) iodide
File:06. Директна синтеза на алуминиум јодид.webm The name "aluminium iodide" is widely assumed to describe the triiodide or its dimer. In fact, a monoiodide also enjoys a role in the Al–I system, although the compound AlI is unstable at room temperature relative to the triiodide:[7]
An illustrative derivative of aluminium monoiodide is the cyclic adduct formed with triethylamine, Al4I4(NEt3)4.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Haynes, William M., ed (2011). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (92nd ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. p. 4.45. ISBN 1439855110.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Perry, Dale L. (19 April 2016). Handbook of Inorganic Compounds, Second Edition. CRC Press. p. 8. ISBN 978-1-4398-1462-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=SFD30BvPBhoC&pg=PA8.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Troyanov, Sergey I.; Krahl, Thoralf; Kemnitz, Erhard (2004). "Crystal structures of GaX3(X= Cl, Br, I) and AlI3". Zeitschrift für Kristallographie 219 (2–2004): 88–92. doi:10.1524/zkri.219.2.88.26320.
- ↑ Watt, George W; Hall, James L; Taylor, William Lloyd; Kleinberg, Jacob (1953). "Aluminum Iodide". Inorganic Syntheses. 4. pp. 117–119. doi:10.1002/9780470132357.ch39. ISBN 9780470132357.
- ↑ Gugelchuk, M. (2004). "Aluminum Iodide". in L. Paquette. Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. New York: J. Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/047084289X.ra083. ISBN 0471936235.
- ↑ Hargittai, Magdolna; Réffy, Balázs; Kolonits, Mária (2006). "An Intricate Molecule: Aluminum Triiodide. Molecular Structure of AlI3and Al2I6 from Electron Diffraction and Computation". The Journal of Physical Chemistry A 110 (10): 3770–3777. doi:10.1021/jp056498e. PMID 16526661.
- ↑ Dohmeier, C.; Loos, D.; Schnöckel, H. (1996). "Aluminum(I) and Gallium(I) Compounds: Syntheses, Structures, and Reactions". Angewandte Chemie International Edition 35 (2): 129–149. doi:10.1002/anie.199601291.
External links
| HI | He | ||||||||||||||||
| LiI | BeI2 | BI3 | CI4 | NI3 | I2O4, I2O5, I4O9 |
IF, IF3, IF5, IF7 |
Ne | ||||||||||
| NaI | MgI2 | AlI3 | SiI4 | PI3, P2I4 |
S | ICl, ICl3 |
Ar | ||||||||||
| KI | CaI2 | Sc | TiI4 | VI3 | CrI3 | MnI2 | FeI2 | CoI2 | NiI2 | CuI | ZnI2 | Ga2I6 | GeI2, GeI4 |
AsI3 | Se | IBr | Kr |
| RbI | SrI2 | YI3 | ZrI4 | NbI5 | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | AgI | CdI2 | InI3 | SnI4, SnI2 |
SbI3 | TeI4 | I | Xe |
| CsI | BaI2 | HfI4 | TaI5 | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | AuI | Hg2I2, HgI2 |
TlI | PbI2 | BiI3 | Po | AtI | Rn | |
| Fr | RaI2 | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | |
| ↓ | |||||||||||||||||
| La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | SmI2 | Eu | Gd | TbI3 | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |||
| Ac | ThI4 | Pa | UI3, UI4 |
Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | EsI3 | Fm | Md | No | Lr | |||
 |
 KSF
KSF