Anol
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 5 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 5 min
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
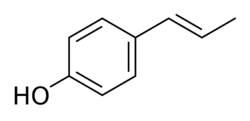
| Formula | C9H10O |
| Molar mass | 134.178 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Anol, also known as para-hydroxypropenylbenzene,[1] is a simple phenol that was derived via demethylation from anethole, an estrogenic constituent of anise and fennel, by Sir Charles Dodds in 1937.[2][3] It was reported to possess extremely potent estrogenic activity on par with that of steroidal estrogens like estrone, with a dose of 1 μg inducing estrus in rats.[2] However, subsequent studies with different preparations of anol failed to confirm these findings, and it was found that dimerization of anol into dianol and hexestrol can rapidly occur and that the latter impurity was responsible for the highly potent estrogenic effects.[4] [2][3][5][6] Dodds later synthesized the structurally related and extremely potent estrogen diethylstilbestrol in 1938.[2][5]
See also
References
- ↑ "Synthetic œstrogens in treatment". The Irish Journal of Medical Science 25 (7): 305–314. 2008. doi:10.1007/BF02950685. ISSN 0021-1265.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Tamoxifen: Pioneering Medicine in Breast Cancer. Springer Science & Business Media. 23 July 2013. pp. 3–. ISBN 978-3-0348-0664-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=p-W5BAAAQBAJ&pg=PA3.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Possibilities in the Realm of Synthetic Estrogens". Vitamins and Hormones. Academic Press. 1 January 1945. pp. 232–. ISBN 978-0-08-086600-0. https://archive.org/details/in.ernet.dli.2015.5563.
- ↑ "The nature of the oestrogenic substances produced during the demethylation of anethole". Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences 128 (851): 253–262. 1940. doi:10.1098/rspb.1940.0009. ISSN 2053-9193. Bibcode: 1940RSPSB.128..253C.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Sex hormones and derivatives: Natural and Synthetic (Non-Steroidal) Estrogen and Androgens". The Evolution of Drug Discovery: From Traditional Medicines to Modern Drugs. John Wiley & Sons. 11 January 2011. pp. 177–. ISBN 978-3-527-32669-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=iDNy0XxGqT8C&pg=PA177.
- ↑ "Synthetic estrogens and the relation between their structure and their activity". Chemical Reviews 37 (3): 481–598. December 1945. doi:10.1021/cr60118a004. PMID 21013428.
 |
 KSF
KSF