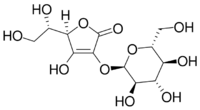
Ascorbyl glucoside
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2R)-2-[(1S)-1,2-Dihydroxyethyl]-3-hydroxy-4-[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-2H-furan-5-one
| |
| Other names
Ascorbic acid 2-O-glucoside; 2-O-alpha-D-Glucopyranosyl-L-ascorbic acid; AA-2G; L-Ascorbic acid 2-O-alpha-glucoside
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H18O11 | |
| Molar mass | 338.265 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Ascorbyl glucoside (AA-2G) is an ascorbic acid derivative that contains at least one glycosyl group. Ascorbyl glucoside is commonly used in cosmetic products to administer vitamin C topically. Ascorbyl glucoside exhibits superior stability and penetration ability compared to ascorbyl phosphate salts, but the rate of its in vivo conversion to ascorbic acid is not known.[1] Ascorbyl glucosides such as AA-2G, like many other derivatives of the ascorbic acid, show antiscorbutic effects.[2] It is also sometimes used in skin whitening products.[3]
Ascorbyl glucoside is synthesized through a glycosylation process catalyzed by glycosyltransferase-class enzymes.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Pullar, Juliet M.; Carr, Anitra C.; Vissers, Margreet C. M. (2017-08-12). "The Roles of Vitamin C in Skin Health". Nutrients 9 (8): 866. doi:10.3390/nu9080866. ISSN 2072-6643. PMID 28805671.
- ↑ Yamamoto, I.; Suga, S.; Mitoh, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Muto, N. (November 1990). "Antiscorbutic activity of L-ascorbic acid 2-glucoside and its availability as a vitamin C supplement in normal rats and guinea pigs". Journal of Pharmacobio-Dynamics 13 (11): 688–695. doi:10.1248/bpb1978.13.688. ISSN 0386-846X. PMID 2093127.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Current research situation and development prospect of ascorbyl glucoside--《Chinese Journal of Bioprocess Engineering》2008年04期". https://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-SWJG200804002.htm.
 |
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Ascorbyl_glucoside36 views | Status: cached on January 25 2026 15:14:20↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF