BOP reagent
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
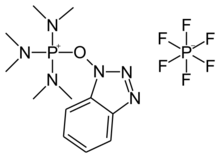
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
((1H-Benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-1-yl)oxy)tris(dimethylamino)phosphonium hexafluorophosphate(V)
| |
| Other names
Castro's reagent
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H22F6N6OP2 | |
| Molar mass | 442.287 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
| Melting point | 136 to 140 °C (277 to 284 °F; 409 to 413 K) |
| Partially soluble in cold water reacts (decomposes) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
BOP (benzotriazol-1-yloxytris(dimethylamino)phosphonium hexafluorophosphate) reagent is a reagent commonly used in the synthesis of peptides. Its use is discouraged because coupling using BOP liberates HMPA which is carcinogenic, although for small scale use in an organic laboratory this is not a great disadvantage as it is in large scale industrial usage.
BOP has been used for peptide coupling, synthesis of esters, esterification of carboxylic acids, or as a catalyst.[1][2] This reagent is advantageous in peptide coupling to other derived reagents because there are no side reactions from the dehydration of asparagine or glutamine.[2] In peptide coupling the BOP reagent works well because it forms reactive intermediates which allow for the amines to bond together with little energy loss.[3] In the reduction of carboxylic acids, using the BOP reagent with NaBH4 resulted in high percent yields.[3]
See also
- PyBOP, a related reagent
References
- ↑ "(Benzotriazol-1-yloxy)tris(dimethylamino)phosphonium hexafluorophosphate 226084". https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/aldrich/226084.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Prasad, KVSRG; Bharathi, K; Haseena, Banu B (5 January 2011). "Applications of Peptide Coupling Reagents- An Update". International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences Review and Research 8 (1): 108–119.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 McGeary, Ross P. (1998-05-14). "Facile and chemoselective reduction of carboxylic acids to alcohols using BOP reagent and sodium borohydride" (in en). Tetrahedron Letters 39 (20): 3319–3322. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(98)00480-8. ISSN 0040-4039.
 |
 KSF
KSF