Bixin
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 4 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 4 min
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
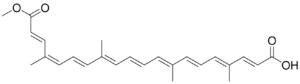
| IUPAC name
(2E,4E,6E,8E,10E,12E,14E,16Z,18E)-20-Methoxy-4,8,13,17-tetramethyl-20-oxoicosa-2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16,18-nonaenoic acid
| |
| Other names
cis-Bixin; α-Bixin; 9-cis-6,6'-Diapo-ψ,ψ-carotenedioic acid, 6-methyl ester
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C25H30O4 | |
| Molar mass | 394.511 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Orange crystals |
| Melting point | 198 °C (cis-isomer) 217 °C (trans-isomer) |
| Insoluble | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Bixin is an apocarotenoid found in the seeds of the achiote tree (Bixa orellana)[2] from which it derives its name. It is commonly extracted from the seeds to form annatto, a natural food coloring, containing about 5% pigments of which 70–80% are bixin.[3]
Applications
- thumb|center|Red seeds of the achiote tree
- thumb|Bixin is one of the colorants used in the snack Cheetos.
Several thousand tons are harvested annually.[4]
Chemical properties
Bixin is unstable. It isomerizes into trans-bixin (β-bixin), the double-bond isomer.[1]
Bixin is soluble in fats and alcohols but insoluble in water. Upon exposure to alkali, the methyl ester is hydrolyzed to produce the dicarboxylic acid norbixin, a water-soluble derivative.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Merck Index, 11th Edition, 1320
- ↑ Bouvier, Florence; Dogbo, Odette; Camara, Bilal (2003). "Biosynthesis of the Food and Cosmetic Plant Pigment Bixin (Annatto)". Science 300 (5628): 2089–2091. doi:10.1126/science.1085162. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 12829782. Bibcode: 2003Sci...300.2089B. https://www.jstor.org/stable/3834418.
- ↑ Executive Summary Bixin , National Toxicology Program
- ↑ Stringheta, Paulo C.; Silva, Pollyanna I.; Costa, André G.V. (2018). "Annatto/Urucum— Bixa orellana". Exotic Fruits. pp. 23–30. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-803138-4.00006-X. ISBN 9780128031384.
 |
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Bixin4 views | ↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF


