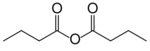
Butyric anhydride
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Butanoic anhydride | |
| Other names
Butyric anhydride
Butanoyl butanoate Butanoic acid anhydride Butyric acid anhydride Butyryl oxide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H14O3 | |
| Molar mass | 158.197 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Clear liquid |
| Density | .967 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −75 °C (−103 °F; 198 K) |
| Boiling point | 198 °C (388 °F; 471 K) |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.413 |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | [1] |
| Related compounds | |
Related acid anhydrides
|
Acetic anhydride Propionic anhydride Valeric anhydride |
Related compounds
|
Butyric acid Butyryl chloride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Butyric anhydride or butanoic anhydride is the chemical compound with the formula (CH3CH2CH2CO)2O. The molecule can be described as a condensation of two molecules of butyric acid with elimination of one water molecule (hence its name).
Butyric anhydride is a clear colorless liquid that smells strongly of butyric acid, which is formed by its reaction to moisture in the air.
Safety
Butyric anhydride is a combustible, corrosive liquid. It is considered water sensitive.[1]
References
- ↑ "MSDS Information". Butyric Anhydride MSDS. http://www.coleparmer.com/catalog/Msds/96914.htm. Retrieved 2011-01-07.
 |
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Butyric_anhydride13 views | Status: cached on January 26 2026 08:51:20↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF