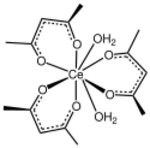
Cerium(III) acetylacetonate
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 3 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 3 min
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
cerium; (Z)-4-hydroxypent-3-en-2-one
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H21CeO6 | |
| Molar mass | 437.443 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Crystalline powder |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Cerium(III) acetylacetonate is a compound with formula Ce(C5H7O2)3(H2O)x. It is typically isolated as the trihydrate. Partial dehydration gives the dihydrate, a red-brown solid.[2]
Reactions
Cerium acetylacetonate is a precursor to mesoporous nanocrystalline ceria using the sol-gel process.[3] It can also be used along with gadolinium acetylacetonate to synthesize gadolinia-doped ceria (GDC) gel powders.[4]
See also
- Cerium(IV) tetrakis(acetylacetonate)
References
- ↑ Cerium acetylacetonate at American Elements
- ↑ Behrsing, Thomas; Bond, Alan M.; Deacon, Glen B.; Forsyth, Craig M.; Forsyth, Maria; Kamble, Kalpana J.; Skelton, Brian W.; White, Allan H. (2003). "Cerium acetylacetonates—new aspects, including the lamellar clathrate [Ce(acac)4]·10H2O". Inorganica Chimica Acta 352: 229–237. doi:10.1016/S0020-1693(03)00147-6.
- ↑ "Formation of mesoporous nanocrystalline ceria from cerium nitrate, acetate or acetylacetonate"
- ↑ "Synthesis of Gadolinia-Doped Ceria Gels and Powders from Acetylacetonate Precursors"
 |
Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 | Source: https://handwiki.org/wiki/Chemistry:Cerium(III)_acetylacetonate2 views | ↧ Download this article as ZWI file
 KSF
KSF