Cyclopentadienyl anion
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Cyclopentadienide
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| [C5H5]− or Cp− | |||
| Molar mass | 65.09 g/mol | ||
| Conjugate acid | Cyclopentadiene | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
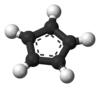
In chemistry, the cyclopentadienyl anion or cyclopentadienide is an aromatic species with a formula of [C5H5]− and abbreviated as Cp−.[1] It is formed by the deprotonation of cyclopentadiene. The cyclopentadienyl anion is a ligand which binds to a metal in organometallic chemistry.[2]
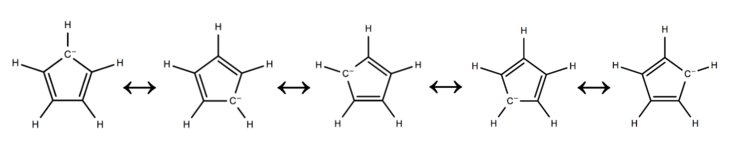
Resonance and aromaticity
The cyclopentadienyl anion is a planar, cyclic, regular-pentagonal ion; it has 6 π-electrons (4n + 2, where n = 1), which fulfills Hückel's rule of aromaticity. Each double bond and lone pair provides 2 π-electrons, which are delocalized into the ring.[3] The cyclopentadienyl anion is a conjugated system because there are alternating π and 𝜎 bonds.[4]
Cyclopentadiene has a pKa of about 16. It is acidic relative to many carbon acids. The enhanced acidity is attributed to stabilization of the conjugate base, cyclopentadienyl anion.
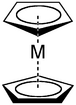
Ligand
Cyclopentadienyl anions form a variety of cyclopentadienyl complexes.[5]
See also
- Cyclopentadienyl radical, [C5H5]•
- Cyclopentadienyl cation, [C5H5]+
- Cyclooctatetraenide anion, [C8H8]2−
References
- ↑ "Cyclopentadienide". National Center for Biotechnology Information. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/3490527#section=Top. Retrieved 14 April 2016.
- ↑ Smith, Michael B.; March, Jerry (2007), Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure (6th ed.), New York: Wiley-Interscience, p. 66, ISBN 978-0-471-72091-1, https://books.google.com/books?id=JDR-nZpojeEC&printsec=frontcover
- ↑ Paul, Satadal; Goswami, Tamal; Misra, Anirban (2015-10-01). "Noncomparative scaling of aromaticity through electron itinerancy". AIP Advances 5 (10): 107211. doi:10.1063/1.4933191. https://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/1.4933191.
- ↑ "Delocalised electrons- Definition and Examples of Delocalized electrons with FAQs" (in en). https://byjus.com/chemistry/delocalized-electrons/.
- ↑ C. Elschenbroich (2006). Organometallics. VCH. ISBN 978-3-527-29390-2.
 KSF
KSF