DNI-Glutamate
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
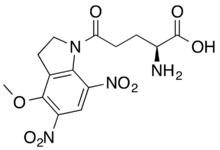
| IUPAC name
2-amino-5-(4-methoxy-5,7-dinitroindolin-1-yl)-5-oxopentanoic acid
| |
| Other names
DNI-Glu
Dinitroindoline-glutamate DMNI-Glu | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H16N4O8 | |
| Molar mass | 368.302 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
DNI-Glutamate ((S)-α-Amino-2,3-dihydro-4-methoxy-5,7-dinitro-δ-oxo-1H-indole-1-pentanoic acid) is a caged form of the glutamate neurotransmitter, which is photocleavable by one- (lexc = 360 nm) as well as two-photon irradiation (lexc = 720 nm). Upon photocleaveage, the bioactive glutamate is released instantly and behaves as a neurotransmitter, which provides information about receptor distribution, channel kinetics and network circuitry of the neuronal network.[1] DNI-Glu is an analogue of the common MNI-Glu compound, but it exhibits cca. 7-10 times larger efficiency in terms of quantum yields compared to the MNI compound. DNI-Glu has low biotoxicity and high water-solubility as well (at physiologic pH).[1] Due to these properties, currently DNI-Glu is thought to be the most advanced caged-glutamate compound for neuroscientific research.
Discovery
DNI-Glu, the molecule itself was first discovered by George Papageorgiou in 2005,[2] but its practical implementation was not mentioned in his publications. Later, in 2009, the compound was reinvestigated in neurophysiological studies and its high efficacy and beneficial properties were reported. The product is commercially available as a trifluoroacetate salt of the compound which was proved to be much more stable and less hygroscopic.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Dénes Pálfi; Balázs Chiovini; Gergely Szalay; Attila Kaszás; Gergely F. Turi; Gergely Katona; Péter Ábrányi-Balogh; Milán Szőri et al. (2018). "High efficiency two-photon uncaging coupled by the correction of spontaneous hydrolysis". Org. Biomol. Chem. 16 (11): 1958–1970. doi:10.1039/C8OB00025E. PMID 29497727.
- ↑ Papageorgiou, George (2005). "Synthetic and photochemical studies of substituted 1-acyl-7-nitroindolines". Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 4 (11): 887–896. doi:10.1039/b508756b. PMID 16252044.
 |
 KSF
KSF