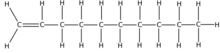
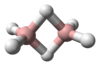Decene
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 6 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 6 min
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Dec-1-ene | |
| Other names
Alpha Olefin C10; Decylene; α-Decene; 1-decene
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3295, 1993 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H20 | |
| Molar mass | 140.270 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.74 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | −66.3 °C (−87.3 °F; 206.8 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 172 °C (342 °F; 445 K)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H226, H304, H410 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P273, P280, P301+310, P303+361+353, P331, P370+378, P391, P403+235, P405, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Related Alkenes
|
Octene Nonene Undecene Dodecene |
Related compounds
|
Decane Decanol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
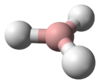
Decene /dɛkiːn/ is an organic compound with the chemical formula C
10H
20. Decene contains a chain of ten carbon atoms with one double bond, making it an alkene. There are many isomers of decene depending on the position and geometry of the double bond. Dec-1-ene is the only isomer of industrial importance. As an alpha olefin, it is used as a comonomer in copolymers and is an intermediate in the production of epoxides, amines, oxo alcohols, synthetic lubricants, synthetic fatty acids and alkylated aromatics.[2]
The industrial processes used in the production of dec-1-ene are oligomerization of ethylene by the Ziegler process or by the cracking of petrochemical waxes.[3]
In ethenolysis, methyl oleate, the methyl ester of oleic acid, converts to 1-decene and methyl 9-decenoate:[4]
Dec-1-ene has been isolated from the leaves and rhizome of the plant Farfugium japonicum and has been detected as the initial product in the microbial degradation of n-decane.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Record in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
- ↑ http://www.ineosoligomers.com/media/files/lao/LAO%20C10%20Data%20Sheet.pdf 1-Decene (Alpha Olefin C10)], ineosoligomers.com
- ↑ Alfa Olefins , SIDS Initial Assessment Report
- ↑ Marinescu, Smaranda C.; Schrock, Richard R.; Müller, Peter; Hoveyda, Amir H. (2009). "Ethenolysis Reactions Catalyzed by Imido Alkylidene Monoaryloxide Monopyrrolide (MAP) Complexes of Molybdenum". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131 (31): 10840–10841. doi:10.1021/ja904786y. PMID 19618951.
External links
- Entry C872059 in Linstrom, Peter J.; Mallard, William G. (eds.); NIST Chemistry WebBook, NIST Standard Reference Database Number 69, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg (MD), http://webbook.nist.gov
 |
 KSF
KSF