Depside
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 2 min
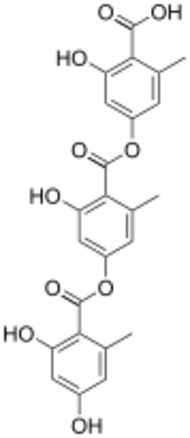
A depside is a type of polyphenolic compound composed of two or more monocyclic aromatic units linked by an ester group. Depsides are most often found in lichens, but have also been isolated from higher plants, including species of the Ericaceae, Lamiaceae, Papaveraceae and Myrtaceae.[1][2][3][4]
Certain depsides have antibiotic, anti-HIV, antioxidant, and anti-proliferative activity in vitro.[4][5][6][7] As inhibitors of prostaglandin synthesis and leukotriene B4 biosynthesis, some depsides have in vitro anti-inflammatory activity.[8][9][10][11]
A depsidase is a type of enzyme that cuts depside bonds. One such enzyme is tannase.[12]
Examples
Gyrophoric acid, found in the lichen Cryptothecia rubrocincta, is a depside. Merochlorophaeic acid, isolated from lichens of the genus Cladonia,[13] is an inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis.
Some depsides are described as anti-HIV.[14]
See also
- Salsalate homodimer formed from self-condensation of salicylic acid to form ester linkage.
References
- ↑ "Antioxidant ortho-benzoyloxyphenyl acetic acid ester, vaccihein A, from the fruit of rabbiteye blueberry (Vaccinium ashei)". Chem. Pharm. Bull. 50 (10): 1416–7. October 2002. doi:10.1248/cpb.50.1416. PMID 12372879.
- ↑ "Variation of free phenolic acids in medicinal plants belonging to the Lamiaceae family". J Pharm Biomed Anal 26 (1): 79–87. August 2001. doi:10.1016/S0731-7085(01)00354-5. PMID 11451645.
- ↑ "Depsides from the petals of Papaver rhoeas". Planta Med. 70 (4): 380–2. April 2004. doi:10.1055/s-2004-818956. PMID 15095160.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Bioactive depsides and anthocyanins from jaboticaba (Myrciaria cauliflora)". J. Nat. Prod. 69 (8): 1228–30. August 2006. doi:10.1021/np0600999. PMID 16933884.
- ↑ "Lichen metabolites. 2. Antiproliferative and cytotoxic activity of gyrophoric, usnic, and diffractaic acid on human keratinocyte growth". J. Nat. Prod. 62 (6): 821–3. June 1999. doi:10.1021/np980378z. PMID 10395495.
- ↑ "Depsides and depsidones as inhibitors of HIV-1 integrase: discovery of novel inhibitors through 3D database searching". J. Med. Chem. 40 (6): 942–51. March 1997. doi:10.1021/jm960759e. PMID 9083483.
- ↑ "Fungl depside, guisinol, from a marine derived strain of Emericella unguis". Phytochemistry 50 (2): 263–265. 1998. doi:10.1016/s0031-9422(98)00517-2.
- ↑ "Structure of the active site of prostaglandin synthase from studies of depsides: an alternate view". Prostaglandins Leukot Med 13 (2): 139–42. February 1984. doi:10.1016/0262-1746(84)90003-9. PMID 6425861.
- ↑ "Depside as potent inhibitor of prostaglandin biosynthesis: a new active site model for fatty acid cyclooxygenase". Prostaglandins 24 (1): 21–34. July 1982. doi:10.1016/0090-6980(82)90174-5. PMID 6812170.
- ↑ "Lichen metabolites. 1. Inhibitory action against leukotriene B4 biosynthesis by a non-redox mechanism". J. Nat. Prod. 62 (6): 817–20. June 1999. doi:10.1021/np9803777. PMID 10395494.
- ↑ "Depsides as non-redox inhibitors of leukotriene B4 biosynthesis and HaCaT cell growth, 2. Novel analogues of obtusatic acid". Eur J Med Chem 35 (4): 405–11. April 2000. doi:10.1016/S0223-5234(00)00132-X. PMID 10858601.
- ↑ "The esterase and depsidase activities of tannase". Biochem. J. 99 (1): 28–31. April 1966. doi:10.1042/bj0990028. PMID 5965343.
- ↑ Shibata, Shoji; Chiang, Hsüch-Ching (1965). "The structures of cryptochlorophaeic acid and merochlorophaeic acid". Phytochemistry 4: 133–139. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)86155-5.
- ↑ Neamati, Nouri; Hong, Huixiao; Mazumder, Abhijit; Wang, Shaomeng; Sunder, Sanjay; Nicklaus, Marc C.; Milne, George W. A.; Proksa, Bohumil et al. (1997). "Depsides and Depsidones as Inhibitors of HIV-1 Integrase: Discovery of Novel Inhibitors through 3D Database Searching†". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 40 (6): 942–951. doi:10.1021/jm960759e. ISSN 0022-2623. PMID 9083483.
 |
 KSF
KSF