Dibromine monoxide
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 4 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 4 min
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Dibromine monoxide
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Bromohypobromite | |
| Other names
Dibromine oxide, bromine monoxide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Br2O | |
| Molar mass | 175.807 g/mol |
| Appearance | dark brown solid |
| Melting point | decomposes around −17.5°C[1] |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
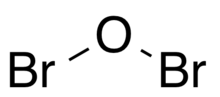
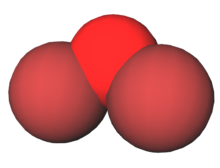
Dibromine monoxide is the chemical compound composed of bromine and oxygen with the formula Br2O. It is a dark brown solid which is stable below −40 °C and is used in bromination reactions.[1] It is similar to dichlorine monoxide, the monoxide of its halogen neighbor one period higher on the periodic table. The molecule is bent, with C2v molecular symmetry. The Br−O bond length is 1.85 Å and the Br−O−Br bond angle is 112°,[2][3] similar to dichlorine monoxide.
Reactions
Dibromine monoxide can be prepared by reacting bromine vapor or a solution of bromine in carbon tetrachloride with mercury(II) oxide at low temperatures:[1][3]
It can also be formed by thermal decomposition of bromine dioxide[2] or by passing an electrical current through a 1:5 mixture of bromine and oxygen gases.[3]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Perry, Dale L.; Phillips, Sidney L. (1995), Handbook of Inorganic Compounds, CRC Press, pp. 74, ISBN 0-8493-8671-3, https://books.google.com/books?id=0fT4wfhF1AsC&q=%22Bromine+dioxide%22&pg=PA74, retrieved 25 August 2015
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Levason, William; Ogden, J. Steven; Spicer, Mark D.; Young, Nigel A. (January 1990). "Characterization of dibromine monoxide (Br2O) by bromine K-edge EXAFS and IR spectroscopy". Journal of the American Chemical Society 112 (3): 1019–1022. doi:10.1021/ja00159a019.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Wiberg, Egon (2001). Wiberg, Nils. ed. Inorganic chemistry (1st ed.). San Diego, Calif.: Academic Press. pp. 464. ISBN 9780123526519.
 |
 KSF
KSF