Dimethylamine
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 4 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 4 min
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
N-Methylmethanamine | |
| Other names
(Dimethyl)amine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3DMet | |
| 605257 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| 849 | |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | dimethylamine |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1032 |
| |
| |
| Properties[1][2] | |
| (CH3)2NH | |
| Molar mass | 45.085 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless gas |
| Odor | Fishy, ammoniacal |
| Density | 649.6 kg m−3 (at 25 °C) |
| Melting point | −93.00 °C; −135.40 °F; 180.15 K |
| Boiling point | 7 to 9 °C; 44 to 48 °F; 280 to 282 K |
| 1.540 kg L−1 | |
| log P | −0.362 |
| Vapor pressure | 170.3 kPa (at 20 °C) |
Henry's law
constant (kH) |
310 μmol Pa−1 kg−1 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 3.29 |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−21 to −17 kJ mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   
|
| GHS Signal word | DANGER |
| H220, H302, H315, H318, H332, H335 | |
| P210, P261, P280, P305+351+338 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | −6 °C (21 °F; 267 K) (liquid) |
| 401 °C (754 °F; 674 K) | |
| Explosive limits | 2.8–14.4% |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
698 mg/kg (rat, oral) 316 mg/kg (mouse, oral) 240 mg/kg (rabbit, oral) 240 mg/kg (guinea pig, oral)[4] |
LC50 (median concentration)
|
4700 ppm (rat, 4 hr) 4540 ppm (rat, 6 hr) 7650 ppm (mouse, 2 hr)[4] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 10 ppm (18 mg/m3)[3] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 10 ppm (18 mg/m3)[3] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
500 ppm[3] |
| Related compounds | |
Related amines
|
|
Related compounds
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Dimethylamine is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2NH. This secondary amine is a colorless, flammable gas with an ammonia-like odor. Dimethylamine is commonly encountered commercially as a solution in water at concentrations up to around 40%. An estimated 270,000 tons were produced in 2005.[5]
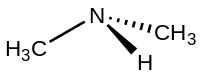
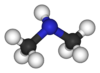
Structure and synthesis
The molecule consists of a nitrogen atom with two methyl substituents and one hydrogen. Dimethylamine is a weak base and the pKa of the ammonium CH3-NH+2-CH3 is 10.73, a value above methylamine (10.64) and trimethylamine (9.79).
Dimethylamine reacts with acids to form salts, such as dimethylamine hydrochloride, an odorless white solid with a melting point of 171.5 °C. Dimethylamine is produced by catalytic reaction of methanol and ammonia at elevated temperatures and high pressure:[6]
- 2 CH3OH + NH3 → (CH3)2NH + 2 H2O
Natural occurrence
Dimethylamine is found quite widely distributed in animals and plants, and is present in many foods at the level of a few mg/kg.[7]
Uses
Dimethylamine is a precursor to several industrially significant compounds.[5][8] It reacts with carbon disulfide to give dimethyl dithiocarbamate, a precursor to zinc bis(dimethyldithiocarbamate) and other chemicals used in the sulfur vulcanization of rubber. Dimethylaminoethoxyethanol is manufactured by reacting dimethylamine and ethylene oxide.[9] Other methods are also available producing streams rich in the substance which then need to be further purified.[10] The solvents dimethylformamide and dimethylacetamide are derived from dimethylamine. It is raw material for the production of many agrichemicals and pharmaceuticals, such as dimefox and diphenhydramine, respectively. The chemical weapon tabun is derived from dimethylamine. The surfactant lauryl dimethylamine oxide is found in soaps and cleaning compounds. Unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine, a rocket fuel, is prepared from dimethylamine.[11]
- (CH3)2NH + NH2Cl → (CH3)2NNH2 ⋅ HCl
It is an attractant for boll weevils.[12]
Reactions
It is basic, in both the Lewis and Brønsted senses. It easily forms dimethylammonium salts upon treatment with acids. Deprotonation of dimethylamine can be effected with organolithium compounds. The resulting LiNMe2, which adopts a cluster-like structure, serves as a source of "Me2N−". This lithium amide has been used to prepare volatile metal complexes such as tetrakis(dimethylamido)titanium and pentakis(dimethylamido)tantalum.
It is also a Lewis base.[13][14]
It reacts with many carbonyl compounds. Aldehydes give aminals. For example reaction of dimethylamine and formaldehyde gives bis(dimethylamino)methane:[15]
- 2 (CH3)2NH + CH2O → [(CH3)2N]2CH2 + H2O
It converts esters to dimethylamides.
Safety
Dimethylamine is not very toxic with the following LD50 values: 736 mg/kg (mouse, i.p.); 316 mg/kg (mouse, p.o.); 698 mg/kg (rat, p.o.); 3900 mg/kg (rat, dermal); 240 mg/kg (guinea pig or rabbit, p.o.).[16]
Although not acutely toxic, dimethylamine undergoes nitrosation to give dimethylnitrosamine, a carcinogen.
See also
References
- ↑ "Dimethylamine". NIST Chemistry WebBook. USA: National Institute of Standards and Technology. http://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/cbook.cgi?ID=C124403&Mask=1#Thermo-Gas.
- ↑ "Dimethylamine 38931 - ≥99.0%". Aldrich. Sigma-Aldrich Co.. https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/US/en/product/aldrich/38931.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0219". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/npgd0219.html.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Dimethylamine". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/idlh/124403.html.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Van Gysel, August B.; Musin, Willy (2000). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a16_535.
- ↑ Corbin D.R.; Schwarz S.; Sonnichsen G.C. (1997). "Methylamines synthesis: A review". Catalysis Today 37 (2): 71–102. doi:10.1016/S0920-5861(97)00003-5.
- ↑ Neurath, G. B. (1977). "Primary and secondary amines in the human environment". Food and Cosmetics Toxicology 15 (4): 275–282. doi:10.1016/s0015-6264(77)80197-1. PMID 590888.
- ↑ Ashford's Dictionary of Industrial Chemicals, 3rd edition, 2011, pages 3284-3286
- ↑ Frank, H., 2007. Preparation of N, N-Dimethylaminoethoxyethanol by Reacting Reacting Di-methylamine with Ethylene Oxide US Patent
- ↑ US8907084B2 - Process for the preparation of 2-(2-aminoethoxy) ethanol (2AEE) and morpholine with 2AEE: morpholine >3 - Google Patents
- ↑ Schirmann, Jean-Pierre; Bourdauducq, Paul (2001). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a13_177.
- ↑ The Merck Index, 10th Ed. (1983), p.470, Rahway: Merck & Co.
- ↑ Laurence, C. and Gal, J-F. Lewis Basicity and Affinity Scales, Data and Measurement, (Wiley 2010) pp 50-51 ISBN 978-0-470-74957-9
- ↑ Cramer, R. E.; Bopp, T. T. (1977). "Graphical display of the enthalpies of adduct formation for Lewis acids and bases". Journal of Chemical Education 54: 612–613. doi:10.1021/ed054p612. The plots shown in this paper used older parameters. Improved E&C parameters are listed in ECW model.
- ↑ Gaudry, Michel; Jasor, Yves; Khac, Trung Bui (1979). "Regioselective Mannich Condensation with Dimethyl(Methylene)ammonium Trifluoroacetate: 1-(Dimethylamino)-4-methyl-3-pentanone". Org. Synth. 59: 153. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.059.0153.
- ↑ Chemical Information Profile for Dimethylamine Borane, National Toxicology Program, NIEHS, NIH (2008), p.4: http://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/ntp/htdocs/Chem_Background/ExSumPdf/DimethylamineBorane508.pdf
External links
- International Chemical Safety Card 0260 (gas)
- International Chemical Safety Card 1485 (aqueous solution)
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0219". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/npgd0219.html.
- Properties from Air Liquide
- MSDS at airliquide.com
 |
 KSF
KSF
