Lactam
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 3 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 3 min
A lactam is a cyclic amide, formally derived from an amino carboxylic acid through cyclization reactions.[1] The term is a portmanteau of the words lactone + amide.
Nomenclature
Greek prefixes in alphabetical order indicate ring size.
| Ring size (number of atoms in the ring) |
Systematic name | IUPAC name | Common name(s) | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | α-Lactam | Aziridin-2-one | α-Acetolactam | 100px |
| 4 | β-Lactam | Azetidin-2-one | β-Propiolactam | 100px |
| 5 | γ-Lactam | Pyrrolidin-2-one |
|
100px |
| 6 | δ-Lactam | Piperidin-2-one |
|
100px |
| 7 | ε-Lactam | Azepan-2-one |
|
100px |
This ring-size nomenclature stems from the fact that hydrolysis of an α-lactam gives an α-amino acid and that of a β-Lactam gives a β-amino acid, and so on.
Synthesis
General synthetic methods are used for the organic synthesis of lactams.
Beckmann rearrangement
Lactams form by the acid-catalyzed rearrangement of oximes in the Beckmann rearrangement.
Schmidt reaction
Lactams form from cyclic ketones and hydrazoic acid in the Schmidt reaction. Cyclohexanone with hydrazoic acid, forms ε - Caprolactum, which upon treatment with excess acid forms Cardiazole, a heart stimulant.
Cyclization of amino acids
Lactams can be formed from cyclisation of amino acids via the coupling between an amine and a carboxylic acid within the same molecule. Lactamization is most efficient in this way if the product is a γ-lactam. For example, Fmoc-Dab(Mtt)-OH, although its side-chain amine is sterically protected by extremely bulky 4-Methyltrityl (Mtt) group, the amine can still intramolecularly couple with the carboxylic acid to form a γ-lactam. This reaction almost finished within 5 minutes with many coupling reagents (e.g. HATU and PyAOP).[2]
Intramolecular nucleophilic substitution
Lactams form from intramolecular attack of linear acyl derivatives from the nucleophilic abstraction reaction.
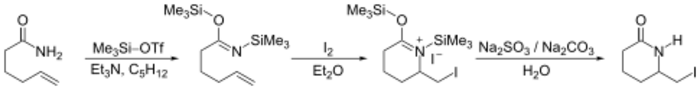
Iodolactamization
An iminium ion reacts with a halonium ion formed in situ by reaction of an alkene with iodine.[3]
Kinugasa reaction
Lactams form by copper-catalyzed 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition of alkynes and nitrones in the Kinugasa reaction
Diels-Alder reaction
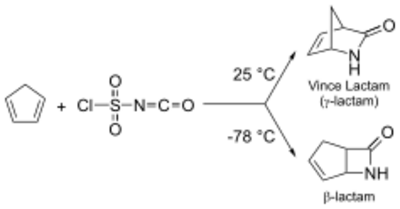
Diels-Alder reaction between cyclopentadiene and chlorosulfonyl isocyanate (CSI) can be utilized to obtain both β- as well as γ-lactam. At lower temp (−78 °C), β-lactam is the preferred product. At optimum temperatures, a highly useful γ-lactam known as Vince Lactam[4] is obtained.[5]
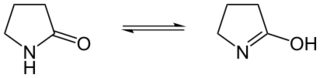
Lactam–lactim tautomerism
A lactim is a cyclic imidic acid compound characterized by an endocyclic carbon-nitrogen double bond. They are formed when lactams undergo tautomerization.
Reactions
- Lactams can polymerize to polyamides.
See also
- Lactone, a cyclic ester.
- β-Lactam
- β-Lactam antibiotics, which includes penicillins
- 2-Pyrrolidone
- 2-Piperidinone
- Caprolactam
References
- ↑ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "Lactams". doi:10.1351/goldbook.L03435
- ↑ Lam, Pak-Lun; Wu, Yue; Wong, Ka-Leung (30 March 2022). "Incorporation of Fmoc-Dab(Mtt)-OH during solid-phase peptide synthesis: a word of caution" (in en). Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry 20 (13): 2601–2604. doi:10.1039/D2OB00070A. ISSN 1477-0539. PMID 35258068. https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2022/ob/d2ob00070a.
- ↑ Spencer Knapp, Frank S. Gibson Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 9, p.516 (1998); Vol. 70, p.101 (1992) Online article
- ↑ Singh, R.; Vince, R. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112 (8), pp 4642–4686."2-Azabicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-en-3-one: Chemical Profile of a Versatile Synthetic Building Block and its Impact on the Development of Therapeutics"
- ↑ Pham, P.-T.; Vince, R. Phosphorus, Sulphur and Silicon 2007, 779-791.
External links
 |
 KSF
KSF