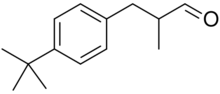
Lilial
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 3 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 3 min
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-(4-tert-Butylphenyl)-2-methylpropanal
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII |
|
| UN number | 3082 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H20O | |
| Molar mass | 204.313 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Clear viscous liquid |
| Density | 0.94 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −20 °C (−4 °F; 253 K) |
| Boiling point | 275 °C (527 °F; 548 K)[1] |
| 0.045 g/L at 20 °C | |
| log P | 4.36 [1] |
| Pharmacology | |
| Topical | |
| Related compounds | |
Related aldehydes
|
Bourgeonal |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Lilial (a trade name for lily aldehyde, also known as lysmeral) is a chemical compound commonly used as a perfume in cosmetic preparations and laundry powders, often under the name butylphenyl methylpropional. It is an aromatic aldehyde, naturally occurring in crow-dipper and tomato plants,[2] and produced synthetically in large scale. It was banned for use in cosmetics by the EU in March 2022 after being found to be harmful to fertility.
Synthesis
Lilial is produced at BASF through a double anodic oxidation of 4-tertbutyl-toluene on >10,000 ton per year scale.[3]
Properties
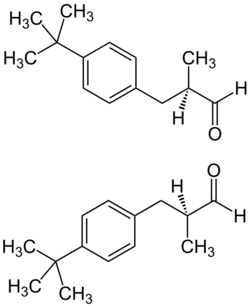
Lilial is commonly produced and sold as a racemic mixture; however, testing has indicated that the different enantiomers of the compound do not contribute equally to its odor. The (R)-enantiomer has a strong floral odor, reminiscent of cyclamen or lily of the valley; whereas the (S)-enantiomer possesses no strong odor.[4]
Like most aldehydes, lilial is not long term stable and tends to slowly oxidize on storage.
Safety
The Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety (SCCS, scientific committee for consumer safety of the EU Commission) concluded in May 2019 that the use of lilial in both rinse-off and leave-on cosmetics "cannot be considered as safe".[5]
After animal studies found it to be toxic for reproduction, it was reclassified as a prohibited substance in the EU, and banned from use in cosmetics as of March 2022.[6]
It can sometimes act as an allergen and may cause contact dermatitis in susceptible individuals.
See also
- Helional
- Bourgeonal
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Haefliger, Olivier P.; Jeckelmann, Nicolas; Ouali, Lahoussine; León, Géraldine (2010). "Real-Time Monitoring of Fragrance Release from Cotton Towels by Low Thermal Mass Gas Chromatography Using a Longitudinally Modulating Cryogenic System for Headspace Sampling and Injection". Analytical Chemistry 82 (2): 729–737. doi:10.1021/ac902460d. ISSN 0003-2700. PMID 20025230.
- ↑ https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Lilial
- ↑ Möhle, S.; Zirbes, M.; Rodrigo, E.; Gieshoff, T.; Wiebe, A.; Waldvogel, S. R. Modern Electrochemical Aspects for the Synthesis of Value-Added Organic Products. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 6018−6041
- ↑ Bartschat, Dietmar; Bürner, Susanne; Mosandl, A.; Bats, Jan W. (1997). "Stereoisomeric flavour compounds LXXVI: direct enantioseparation, structure elucidation and structure-function relationship of 4-tert-butyl-α-methyldihydrocinnamaldehyde". Zeitschrift für Lebensmitteluntersuchung und -Forschung A 205 (1): 76–79. doi:10.1007/s002170050127. ISSN 1431-4649.
- ↑ Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety (2019-05-10). "OPINION ON the safety of Butylphenyl methylpropional (p-BMHCA) in cosmetic products" (in en). https://ec.europa.eu/health/sites/health/files/scientific_committees/consumer_safety/docs/sccs_o_213.pdf. "On individual product basis, Butylphenyl methylpropional (p-BMHCA) (CAS 80-54-6) with alpha-tocopherol at 200 ppm, can be considered safe when used as fragrance ingredient in different cosmetic leave-on and rinse-off type products. However, considering the first-tier deterministic aggregate exposure, arising from the use of different product types together, Butylphenyl methylpropional at the proposed concentrations cannot be considered as safe."
- ↑ "COMMISSION REGULATION (EU) 2021/1902 OF 29 October 2021 amending Annexes II, III and V to Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards the use of cosmetic products of certain substances classified as carcinogenic, mutagenic or toxic for reproduction". https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32021R1902&from=EN. "CAS No. 80-54-6"
 |
 KSF
KSF