Table of Contents
- 1 Orbitals
- 2 Periodic table
- 3 Properties of elements
- 4 Reactions and ions
- 5 Compounds
- 6 Organic chemistry
- 7 Biochemistry
- 8 See also
- 9 References
- 10 External links Categories
- Sober Physicists Don't Find Giraffes Hiding In Kitchens.
H He Li Be B C N O F Ne Na (Sodium) Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar - Happy Henry Likes Beans Brownies and Chocolate Nuts Over Friday's News.
- Happy Harry Listens B B C Network Over France Nevertheless Nothing More Arose So Peter Stopped Cleaning Airgun K Ca.[3] (also Happy Henry Listens B B C Network Over France Nevertheless Nothing More Arose So Peter Stopped Cleaning Airgun K Ca.)
- Ha. Healthy Little Beggar Boys Catching Newts Or Fish.[4]
- Hi, Here Little Beatniks Brandish Countless Number Of Flick kNives.[5] Nagging Maggie Always Sighs, "Please Stop Clowning Around." [6] (adapted)
- Hi Helium. Little Berries Borrow Carbs, NO Fight Needed.
- Hi Hello! Lion Beneath the Burning Car Needs Oxygen For New life.
- Native Magpies Always Sit Peacefully Searching Clear Areas.[7]
- Naval Magistrates Always Signal Per Siren, Claiming Adequacy.[8]
- Naughty Margaret Always Sighs, "Please Stop Clowning Around."[6]
- Nellie's Naughty Magpie Always Sings Pop Songs Clearly After Killing Cathy.[6]
- Shoddy Magician Aligned Six Phones Successfully, Classic Art!
- All Silicon Ports. Superman Clean Argon's K-Capture.[9]
K (Potassium) Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr - Kindly Cannibals Scare Timid Visitors, 'n' Cruelly Menace Female Communist Nitwits Cuddling Zany Gabbling Geese Astride Several Brutal Kangaroos.[8]
- In reverse order: Kry Brother! SeAs of Germany and Gaul sink copper ships Nice and Cold From Manx to Crimea, Vancouver to Timor, and Scandinavia to the California Koast.[10]
- Kind Cats Scare Tiny Vicious Creatures, Maintaining Feline Connections Nice, Cute & Zen. Gallium Germinates As Selene Brings Krypton.
- Ruby, Sir, Yells "Zircon Nebulas !". Most Technicians Rule Rhodes and Paddle Against Cadence". India Sent Sebastian to Tell "Io Xe.
- Ruby Stuck in Yuck Zoo, Nice Monk Tackled Rude Rhino. Pay Silver Coin In Tin And Tell I eXeed.
Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn - Scary Tiny Vicious Creatures are Mean; Females Come to NightClub Zen.[11]
- Scary Tiny Vicious Creatures Might Fear Cows and Nice Cute Zebras.
- SucTion VelCro Man Fears CoNiC uZi.
- ScienTist ViCroMan Iron(Fe) Comes from NiCuZan.
Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd - Yes S(Z)ir, Nob. Most Technicians Ruin Rob's Pale Silver Cadillac.[11]
La ... Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg - Larry's Half Taken, Wendy Reached Out H(I)er Plate Audibly, Helga.[11]
- Late Harry Took Walk, Reached Office In Pajamas, After an Hour.
- La'me Horned-Fox's Tail got Wet. Restless Ostrich Irrelevantly Painted Gold(AU) on Mercury(HG).
(La) Ce Pr Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu - Ladies Can't Put Needles Properly in Slot-machines. Every Girl Tries Daily, However, Every Time You'd Lose.[12]
- Languid Centaurs Praise Ned's Promise of Small European Garden Tubs; Dinosaurs Hobble Erratically Thrumming Yellow Lutes.[13]
- Lately, Central Park Needed Primroses. Small Entire Golden Tassels Dyeing the Hollow Earth, Tempting Your Love.
(Ac) Th Pa U Np Pu Am Cm Bk Cf Es Fm Md No Lr - Radiant Acting Thoroughly Protects yoUr Nepotism, Plutocratic America Cures-me & Berkeley California, Einstein Firmly Mended Noble Lawreins.[14]
- Ace Thor Protects Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto. Army Cured Bark. In California Einstein and Fermi Made Noble Laws.[11]
- Actually Thor Protects Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto. Army Cured Bark. In California Einstein and Fermi Made Noble Laws.
H He Li Be B C N O F Ne Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar
K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr
Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te I Xe
Cs Ba- Here Lies Benjamin Bones. Cry Not Oh Friend Needlessly. Nature Magnifies All Simple People Sometimes Clowns And Kings Can Scream Till Vast Crowds Moan. Fear Conquers Neither Courageous Zealous Gallant Gents. As Seen Brown Karate Robes Strip Yobs. Zurich Noble Mortals Track Ruddy Rhubarb. Paid Silver Candid Indian Sons Sobbing Tears In Xcess Cease Bawling.[9]
Li Na K Rb Cs Fr - Little Nasty Kids Rub Cats Fur
- Little Naughty Kids Robs Cents From (me)
- Little Naughty Kids Ruin Ben's Convenient Store Forever
- Little Nathan Knew Rubies Cost Fortunes
- Little Naughty Kids Rob Crispy Fries
Be Mg Ca Sr Ba Ra - Bearded Muggers Came Straight Back Rapidly.
- Beer Mugs Can Serve Bar Rats.[11]
- Ben Meg & Casia Stroll away to Bar of Radium
B Al Ga In Tl - BAlm Game In Tail
- Bowler Ali Gave Instant Tea
- BAG IT
- Bears Always Gave Indians Trouble
C Si Ge Sn Pb - CSI Gets Stan Plums (comment: plum and plumb are homophones)
- Can Simple Germans Snare (Tiny) Public (Lead)?[11]
- Chemistry Sir Gets Snacks Publicly
N P As Sb Bi - No Person can Assassinate Sebastian Billy in Moscow (place).
O S Se Te Po Lv - Old Style Sets TemPo
- Old TSangpo Seems Terribly Polluted Lately.[11]
- Ottoman Sultan Sends Textiles to Poor Ladies.
F Cl Br I At Ts - Funny Clowns Broil Innocent Ants.[11]
- Fast Clouds Break In Atlantis.[14]
- Father Clark B(r)lesses Ivan A(s)tlast.
- First Class Briyani In Australia[15]
He Ne Ar Kr Xe Rn - Hero Never Argues, Kryptonite Xterminates Rao
- Hero Needs Arguable Kryptic Xes. Right-on.[14]
- He Never Arrived; Karen eXited with Ron.[11]
- He Needs A Kickin', Xylophone-playin' Racehorse! (And... Oh, gee, now we need to add Oganesson (Og)!)
- Only Strong Athletes In College Study Past Midnight
- Oh, see(Si), Alfie(Fe) Cannot(Na) Kiss Meg(Mg)
- Please Stop Calling Me A Cute Zebra Crab I Like Her Call Smart Goat
- Please Stop Calling Me A Carless Zebra Crab Instead Try Learning How Copper Miners Save Gold Pit
- Popular Scientists Can Make A Zoo In Low Humid Climate ...
- Kangaroos Naturally Muck About in Zoos For Purple Hippos Chasing Aardvarks.[16]
- Katty's Naughty Cat Mingled with Alice and Zarina; Fearlessly Plundering Her Cupboard of Gold.[17]
- Papa Said Call Me After Zinc Interacts Tin Leading Hydrogen Co-operate Mr. Sylvester to Gain Popularity.[18]
- Pretty(Potassium) Sally(Sodium) Could(Calcium) Marry(Magnesium) A(Aluminium) Crazy(Carbon) Zulu(Zinc) IN(Iron/Nickel) Tree(Tin) Lined(Lead) House(Hydrogen) Causing(Copper) Strangely(Silver) Glancing(Gold) People(Platinum).
- Pronounce: FOClN BrIS CHP.[19]
- Paddy Still Could Marry A Zulu In The Lovely Honolulu Causing Strange Gazes.
- Passive Sarcasm Can Mutate Angry Zombies InTo Large Hypocritical Cold Sexy Guys.
- Poor Science Course Makes A Zany Idiot Totally Lose His Composure, Sir! Good!
- Leo says Ger! or Leo the lion, Ger! can be used to represent Loss of electron is oxidation; Gain of electron is reduction.[20][21]
- Oil Rig: Oxidation is loss; Reduction is gain (of electrons).[22]
- Cats have paws ⇔ Cations are pawsitive.[23]
- Ca+ion: The letter t in cation looks like a + (plus) sign.[24]
- An anion is a negative ion. (An
egativeion ⇒ Anion).[25] - AN OIL RIG CAT:
- At the ANode, Oxidation Involves Loss of electrons.
- Reduction Involves Gaining electrons at the CAThode.[26]
- LOAN - Left Anode Oxidation Negative.
- In written representation of galvanic cell, anode is written on the left. It is the electrode where oxidation takes place. It is the negative electrode. Obviously, the opposite properties (Right/Cathode/Reduction/Positive) are found on the cathode. Hence, by remembering LOAN mnemonic, we can arrive at the corresponding properties for the cathode.
- LEO the lion says GER [grr]:
- "Loss of Electrons, Oxidation; Gain of Electrons, Reduction".[27]
- Red cat: Reduction at cathode
- An ox: Anode for oxidation.[28]
- The words oxidation and anode, both begin with vowels.
- Also, both reduction and cathode begin with consonants.[25]
- Fat Cat: electrons flow From Anode To Cathode
- LOAN: Left side;Oxidation;Anode;Negative.
- ACID: Anode Current Into Device
- Have No Fear Of Ice Cold Beer. [29]
- Horses Need Oats For Clear Brown Eyes (I's).
- Her Nana's Only Functioning Clicker Broke Instantly.[30]
- BrINClHOF: say Brinkelhof.[31]
- I Bring Clay For Our New House.[11]
- Hydrogen is FON! (fun).[25]
- Super Popeye Constantly Clubbed Brutus In Nevada.
- Nick Brit the Camel ate an Inky Clam with Crêpes for Supper in Phoenix.
- Monkeys Eat Peeled Bananas
- Many Elephants Pee Behind Plants
- Frogs Are Polite, Being Very Courteous.[32]
- Oh My, Such Good Apples.[33]
- Oh My Stars, Green Apples.
- Oh My, Such Good Apple Pie, Sweet As Sugar.[34][35]
- Oh My Stars, Go Ahead Please[25]
- OMSGAP - is a phonetic word for the first letters of the first six dicarboxylic acids above in sequence can be said as below.
- Oh My Sir, Give A Party.
- Queen Elizabeth Second's Navy Commands, Controls, Communicates.[36]
- AHA AHA P.[36]
- Benzene likes to ROMP.
- PVT TIM HaLL[37] and TT HALL Very IMPortant.[38]
- These Ten Valuable Acids Have Long Preserved Life In Men
- MATT HILL, VP
- LIFT HIM KIW(V)I
- TV FILM HW(R)K.
- FM TK HW RIVL
- Any Help In Learning These Little Molecules Proves Truly Valuable.[39] This method begins with the two amino acids that need some qualifications as to their requirements.
- Caesar's Armies Invaded Other Kingdoms Searching For Many Oranges.[19]
- Citric Acid Is One Key Substrate For Mitochondrial Oxidation
- C (see) Hopkins CaFe, Mighty-good Man, Cu (see your) Money, hope they are Closed or out of Business.[40]
- C. HOPKiN'S Ca Mg (C. Hopkins coffee mug).
- MagiCal CKN SHOP (Magical Chicken SHOP).
- Chopin's CaFe
- I.P. Cohn's CaFe
- List of medical mnemonics
- List of mnemonics
- ↑ "Mnemonic devices for: Chemistry". Mnemonic-device.eu. http://www.mnemonic-device.eu/chemistry/.
- ↑ Zumdahl, Steven S. and Zumdahl, Susan A. (2000), Chemistry, Houghton Mifflin, 5th ed., p. 324 ISBN 0-395-98583-8
- ↑ Chemical formula. "Periodic table mnemonic (memory device)". Chemicalformula.org. http://www.chemicalformula.org/chemistry-help/periodic-table-mnemonic-memory-device.
- ↑ "Kids Tips for Easy Learning - Mnumonics". Betterendings.org. http://www.betterendings.org/homeschool/fun/mnemonic.htm.
- ↑ Martin Berry (30 Nov 1972). A dictionary of mnemonics. Reed Business Information. (Eyre Mithuen). p. 535. https://books.google.com/books?id=dkUzDol9AcQC&q=Periodic+table+mnemonic&pg=PA535.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 "Mnemonic: Sentences to remember the elements". Ict4us.com. http://ict4us.com/r.kuijt/en_chemistry.htm.
- ↑ Hara, Jaclyn R.; Stanger, Gordon R.; Leony, Denisse A.; Renteria, Sandra S.; Carrillo, Alejandro; Michael, Katja (2007). "Multilingual Mnemonics for the Periodic Table". Journal of Chemical Education 84 (12): 1918. doi:10.1021/ed084p1918. ISSN 0021-9584. Bibcode: 2007JChEd..84.1918H.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 "Periodic Table of Elements". http://www.eudesign.com/mnems/elements.htm.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 "Science Jokes:11. MNEMONICS : 11.5 CHEMISTRY". Jcdverha.home.xs4all.nl. http://jcdverha.home.xs4all.nl/scijokes/11_5.html#subindex.
- ↑ "CHEMISTRY AND BIOCHEMISTRY A very nice site of Anatomy Mnemonics by John Berger". Img.com.tripod.com. http://img.com.tripod.com/mnemonics/chemistry.htm.
- ↑ 11.00 11.01 11.02 11.03 11.04 11.05 11.06 11.07 11.08 11.09 Mnemonic bradley.edu
- ↑ Carl C. Gaither; Alma E. Cavazos-Gaither (2002). Chemically Speaking: A Dictionary of Quotations/selected and Arranged by Carl C. Gaither and Alma E. Cavazos-Gaither. CRC Press. pp. 82–83. ISBN 978-0-7503-0682-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=j7p5O0HbhHkC&pg=PA82. Retrieved 28 December 2012.
- ↑ "Holmium (new)". Periodic Videos.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 Mezl, Vasek A. (1997). "Mnemonics for the Entire Periodic Table". The Chemical Educator 2: 1–7. doi:10.1007/s00897970109a.
- ↑ Purvesh Mule : This is an Indian Mnemonics
- ↑ "Sprowston Community High School - Specialist School for Performance Arts & Media". http://www.sprowstonhigh.org/moodle/mod/resource/view.php?inpopup=true&id=1138.
- ↑ Oon Hock Leong/ Edmund Ang Joon Aik (2007). Chemistry expression: an inquiry approach. 'O' level science (chemistry) [textbook]. Panpac Education Pte Ltd. p. 243. ISBN 9789812711656. https://books.google.com/books?id=s_i8oPwYLWEC&q=mnemonic+for+remember+alkali+metals&pg=PA243. Retrieved 27 January 2012.
- ↑ Syamal, Arun. "Metals, Non-metals and Metallurgy". Living Science Chemistry 10. Ratna Sagar. p. 97. ISBN 9788183322898. https://books.google.com/books?id=UMiO4OHq5YgC&q=mnemonic+for+remember+alkali+metals&pg=PA97. Retrieved 27 January 2012.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 "Mnemonics for chem 3 2010.ppt". http://www.chem.uic.edu/marek/marek_downloads/documents/Mnemonics%20for%20chem%203%202010.ppt.pdf.
- ↑ Nick Lane (26 March 2004). Oxygen: The Molecule that Made the World. Oxford University Press. pp. 18–. ISBN 978-0-19-860783-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=ziVk6CI82WgC&pg=PA18. Retrieved 10 August 2012.
- ↑ Rene Fester Kratz (2 June 2009). Molecular and Cell Biology For Dummies. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 70–. ISBN 978-0-470-43066-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=gux4J6ctaeIC&pg=PT70. Retrieved 10 August 2012.
- ↑ "Chemistry - Mnemonic". Chemistrydaily.com. http://www.chemistrydaily.com/chemistry/Mnemonic_device.
- ↑ Peter J. Mikulecky; Michelle Rose Gilman; Kate Brutlag (2008). "Cats+have+paws"+chem&pg=PA30 AP Chemistry For Dummies (Illustrated ed.). John Wiley & Sons, 2008. p. 30. ISBN 9780470389768. https://books.google.com/books?id=g2lXnvqtnIwC&q="Cats+have+paws"+chem&pg=PA30.
- ↑ Kevin M. Dunn (16 March 2010). Scientific Soapmaking: The Chemistry of the Cold Process. Clavicula Press. pp. 386–. ISBN 978-1-935652-09-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=DL0d6AoATfwC&pg=PA386. Retrieved 10 August 2012.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 25.2 25.3 Subhash Jain (1 January 2009). Improve Your Memory. Prabhat Prakashan. p. 117. ISBN 978-81-8430-035-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=J2YMat4HXI8C&pg=PA117. Retrieved 28 December 2012.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 26.2 26.3 "MedicalMnemonics Full Abridged". Medicalmnemonics.com. pp. 36. http://www.medicalmnemonics.com/pdf/2002_09_full_abr_a4.pdf.
- ↑ Zumdahl, Steven S. and Zumdahl, Susan A. (2000), Chemistry, Houghton Mifflin, 5th ed., p. 169 ISBN 0-395-98583-8
- ↑ Mrs Jacqueline Hilary Briggs; Rex M Heyworth. Lcg Ol Chemistry. Pearson Education South Asia. pp. 142–. ISBN 978-981-06-0008-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=4bey4gVjLeAC&pg=PA142. Retrieved 10 August 2012.
- ↑ "Chemistry Mnemonics". Bookbuilder.cast.org. http://bookbuilder.cast.org/view.php?op=view&book=20878&page=4.
- ↑ Zack Ouellette
- ↑ http://www.freechemteacher.org/Recommended_Resources_files/Mnemonics [|permanent dead link|dead link}}] for Chemistry.pdf
- ↑ Jonathan Dee; H. Stephen Stoker (2009). Organic and Biological Chemistry (5 ed.). Cengage Learning. p. 157. ISBN 9780547168043. https://books.google.com/books?id=ZnAeHVeVZ3kC&q=Mnemonic++Remember+diCarboxylic+acids&pg=PA157.
- ↑ William Henry Brown; Brent L. Iverson (2009). Organic chemistry (5, illustrated ed.). Cengage Learning. p. 621. ISBN 9780495388579. https://books.google.com/books?id=mTHQB7MkUFsC&q=Mnemonic++Remember+Carboxylic+acids&pg=PA621. Retrieved 27 January 2012.
- ↑ "Mnemonic: Dicarboxilic Acids". Ict4us.com. http://ict4us.com/r.kuijt/en_dicarboxilicacids.htm.
- ↑ "Organic Chemistry Nomenclature". Translationjournal.net. 1997-11-24. http://translationjournal.net/journal/03org.htm.
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 "MCAT Mnemonics Organic Chemistry Flash Cards". Cram.com. 2008-08-16. http://www.cram.com/cards/mcat-mnemonics-organic-chemistry-645732.
- ↑ MedicalMnemonics.com: 442 128
- ↑ ;MATT VIL PLy Essential amino acids Essential amino acids, Mnemonic.
- ↑ Williams, R.A.D.; Eliot, J.C. (1989). Basic and Applied Dental Biochemistry. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 149. ISBN 0-443-03144-4.
- ↑ "Mnemonic: Elements necessary for agriculture". Ict4us.com. http://ict4us.com/r.kuijt/en_agriculture.htm.
Contents
List of chemistry mnemonics
Topic: Chemistry
 From HandWiki - Reading time: 16 min
From HandWiki - Reading time: 16 min
A mnemonic is a memory aid used to improve long-term memory and make the process of consolidation easier. Many chemistry aspects, rules, names of compounds, sequences of elements, their reactivity, etc., can be easily and efficiently memorized with the help of mnemonics. This article contains the list of certain mnemonics in chemistry.
Orbitals
Sequence of orbitals
| s p d f g h i k |
Note: After the k shell, they follow alphabetical order (skipping s and p as they came earlier).[1]
Aufbau principle
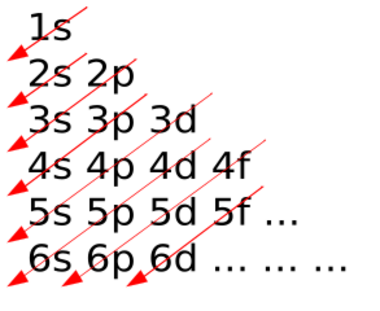
| 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 ... |
The order of sequence of atomic orbitals (according to Madelung rule or Klechkowski rule) can be remembered by the following.[2]
Periodic table
Periods
Periods 1, 2 and 3
Period 4
Period 5
| Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag (Silver) Cd In Sn (Tin) Sb (Antimony) Te I Xe |
Transition metals
First
Second
Third
Lanthanides and actinides
Lanthanides
Actinides
56 elements in sequence
Groups
Group 1 (alkali metals)
Lithium, Sodium, Potassium, Rubidium, Caesium, Francium
Group 2 (alkaline earth metals)
Beryllium, Magnesium, Calcium, Strontium, Barium, Radium
Group 13
Boron, Aluminium, Gallium, Indium, Thallium
Group 14
Carbon, Silicon, Germanium, Tin (stannum in Latin), Lead (plumbum in Latin)
Group 15 (Pnictogens)
Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Arsenic, Antimony, Bismuth, Moscovium.
Group 16 (Chalcogens)
Oxygen, Sulfur, Selenium, Tellurium, Polonium
Group 17 (Halogens)
Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine, Iodine, Astatine, Tennessine
Group 18 (noble gases)
Helium, Neon, Argon, Krypton, Xenon, Radon.
Properties of elements
Abundance of elements on Earth's crust
| [Oxygen(O)] > [Silicon(Si)] > [Aluminium(Al)] > [Iron(Fe)] > [Calcium(Ca)] > [Sodium (Na)] > [Potassium(K)] > [Magnesium (Mg)] |
| (The rest makes only 1%) |
As they are present in trace quantities they are measured in parts per million(ppm).
Activity series of metals
| Potassium>Sodium>Calcium>Magnesium>Aluminium>(Carbon)*>Zinc>Chromium>Iron>Tin>Lead>(Hydrogen)*>Copper>Mercury>Silver>Gold>Platinum |
Note that Carbon and Hydrogen are non-metals, used as a baseline.
| K > Na > Mg > Al > Zn > Cr > Fe > Pb > H > Cu > Au |
| K > Na > Ca > Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Ni > Sn > Pb > Cu > Ag > Au >Pt |
| Li > K > Ba > Sr > Ca > Na > Mg > Al > Mn > Zn > Cr > Fe > Cd > Co > Ni > Sn > Pb |
Electronegativity
| Fluorine > Oxygen > Chlorine > Nitrogen > Bromine > Iodine > Sulfur > Carbon > Hydrogen ≥ Phosphorus |
(F)irst (O)ff, (Cl)ean (N)ow; (Br)ing (I)n (S)ome (C)lothes, (H)ats, and (P)ants. (First off, clean now. Bring in some caps, hats {and} pants.)
Electrochemical series
| Potassium > Sodium > Calcium > Magnesium > Aluminium > Zinc > Iron > Tin > Lead > Hydrogen > Copper > Silver > Gold |
Reactions and ions
Redox reactions
A redox reaction is a chemical reaction in which there is a change in oxidation state of atoms participating in the reaction.
Ions
An atom (or ion) whose oxidation number increases in a redox reaction is said to be oxidized (and is called a reducing agent). It is accomplished by loss of one or more The atom whose oxidation number decreases gains (receives) one or more electrons and is said to be reduced. This relation can be remembered by the following mnemonics.
Cations and anions
Cations are positively (+) charged ions while anions are negatively (−) charged. This can be remembered with the help of the following mnemonics.
Oxidation vs. reduction: electrochemical cell and electron gain/loss
Electrodes
An electrode in which oxidation takes place is called an anode while in that which reduction takes place is called cathode. This applies for both electrolytic and electrochemical cells, though the charge on them reverses. The red cat and an ox mnemonics are useful to remember the same.
Compounds
Diatomic molecules
Molecules exhibiting diatomic structures can be remembered through the following mnemonics.
| Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine, Iodine |
Hydrogen bonds
Hydrogen forms hydrogen bonds with three elements which are nitrogen (N), oxygen (O) and fluorine (F). The names of these elements can be remembered by the following mnemonic.
Polyatomic ions: −ate and -ite ions
| Sulfite, Phosphite, Carbonate, Chlorate, Bromate, Iodate, Nitrate |
| Nitrate, Bromate, Carbonate, Iodate, Chlorate, Chromate, Sulfate, Phosphate |
Number of consonants denotes number of oxygen atoms. Number of vowels denotes negative charge quantity. Inclusion of the word "ate" signifies that each ends with the letters a-t-e. To use this for the -ite ions, simply subtract one oxygen but keep the charge the same.
Organic chemistry
Prefixes for naming carbon chains
The prefixes for naming carbon chains containing one to four carbons. For chains containing five or more carbons, the inorganic prefixes (pent, hex, etc.) are used.
| Meth | Eth | Prop | But |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
For the first five chains.
Carboxylic acids
Common names of homogeneous aliphatic carboxylic acids,
| Formic, Acetic, Propionic, Butyric, Valeric, Caproic |
Dicarboxylic acids
The sequence of dicarboxylic acids can be remembered with following mnemonics.
| Oxalic, Malonic, Succinic, Glutaric, Adipic, Pimelic, Suberic, Azelaic, Sebacic |
Aromatic compounds
m-directing groups
| Quaternary amino | Ester | Sulfonic acid | Nitro | Carbonyl | Carboxyl | Cyano |
| (-NR3+) | (-COOR) | (-SO3H) | (-NO2) | (-CHO) | (-COOH) | (-CN) |
o,p-directing groups
| Alkyl | Halogen | Alkoxyl | Amino | Hydroxyl | Amide | Phenyl | ||
| (R) | (X) | (OR) | (-NH2 | -NHR | -NR2) | (OH) | (NHCOR | (C6H5) |
Note: -NH2,-NHR and NR2 are para directing groups but not -NR3+
E-Z notation for isomers
"E" for 'enemies'. i.e higher priority groups on opposite sides. Z form has higher priority groups on same side.[26]
"Z" means 'zame zide' (same side) i.e. high priority groups on same side.
Cis–trans isomerism
Cis starts with a C and the functional groups form a C.
Trans, therefore is the other one by default.[26]
Benzene ring: order of substitutes
From R group moving around the ring:[26]
| R group, Ortho, Meta, Para |
Biochemistry
Essential amino acids
| Isoleucine, Leucine, Lysine, Arginine, Methionine, Phenylalanine, Threonine, Tryptophan, Histidine, Valine |
Krebs cycle
To remember Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle, tricarboxylic acid cycle);
| Citrate → Aconitate → Isocitrate → Oxalosuccinate → α-Ketoglutarate → Succinate → Fumarate → Malate → Oxaloacetate |
Plant nutrients
To remember the elements necessary for agriculture;
| Carbon, Hydrogen, Calcium, Iron (Fe), Magnesium (Mg), Manganese (Mn), Copper (Cu), Molybdenum, Chlorine (Cl), Boron |
For remembering macronutrients;
| Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Potassium, Nitrogen, Sulfur, Calcium, and Magnesium |
Elements Comprising the Human Body
To remember the elements comprising the human body;
| Iodine, Phosphorus, Carbon, Oxygen, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Sulfur, Calcium (Ca), Iron (Fe) |
See also
References
External links
Science mnemonics | |
|---|---|
 | 0.00      (0 votes) (0 votes) |
 KSF
KSF